Steaming noodles preserves their texture and flavor better than boiling by preventing them from absorbing excess water, resulting in a firmer bite. Boiling can cause noodles to become soggy and lose nutrients due to direct contact with water. For optimal noodle quality, steaming offers a gentler cooking method that maintains the integrity and taste of the noodles.
Table of Comparison
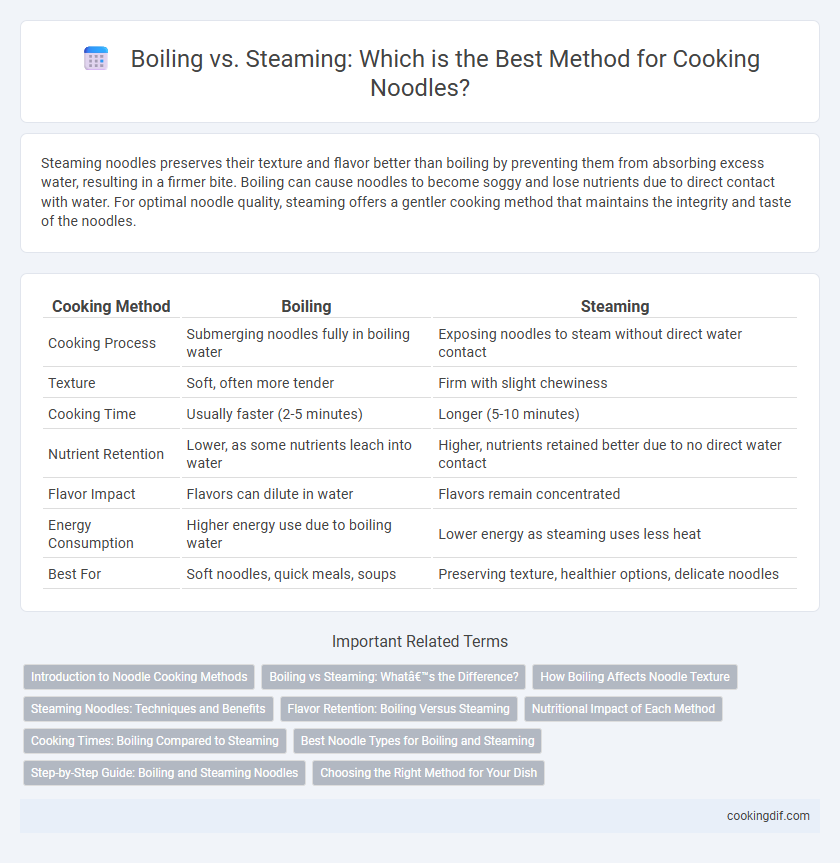
| Cooking Method | Boiling | Steaming |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Process | Submerging noodles fully in boiling water | Exposing noodles to steam without direct water contact |
| Texture | Soft, often more tender | Firm with slight chewiness |
| Cooking Time | Usually faster (2-5 minutes) | Longer (5-10 minutes) |
| Nutrient Retention | Lower, as some nutrients leach into water | Higher, nutrients retained better due to no direct water contact |
| Flavor Impact | Flavors can dilute in water | Flavors remain concentrated |
| Energy Consumption | Higher energy use due to boiling water | Lower energy as steaming uses less heat |
| Best For | Soft noodles, quick meals, soups | Preserving texture, healthier options, delicate noodles |
Introduction to Noodle Cooking Methods
Boiling noodles involves submerging them in rapidly boiling water, ensuring even cooking and a tender texture through consistent heat transfer. Steaming noodles uses hot vapor to cook the dough, preserving a chewier bite and maintaining subtle flavors without direct water contact. Both methods influence noodle texture and taste, with boiling favored for softer results and steaming preferred for denser, more elastic noodles.
Boiling vs Steaming: What’s the Difference?
Boiling noodles involves submerging them in rapidly boiling water, which cooks them quickly and evenly by direct heat transfer. Steaming noodles uses moist heat from boiling water vapor, resulting in a softer texture and less water absorption. The choice between boiling and steaming affects noodle texture, cooking time, and nutrient retention.
How Boiling Affects Noodle Texture
Boiling noodles cooks them through direct contact with hot water, resulting in a uniform, tender texture that allows the starches to gelatinize fully, creating a smooth and pliable bite. The agitation during boiling helps prevent clumping and promotes even cooking, producing noodles that are soft yet resilient. Overboiling can cause the noodles to become mushy as the starch granules break down excessively, highlighting the importance of precise timing in boiling methods.
Steaming Noodles: Techniques and Benefits
Steaming noodles preserves their texture and nutritional value better than boiling by cooking them evenly with gentle moisture and heat. This method prevents the noodles from becoming waterlogged or mushy, maintaining a firm, chewy consistency ideal for various Asian dishes. Steaming also reduces nutrient loss, especially in whole-grain or gluten-free noodles, ensuring a healthier and more flavorful meal.
Flavor Retention: Boiling Versus Steaming
Steaming noodles preserves more natural flavors and nutrients by avoiding direct contact with boiling water, which can leach out soluble compounds. Boiling often results in flavor dilution as starches and seasonings escape into the cooking water. Steamed noodles maintain a firmer texture and a richer taste profile, enhancing overall flavor retention.
Nutritional Impact of Each Method
Boiling noodles causes some loss of water-soluble vitamins like B vitamins and minerals due to leaching into the cooking water, while steaming preserves more nutrients as it avoids direct contact with water. Steamed noodles retain higher amounts of antioxidants and essential nutrients, making them a healthier choice compared to boiling. Nutrient retention differences between methods can affect overall dietary intake, especially for individuals relying on noodles as a primary food source.
Cooking Times: Boiling Compared to Steaming
Boiling noodles typically takes between 5 to 10 minutes, depending on the type and thickness, offering a rapid cooking method that ensures even heat distribution throughout the noodles. Steaming noodles requires a longer duration, often 10 to 20 minutes, as the heat penetrates more gradually, preserving texture and nutrient content. The choice between boiling and steaming impacts not only cooking time but also noodle texture, with boiling yielding softer noodles and steaming retaining a firmer bite.
Best Noodle Types for Boiling and Steaming
Wheat-based noodles like spaghetti and ramen are best suited for boiling because the direct heat quickly cooks the dough, yielding a soft, chewy texture. Rice noodles and delicate glass noodles are ideal for steaming, as this gentle method preserves their subtle flavor and prevents them from becoming overly soggy. Choosing the right cooking technique based on noodle type enhances texture, taste, and overall dish quality.
Step-by-Step Guide: Boiling and Steaming Noodles
Boiling noodles involves placing them in a pot of rapidly boiling water for 8-12 minutes, stirring occasionally to prevent sticking and ensuring even cooking. Steaming noodles requires soaking them briefly, then arranging them in a steaming basket over boiling water, covered and steamed for about 10-15 minutes until tender. Both methods enhance texture differently: boiling yields softer noodles, while steaming retains a firmer, chewier consistency.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Dish
Boiling noodles is ideal for achieving a uniformly soft texture, perfect for soups and stir-fries where the noodles absorb surrounding flavors. Steaming preserves the noodle's firmness and enhances chewier textures, making it suitable for delicate dishes like rice noodle rolls or dim sum. Selecting the right method depends on the desired texture and how the noodles will complement other ingredients in your recipe.
Boiling vs steaming for noodle cooking method Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com