Spanish tortilla and Japanese tamagoyaki represent two iconic variations of world omelettes, each with distinct textures and flavors. The Spanish tortilla is a thick, hearty dish made with eggs, potatoes, and often onions, offering a savory and satisfying taste. In contrast, Japanese tamagoyaki is a delicate, slightly sweet rolled omelette made by layering thin egg mixtures, showcasing a refined and balanced flavor profile.
Table of Comparison
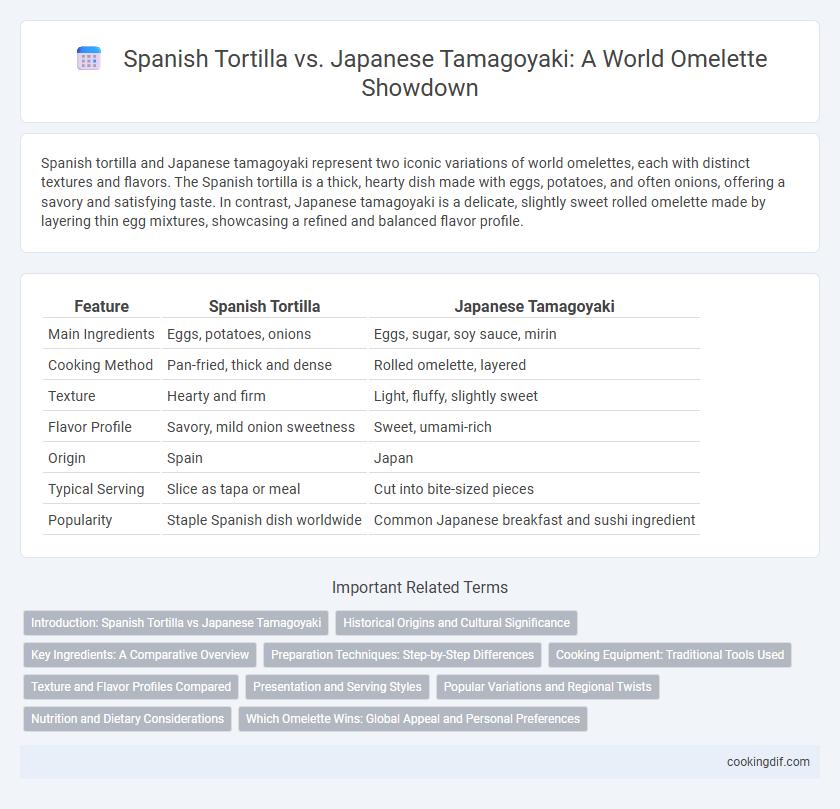
| Feature | Spanish Tortilla | Japanese Tamagoyaki |
|---|---|---|
| Main Ingredients | Eggs, potatoes, onions | Eggs, sugar, soy sauce, mirin |
| Cooking Method | Pan-fried, thick and dense | Rolled omelette, layered |
| Texture | Hearty and firm | Light, fluffy, slightly sweet |
| Flavor Profile | Savory, mild onion sweetness | Sweet, umami-rich |
| Origin | Spain | Japan |
| Typical Serving | Slice as tapa or meal | Cut into bite-sized pieces |
| Popularity | Staple Spanish dish worldwide | Common Japanese breakfast and sushi ingredient |
Introduction: Spanish Tortilla vs Japanese Tamagoyaki
Spanish tortilla features a hearty blend of eggs, potatoes, and onions cooked into a thick, golden omelette rich in texture and flavor, symbolizing traditional Mediterranean cuisine. Japanese tamagoyaki offers a delicate, slightly sweet layered egg omelette crafted by rolling multiple thin layers in a rectangular pan, highlighting precision and subtlety characteristic of Japanese culinary art. Both dishes showcase unique regional techniques and ingredients, representing diverse global interpretations of the classic omelette concept.
Historical Origins and Cultural Significance
Spanish tortilla, originating in the early 19th century during Spain's Carlist Wars, symbolizes resilience and communal dining, featuring potatoes and onions bound by eggs. Japanese tamagoyaki, with roots in the Edo period, reflects precision and aesthetic harmony, crafted by layering seasoned eggs into a sweet, savory roll. Both dishes embody regional identities, showcasing distinct cooking techniques and cultural values within global omelette traditions.
