Mild chili peppers offer a gentle heat that enhances dishes without overwhelming the palate, making them ideal for those who prefer subtle spice. Hot chili peppers deliver a fiery intensity that can elevate flavors and add a bold kick to recipes, appealing to spice enthusiasts. Choosing between mild and hot chili depends on the desired heat level and flavor profile in your culinary creations.
Table of Comparison
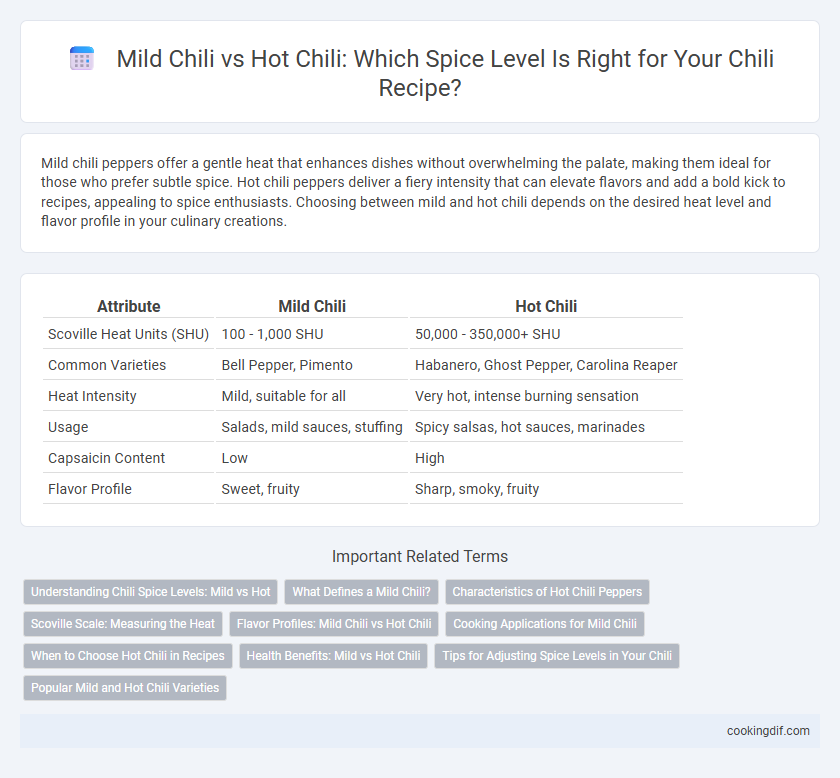
| Attribute | Mild Chili | Hot Chili |
|---|---|---|
| Scoville Heat Units (SHU) | 100 - 1,000 SHU | 50,000 - 350,000+ SHU |
| Common Varieties | Bell Pepper, Pimento | Habanero, Ghost Pepper, Carolina Reaper |
| Heat Intensity | Mild, suitable for all | Very hot, intense burning sensation |
| Usage | Salads, mild sauces, stuffing | Spicy salsas, hot sauces, marinades |
| Capsaicin Content | Low | High |
| Flavor Profile | Sweet, fruity | Sharp, smoky, fruity |
Understanding Chili Spice Levels: Mild vs Hot
Mild chili typically contains low levels of capsaicin, resulting in a gentle, subtle heat that enhances flavor without overwhelming the palate. Hot chili varieties, such as habanero or ghost pepper, have significantly higher Scoville Heat Units (SHU), delivering intense, fiery spice that can cause a burning sensation. Understanding the Scoville scale helps distinguish between mild chilies, usually under 5,000 SHU, and hot chilies, which often exceed 100,000 SHU, allowing cooks to select the right spice level for their dishes.
What Defines a Mild Chili?
Mild chili is defined by its lower capsaicin content, typically ranging from 100 to 1,000 Scoville Heat Units (SHU), which produces a gentle warmth without overwhelming heat. Varieties like poblano, Anaheim, and bell peppers fall into this category, offering subtle spice and rich flavor profiles ideal for those sensitive to intense heat. The balance of mild chili enhances dishes by adding depth without dominating other ingredients, contrasting sharply with hot chili varieties that can exceed 100,000 SHU.
