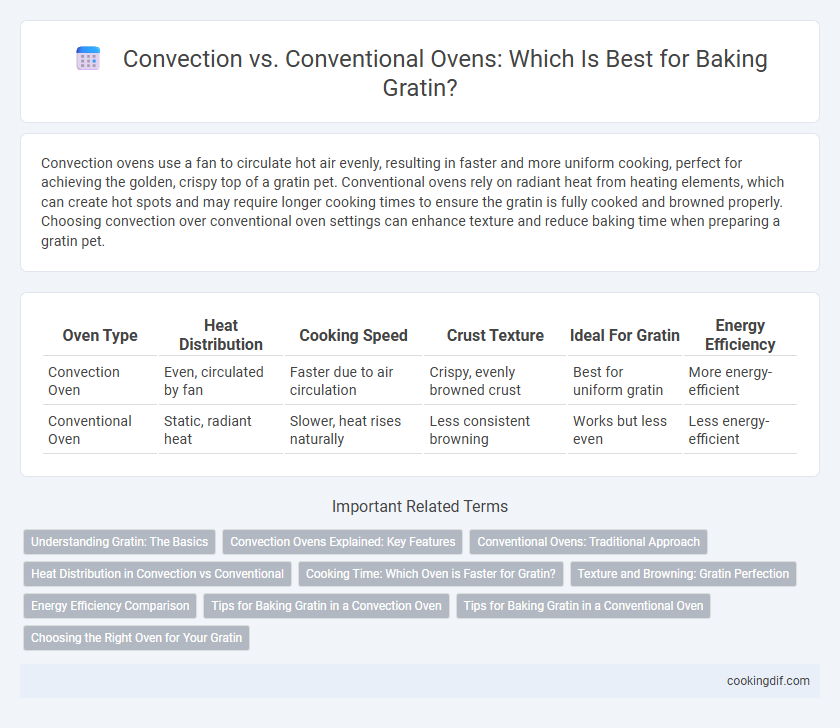
Convection ovens use a fan to circulate hot air evenly, resulting in faster and more uniform cooking, perfect for achieving the golden, crispy top of a gratin pet. Conventional ovens rely on radiant heat from heating elements, which can create hot spots and may require longer cooking times to ensure the gratin is fully cooked and browned properly. Choosing convection over conventional oven settings can enhance texture and reduce baking time when preparing a gratin pet.
Table of Comparison
| Oven Type | Heat Distribution | Cooking Speed | Crust Texture | Ideal For Gratin | Energy Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Convection Oven | Even, circulated by fan | Faster due to air circulation | Crispy, evenly browned crust | Best for uniform gratin | More energy-efficient |
| Conventional Oven | Static, radiant heat | Slower, heat rises naturally | Less consistent browning | Works but less even | Less energy-efficient |
Understanding Gratin: The Basics
Convection ovens circulate hot air evenly around gratin dishes, promoting faster and more uniform browning of the cheese crust compared to conventional ovens. Conventional ovens rely on radiant heat from the top and bottom, which can result in uneven cooking and longer baking times for gratins. Understanding the benefits of convection helps achieve a perfectly crisp, golden-brown surface while maintaining a creamy interior in classic gratin recipes.
Convection Ovens Explained: Key Features
Convection ovens feature a built-in fan that circulates hot air evenly, ensuring uniform browning and crispy gratin toppings. This improved heat distribution reduces cooking times and enhances texture compared to conventional ovens, which rely on static heat sources. The consistent temperature control of convection ovens is ideal for achieving the perfect golden crust essential in gratin dishes.
Conventional Ovens: Traditional Approach
Conventional ovens use heating elements at the top and bottom to cook gratins with steady, radiant heat, promoting even browning and a crisp, golden crust. This traditional approach ensures that the dish's creamy textures develop fully while the surface forms a rich, savory topping. Unlike convection ovens, conventional heat avoids forced air circulation, resulting in slower, more uniform cooking ideal for classic gratin recipes.
Heat Distribution in Convection vs Conventional
Convection ovens use a fan to circulate hot air evenly around the gratin, promoting uniform heat distribution and consistent browning on the surface. Conventional ovens rely on radiant heat from the top and bottom elements, which can create hot spots and uneven cooking, often requiring rotation of the dish. This difference in heat distribution affects the gratin's texture, with convection ovens delivering a crispier crust and more evenly cooked interior.
Cooking Time: Which Oven is Faster for Gratin?
Convection ovens cook gratin faster than conventional ovens due to their efficient hot air circulation, which evenly distributes heat and reduces cooking time by up to 25%. Conventional ovens rely on static heat, often requiring longer baking periods and resulting in less uniform browning of the gratin's surface. Choosing a convection oven enhances the gratin's texture with a crispy top and tender interior in a shorter timeframe.
Texture and Browning: Gratin Perfection
Convection ovens circulate hot air evenly, resulting in a consistently crispy, golden-brown crust on gratins, enhancing texture through uniform heat distribution. Conventional ovens often produce a softer top layer with uneven browning due to stagnant heat, which can affect the gratin's overall crunch. For gratin perfection, convection settings optimize both texture and browning by promoting moisture evaporation and caramelization.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Convection ovens utilize a fan to circulate hot air, resulting in faster and more even cooking for gratin dishes, which reduces overall energy consumption compared to conventional ovens. Conventional ovens rely on stationary heating elements, requiring longer cooking times and higher temperatures, thus increasing energy usage. Energy efficiency studies show convection ovens can save up to 20% on electricity when baking gratins.
Tips for Baking Gratin in a Convection Oven
Baking gratin in a convection oven promotes even browning and crispier textures due to the consistent air circulation at approximately 25degF lower than conventional oven temperatures, typically set around 350degF. Use a shallow, wide dish to maximize exposure to the hot air, ensuring the top layer achieves a golden crust while the interior remains creamy. Monitor closely near the end of cooking, as convection ovens can brown gratins faster, often reducing total baking time by 10-15 minutes compared to conventional ovens.
Tips for Baking Gratin in a Conventional Oven
For baking gratin in a conventional oven, maintain a consistent temperature of 350degF to 375degF to ensure even cooking without burning the top. Use a shallow baking dish to promote uniform heat distribution and avoid soggy layers. Cover the gratin with foil during the initial baking phase to prevent excessive browning, then uncover in the last 10 minutes for a golden, crispy crust.
Choosing the Right Oven for Your Gratin
Choosing the right oven for your gratin significantly impacts its texture and flavor development. Convection ovens circulate hot air to create an even, crispy golden crust while maintaining creamy layers beneath, making them ideal for gratins. Conventional ovens provide consistent heat from the bottom up, which works for slow cooking but may require careful monitoring to avoid uneven browning or sogginess.
Convection vs Conventional for oven type Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com