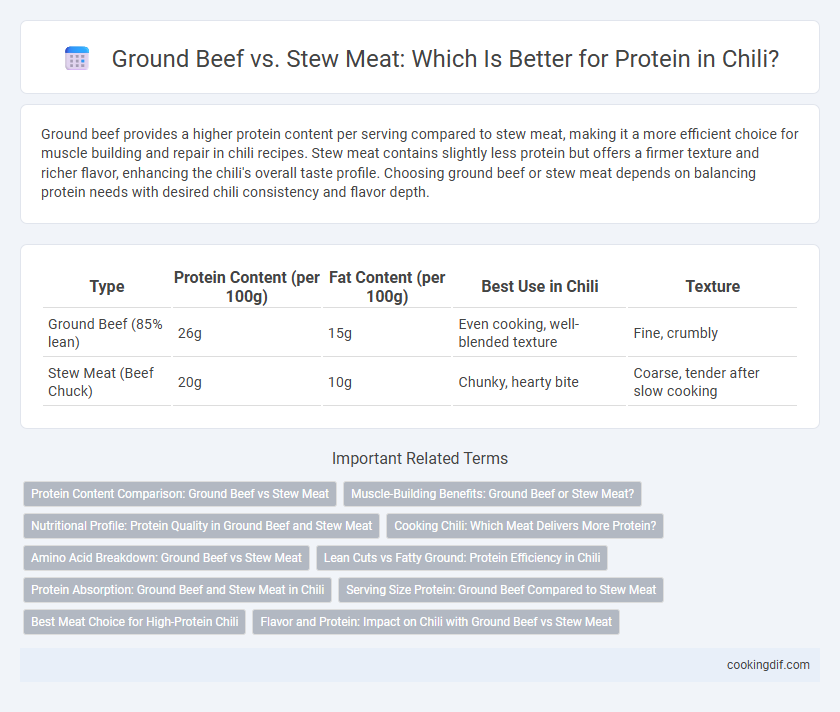
Ground beef provides a higher protein content per serving compared to stew meat, making it a more efficient choice for muscle building and repair in chili recipes. Stew meat contains slightly less protein but offers a firmer texture and richer flavor, enhancing the chili's overall taste profile. Choosing ground beef or stew meat depends on balancing protein needs with desired chili consistency and flavor depth.
Table of Comparison
| Type | Protein Content (per 100g) | Fat Content (per 100g) | Best Use in Chili | Texture |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ground Beef (85% lean) | 26g | 15g | Even cooking, well-blended texture | Fine, crumbly |
| Stew Meat (Beef Chuck) | 20g | 10g | Chunky, hearty bite | Coarse, tender after slow cooking |
Protein Content Comparison: Ground Beef vs Stew Meat
Ground beef typically contains around 20-25 grams of protein per 3-ounce cooked serving, offering a balanced mix of fat and protein suited for chili recipes. Stew meat, often cut from tougher muscles like chuck or round, provides approximately 22-26 grams of protein per 3-ounce cooked portion, making it a slightly leaner alternative with a richer protein density. Choosing between ground beef and stew meat for chili depends on desired texture and fat content, but both deliver robust protein levels essential for a hearty, nutritious meal.
Muscle-Building Benefits: Ground Beef or Stew Meat?
Ground beef contains approximately 22 grams of protein per 4-ounce serving, making it a rich source for muscle-building due to its higher fat content that supports sustained energy release. Stew meat, typically leaner with around 20 grams of protein per 4-ounce serving, offers a lower fat option that enhances lean muscle gains while promoting easier digestion. Both ground beef and stew meat contribute essential amino acids crucial for muscle repair and growth, but ground beef's higher calorie content may better support intense workout recovery phases.
Nutritional Profile: Protein Quality in Ground Beef and Stew Meat
Ground beef typically contains higher fat content but offers a rich source of complete protein with all essential amino acids, making it ideal for muscle repair and growth in chili recipes. Stew meat, often leaner and derived from tougher cuts like chuck or round, provides slightly less fat while maintaining a high-quality protein profile beneficial for sustained energy release. Choosing between ground beef and stew meat depends on desired fat content and protein density, influencing both the nutritional value and texture of the chili.
Cooking Chili: Which Meat Delivers More Protein?
Ground beef typically contains around 20-25 grams of protein per 100 grams, making it a dense source of protein ideal for chili recipes. Stew meat, often cut from tougher, leaner parts, offers slightly less protein per serving but delivers a richer, more tender texture after slow cooking. Choosing ground beef enhances protein content, while stew meat adds depth and tenderness to chili's flavor profile.
Amino Acid Breakdown: Ground Beef vs Stew Meat
Ground beef typically contains a higher concentration of essential amino acids like leucine, isoleucine, and valine, which are crucial for muscle protein synthesis compared to stew meat. Stew meat, often derived from tougher cuts, offers a slightly different amino acid profile with a higher collagen content that supports joint health but may have lower levels of branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs). For chili recipes aiming for optimal protein quality and muscle recovery, ground beef provides a more balanced and bioavailable amino acid composition.
Lean Cuts vs Fatty Ground: Protein Efficiency in Chili
Lean cuts of ground beef offer higher protein content per serving compared to fattier ground options, making them more protein-efficient for chili recipes. Stew meat, typically from tougher cuts like chuck, balances moderate fat with substantial protein but often requires longer cooking times to tenderize. Choosing lean ground beef optimizes protein intake in chili without excess fat, enhancing both nutrition and texture.
Protein Absorption: Ground Beef and Stew Meat in Chili
Ground beef in chili provides a higher surface area that enhances protein absorption during digestion, making its amino acids more readily available for muscle repair and growth. Stew meat, typically composed of larger, tougher cuts, requires longer cooking times to break down collagen, which can slow protein bioavailability despite its rich collagen content. Choosing ground beef in chili recipes optimizes protein uptake due to its finer texture and more efficient breakdown in the digestive system.
Serving Size Protein: Ground Beef Compared to Stew Meat
A 4-ounce serving of ground beef typically contains about 22 grams of protein, making it a dense protein source for chili recipes. Stew meat, often cut from tougher, leaner cuts, provides around 19 grams of protein per 4-ounce serving. The slightly higher fat content in ground beef can also influence the protein concentration, making it a popular choice for richer, protein-packed chili dishes.
Best Meat Choice for High-Protein Chili
Ground beef typically contains about 20-25 grams of protein per 100 grams, making it a rich source of protein ideal for high-protein chili recipes. Stew meat, often comprising tougher cuts like chuck or round, provides slightly less protein per serving but offers a more robust texture and flavor when slow-cooked. For maximizing protein content while maintaining a hearty taste, lean ground beef is the best meat choice for high-protein chili.
Flavor and Protein: Impact on Chili with Ground Beef vs Stew Meat
Ground beef offers a higher protein content with a fine texture that blends seamlessly into chili, enhancing its rich flavor while providing a tender bite. Stew meat, typically from tougher cuts like chuck, delivers a deeper, beefier flavor due to slow cooking, but has a slightly lower protein concentration and a chunkier texture. Choosing between ground beef and stew meat affects chili's protein density and flavor profile, with ground beef maximizing protein and stew meat intensifying savory complexity.
Ground beef vs stew meat for protein Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com