Characteristics of Hot Chili Peppers
Hot chili peppers contain higher levels of capsaicin, the compound responsible for their intense heat, measured on the Scoville Heat Scale often exceeding 50,000 units. Their fiery flavor profile is accompanied by a sharper, more pungent aroma and thinner flesh compared to mild varieties, which contributes to a more intense sensory experience. Nutritionally, hot chili peppers are rich in vitamins A and C, and their heat stimulates metabolism and endorphin release, making them popular in both culinary and medicinal uses.
Scoville Scale: Measuring the Heat
The Scoville Scale quantifies chili pepper heat by measuring capsaicin concentration, ranging from 0 SHU in mild peppers like bell peppers to over 1,000,000 SHU in hot varieties such as the Carolina Reaper. Mild chilies typically score under 1,000 Scoville Heat Units (SHU), providing subtle warmth, while hot chilies exceed 100,000 SHU, delivering intense spiciness. This scale is essential for distinguishing spice levels in culinary applications and for consumers seeking precise heat tolerance.
Flavor Profiles: Mild Chili vs Hot Chili
Mild chili offers a subtle heat with a rich, sweet, and earthy flavor profile, often enhanced by fruity or smoky undertones that complement dishes without overwhelming the palate. Hot chili delivers intense spiciness characterized by sharp, pungent notes and a lingering heat that intensifies the overall taste experience while adding complexity through floral or citrus hints. The contrast between mild and hot chili hinges on the concentration of capsaicin, which directly influences the perceived heat and enhances different facets of the chili's flavor spectrum.
Cooking Applications for Mild Chili
Mild chili peppers, such as Anaheim or Poblano, offer a gentle heat ideal for recipes requiring subtle spice without overwhelming flavor. Their mild heat level allows for versatile use in sauces, soups, and stews, enhancing dishes with a rich, smoky undertone. These chilies are perfect for cooking applications where a balanced spice level complements other ingredients, especially in family-friendly meals and traditional Mexican cuisine.
When to Choose Hot Chili in Recipes
Select hot chili in recipes when aiming to intensify spice levels, enhance bold flavors, or complement robust ingredients like beef, dark chocolate, or smoky components. Hot chili varieties such as habanero, bird's eye, or cayenne deliver significant heat measured in Scoville Heat Units (SHU), ranging from 100,000 to over 350,000 SHU, making them ideal for dishes requiring a pronounced spicy kick. Use hot chili carefully to balance heat with flavor complexity in salsas, stews, barbecue sauces, or spicy marinades.
Health Benefits: Mild vs Hot Chili
Mild chili contains lower levels of capsaicin, making it easier on the digestive system while still providing antioxidants and vitamins like vitamin C and A. Hot chili, rich in high capsaicin content, offers enhanced metabolism-boosting effects and pain relief properties due to its anti-inflammatory compounds. Both types contribute to cardiovascular health and immune system support, but hot chili delivers more potent health benefits linked to its spiciness.
Tips for Adjusting Spice Levels in Your Chili
When adjusting spice levels in chili, start with mild chili peppers like ancho or poblano for a subtle heat that won't overpower other flavors. Gradually introduce hotter varieties such as jalapeno or habanero to increase spice intensity while maintaining balance. Controlling the amount of seeds and membranes in the peppers can fine-tune the heat, allowing you to customize the chili to your preferred spice level.
Popular Mild and Hot Chili Varieties
Popular mild chili varieties include Anaheim, Poblano, and Banana peppers, which typically range from 100 to 1,000 Scoville Heat Units (SHU), offering gentle warmth suitable for most palates. Hot chili options like Habanero, Scotch Bonnet, and Ghost peppers significantly raise spice levels, with SHU values ranging from 100,000 up to over 1,000,000, delivering intense heat for spice enthusiasts. Selecting between mild and hot chilies depends on the desired culinary impact, ranging from subtle flavor enhancement to fiery heat intensity.
Mild chili vs hot chili for spice level Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com