Gelatin provides a smooth, creamy texture and is ideal for traditional cake fillings and mousses, but it requires refrigeration to set properly. Agar-agar, derived from seaweed, sets more firmly and can be used at room temperature, making it suitable for vegan and vegetarian cakes. Both agents offer unique setting properties, but the choice depends on dietary preferences and the desired firmness of the cake.
Table of Comparison
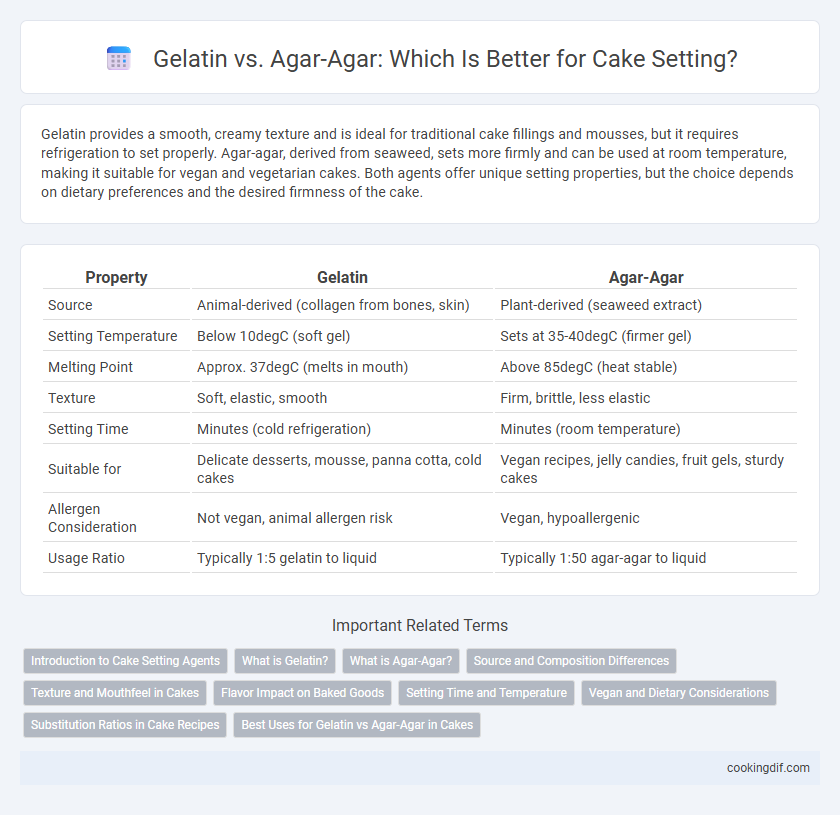
| Property | Gelatin | Agar-Agar |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Animal-derived (collagen from bones, skin) | Plant-derived (seaweed extract) |
| Setting Temperature | Below 10degC (soft gel) | Sets at 35-40degC (firmer gel) |
| Melting Point | Approx. 37degC (melts in mouth) | Above 85degC (heat stable) |
| Texture | Soft, elastic, smooth | Firm, brittle, less elastic |
| Setting Time | Minutes (cold refrigeration) | Minutes (room temperature) |
| Suitable for | Delicate desserts, mousse, panna cotta, cold cakes | Vegan recipes, jelly candies, fruit gels, sturdy cakes |
| Allergen Consideration | Not vegan, animal allergen risk | Vegan, hypoallergenic |
| Usage Ratio | Typically 1:5 gelatin to liquid | Typically 1:50 agar-agar to liquid |
Introduction to Cake Setting Agents
Gelatin and agar-agar serve as essential cake setting agents, each offering unique properties for dessert preparation. Gelatin, derived from animal collagen, provides a smooth, elastic texture and requires refrigeration to set, ideal for mousses and panna cotta. Agar-agar, a plant-based alternative extracted from seaweed, sets firmer and more quickly at room temperature, making it perfect for vegan cakes and jellies.
What is Gelatin?
