Heavy cream enhances a gratin's richness with its higher fat content, creating a luxuriously creamy texture and a golden, silky crust. Milk, while lighter, results in a more delicate, less decadent dish, allowing other flavors to shine through without overpowering. Choosing heavy cream intensifies the indulgence, while milk keeps the gratin subtle and balanced.
Table of Comparison
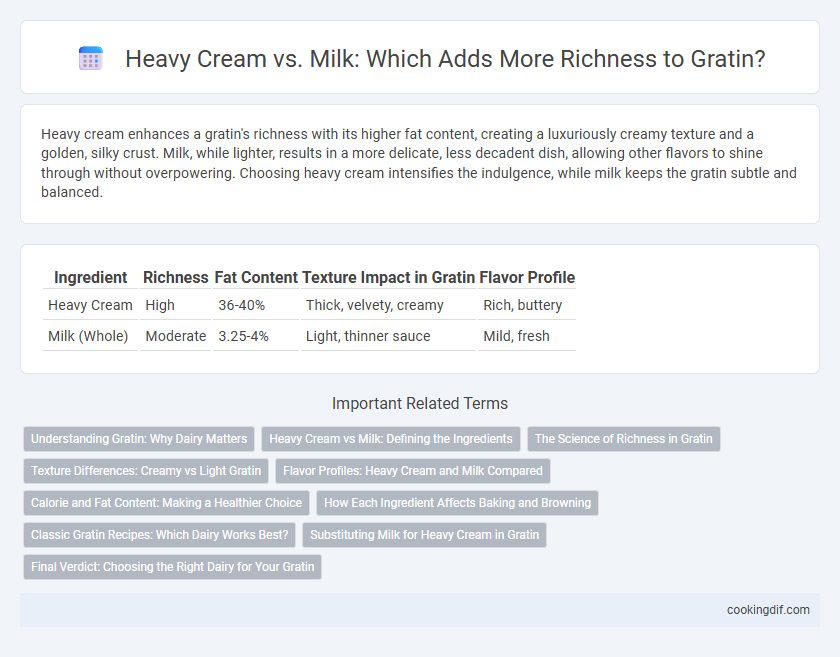
| Ingredient | Richness | Fat Content | Texture Impact in Gratin | Flavor Profile |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heavy Cream | High | 36-40% | Thick, velvety, creamy | Rich, buttery |
| Milk (Whole) | Moderate | 3.25-4% | Light, thinner sauce | Mild, fresh |
Understanding Gratin: Why Dairy Matters
Heavy cream enhances gratin's richness due to its high fat content, creating a luxurious, velvety texture and deeper flavor profile compared to milk. Milk, with lower fat, results in a lighter, less creamy dish, which may benefit those seeking a balance between creaminess and calorie control. Choosing the right dairy impacts the gratin's mouthfeel and overall indulgence, making heavy cream the preferred option for traditional, richly textured gratins.
Heavy Cream vs Milk: Defining the Ingredients
Heavy cream contains about 36-40% fat, providing a rich, velvety texture ideal for gratins, while milk typically has 3-4% fat, resulting in a lighter, less creamy dish. The higher fat content in heavy cream enhances the gratin's golden-brown crust and smooth consistency, ensuring a decadent mouthfeel. Using heavy cream intensifies the dish's richness, whereas milk creates a subtler, more delicate flavor profile suitable for lighter gratin variations.
The Science of Richness in Gratin
Heavy cream contains a higher fat content, typically around 36-40%, which emulsifies with cheese and other ingredients to create a velvety, rich texture in gratin. Milk, with a fat content of about 3-4%, results in a lighter consistency but less depth of flavor due to lower fat molecules and reduced emulsification capability. The science of richness in gratin hinges on fat's role in mouthfeel and flavor release, making heavy cream the optimal choice for a creamy, decadent finish.
Texture Differences: Creamy vs Light Gratin
Heavy cream enhances gratin with a rich, velvety texture due to its high fat content, creating a creamy mouthfeel that intensifies flavor and adds a luxurious density. Milk produces a lighter, more delicate texture, allowing the other ingredients to stand out while maintaining moisture without overwhelming richness. Choosing heavy cream results in a decadent, thick gratin, whereas milk provides a subtly creamy finish with a more airy consistency.
Flavor Profiles: Heavy Cream and Milk Compared
Heavy cream offers a rich, velvety texture and a pronounced buttery flavor that enhances the depth of a gratin, creating a luxurious mouthfeel. Milk provides a lighter, more subtle creaminess with a mild, slightly sweet taste that allows other ingredients like cheese and herbs to shine. Choosing heavy cream results in a richer, more indulgent gratin, while milk yields a delicate balance of flavors with less fat content.
Calorie and Fat Content: Making a Healthier Choice
Heavy cream contains significantly more calories and fat than milk, making it richer and creamier for gratin dishes. A typical heavy cream has around 400 calories and 43 grams of fat per cup, while milk averages 150 calories and 8 grams of fat per cup. Choosing milk reduces calorie and fat intake, offering a lighter alternative without sacrificing moisture in gratin recipes.
How Each Ingredient Affects Baking and Browning
Heavy cream enhances the richness of gratin by adding higher fat content, which promotes a creamy texture and deeper browning due to Maillard reactions during baking. Milk, containing less fat and more water, results in a lighter texture with less browning, yielding a milder flavor development. The choice between heavy cream and milk directly impacts gratin's richness, texture, and golden crust formation, influencing the dish's overall sensory appeal.
Classic Gratin Recipes: Which Dairy Works Best?
Heavy cream provides a richer, creamier texture and enhances the luxurious mouthfeel in classic gratin recipes, making it ideal for achieving that signature golden crust and velvety interior. Milk, while lighter and less fat-dense, results in a subtler creaminess and allows the natural flavors of ingredients like potatoes and cheese to shine without overwhelming the dish. For traditional gratins, heavy cream is often preferred because its higher fat content contributes to a more indulgent dish with a depth of flavor that milk cannot fully replicate.
Substituting Milk for Heavy Cream in Gratin
Substituting milk for heavy cream in gratin reduces the dish's richness and creamy texture due to milk's lower fat content, typically around 3.5%, compared to heavy cream's 36-40%. To maintain a similar level of velvety smoothness and luxurious mouthfeel, incorporating a roux or increasing cheese content can compensate for the difference. Milk-based gratins tend to be lighter and less dense, offering a milder flavor profile but requiring careful seasoning to enhance overall taste.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Right Dairy for Your Gratin
Heavy cream enhances gratin with its high fat content, providing a rich, velvety texture and deeper flavor. Milk offers a lighter alternative, producing a less dense dish with a more delicate taste that allows the other ingredients to shine. Selecting heavy cream or milk ultimately depends on desired richness and calorie preferences, with cream favored for indulgence and milk suited for a subtler, lower-fat option.
Heavy cream vs Milk for richness Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com