Key Ingredients: A Comparative Overview
Spanish tortilla primarily features potatoes, eggs, and onions, creating a dense and hearty texture, while Japanese tamagoyaki emphasizes eggs, sugar, and soy sauce for a sweet and savory flavor profile. The Spanish tortilla uses olive oil for frying potatoes and onions, contributing to its rich taste, whereas tamagoyaki relies on a precise rolling technique in a rectangular pan to achieve its layered appearance. These key ingredient differences highlight cultural preferences in omelette preparation, reflecting regional culinary traditions.
Preparation Techniques: Step-by-Step Differences
Spanish tortilla preparation involves thinly sliced potatoes and onions slowly cooked in olive oil before mixing with beaten eggs, then gently cooked in a skillet until firm, often flipped to cook both sides evenly. Japanese tamagoyaki requires beating eggs with sugar, mirin, and soy sauce, then cooking in thin layers rolled repeatedly in a rectangular pan to create delicate, layered folds. These distinct step-by-step techniques highlight the Spanish emphasis on texture and hearty ingredients versus the Japanese focus on precise layering and subtle sweetness.
Cooking Equipment: Traditional Tools Used
Spanish tortilla traditionally relies on a heavy, flat cast-iron skillet called a "sarten" for even heat distribution and optimal cooking of the egg and potato mixture. Japanese tamagoyaki is prepared using a specialized rectangular or square pan called a "makiyakinabe" or "tamagoyakiki," which facilitates the rolling technique essential for creating its layered texture. Both tools are integral to achieving the distinct textures and shapes that define these iconic global omelettes.
Texture and Flavor Profiles Compared
Spanish tortilla offers a dense, hearty texture with rich flavors from slow-cooked potatoes and onions, delivering a savory and slightly sweet profile. Japanese tamagoyaki features a light, fluffy texture achieved through multiple layers of sweetened, perfectly seasoned eggs, creating a delicate balance of umami and subtle sweetness. Both omelettes showcase unique cultural techniques influencing their contrasting textures and flavor nuances celebrated worldwide.
Presentation and Serving Styles
Spanish tortilla features a thick, round, and rustic presentation, often served in wedge-shaped slices at room temperature, making it ideal for tapas or casual gatherings. Japanese tamagoyaki offers a delicate, rolled appearance with layered textures, typically sliced into neat rectangular pieces and served warm or chilled alongside sushi or as part of a bento box. Both omelettes highlight cultural aesthetics through their distinct serving styles, emphasizing either hearty comfort or refined elegance.
Popular Variations and Regional Twists
Spanish tortilla, known for its thick, hearty layers of potato and onion bound by eggs, is a staple of Spanish cuisine with regional twists including additions like chorizo or red peppers. Japanese tamagoyaki, a delicate, slightly sweet rolled omelette, is crafted by folding multiple thin layers of seasoned egg, often flavored with soy sauce and mirin, showcasing a distinct approach from the Mediterranean style. Both variations highlight how cultural preferences influence texture and flavor profiles, making them iconic representatives of world omelette diversity.
Nutrition and Dietary Considerations
Spanish tortilla, rich in protein and fiber, is made from eggs, potatoes, and onions, offering a hearty source of vitamins B6 and C, while being higher in calories due to its starch content. Japanese tamagoyaki, a slightly sweet, layered omelette crafted from beaten eggs, dashi, and sugar, provides a lower-calorie option with a balanced profile of protein and carbohydrates, favored for its lighter texture and digestibility. Both omelettes serve distinct dietary needs: Spanish tortilla supports energy-dense diets with essential nutrients, whereas tamagoyaki aligns with low-fat, low-calorie preferences while maintaining adequate protein intake.
Which Omelette Wins: Global Appeal and Personal Preferences
Spanish tortilla features a thick, hearty texture made from eggs, potatoes, and onions that appeals to those seeking a savory and filling omelette experience. Japanese tamagoyaki offers a sweet and delicate layered taste, favored for its lightness and artistic presentation. Global appeal depends on cultural preferences, with Spanish tortilla dominating Mediterranean diets while tamagoyaki remains integral to Japanese cuisine, reflecting varied personal tastes in omelette enjoyment.
Spanish tortilla vs Japanese tamagoyaki for world omelettes Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com