Gelatin is a natural protein derived from collagen found in animal bones, skin, and connective tissues, widely used in baking for its excellent gelling and thickening properties. It melts at body temperature, providing a smooth, melt-in-the-mouth texture ideal for cakes and desserts. Unlike agar-agar, gelatin requires refrigeration to set firmly and delivers a soft, flexible gel that enhances the overall texture of mousse cakes and layered desserts.
What is Agar-Agar?
Agar-agar is a natural gelling agent derived from red algae, commonly used as a vegetarian alternative to gelatin in cake recipes. It sets more firmly and at room temperature, making it ideal for creating stable, clear gels in desserts without refrigeration. Rich in dietary fiber, agar-agar provides a vegan-friendly and allergen-free option that enhances texture while maintaining the flavor integrity of cakes.
Source and Composition Differences
Gelatin is derived from animal collagen, primarily sourced from pig skin and bovine bones, making it unsuitable for vegetarians and vegans. Agar-agar, a plant-based alternative, is extracted from red algae and composed mainly of polysaccharides, offering a vegan-friendly option with different gelling properties. The chemical composition of gelatin allows for a soft, melt-in-the-mouth texture, while agar-agar sets firmer and remains stable at higher temperatures.
Texture and Mouthfeel in Cakes
Gelatin creates a smooth, creamy texture in cakes with a melt-in-your-mouth mouthfeel due to its animal protein content, making it ideal for mousse and delicate desserts. Agar-agar, derived from seaweed, provides a firmer, slightly brittle set with a more jelly-like consistency, often resulting in a less creamy texture but a clean break. Choosing between gelatin and agar-agar impacts the cake's texture and mouthfeel, influencing the dessert's overall sensory experience based on whether a silky or more structured finish is desired.
Flavor Impact on Baked Goods
Gelatin provides a subtle, neutral flavor that preserves the original taste of baked goods, making it ideal for delicate desserts requiring a soft, smooth set. Agar-agar imparts a slightly vegetal or seaweed-like flavor that can subtly alter the profile of cakes and pastries, especially in lighter or more delicate recipes. When choosing between gelatin and agar-agar, consider the flavor sensitivity of the baked item to maintain the intended taste experience.
Setting Time and Temperature
Gelatin sets at a cooler temperature, typically requiring refrigeration at around 4degC (39degF) and taking approximately 4 hours to fully solidify, while agar-agar sets much faster at room temperature, usually within 30 to 60 minutes, and remains stable up to 85degC (185degF). Agar-agar's higher melting point and quicker setting time make it ideal for cakes that need to hold their shape in warmer environments. Gelatin, derived from animal collagen, provides a smoother texture but demands precise temperature control to achieve optimal firmness.
Vegan and Dietary Considerations
Gelatin, derived from animal collagen, is widely used for its strong setting properties but is unsuitable for vegans and those with dietary restrictions avoiding animal products. Agar-agar, sourced from seaweed, provides a firm and clear gel while catering to vegan, vegetarian, and kosher diets, making it a preferred alternative. Its higher setting temperature and neutral flavor enhance its versatility in plant-based and allergen-friendly cake recipes.
Substitution Ratios in Cake Recipes
Gelatin and agar-agar serve as common gelling agents in cake recipes, with substitution ratios varying due to their different setting strengths. Typically, 1 teaspoon of gelatin powder equates to approximately 1 teaspoon of agar-agar powder, but agar-agar sets more firmly and at room temperature, often requiring adjustments such as reducing the amount to 0.5 - 0.75 teaspoons for similar firmness. Understanding these ratios ensures proper texture and stability when substituting gelatin with plant-based agar-agar in cake preparation.
Best Uses for Gelatin vs Agar-Agar in Cakes
Gelatin offers a smooth, elastic texture ideal for mousse cakes and delicate desserts requiring a clear, glossy finish. Agar-agar provides a firm, brittle set perfect for vegan or vegetarian cakes and recipes needing a more stable structure at room temperature. Choosing gelatin or agar-agar depends on cake type, dietary preferences, and desired texture consistency.
Gelatin vs Agar-Agar for setting Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com