Electric ovens provide consistent heat using heating elements, ideal for baking cakes with even browning and stable temperatures. Convection ovens use a fan to circulate hot air, promoting faster and more uniform baking, which helps achieve a lighter crumb and crisp crust. Choosing between the two depends on whether precise, gradual heat or quicker, circulated heat is preferred for the cake's texture and finish.
Table of Comparison
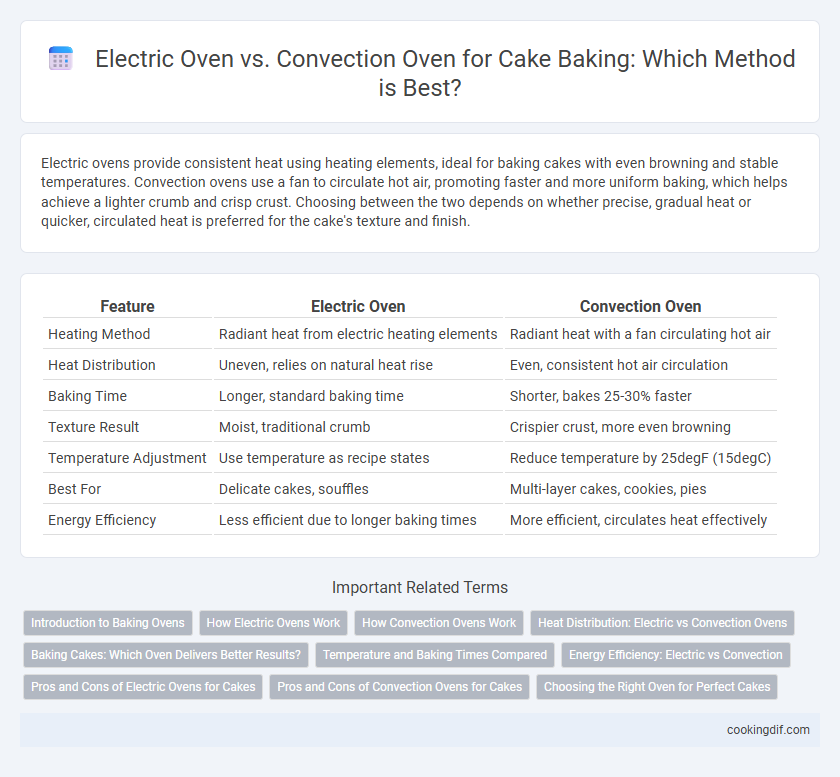
| Feature | Electric Oven | Convection Oven |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Radiant heat from electric heating elements | Radiant heat with a fan circulating hot air |
| Heat Distribution | Uneven, relies on natural heat rise | Even, consistent hot air circulation |
| Baking Time | Longer, standard baking time | Shorter, bakes 25-30% faster |
| Texture Result | Moist, traditional crumb | Crispier crust, more even browning |
| Temperature Adjustment | Use temperature as recipe states | Reduce temperature by 25degF (15degC) |
| Best For | Delicate cakes, souffles | Multi-layer cakes, cookies, pies |
| Energy Efficiency | Less efficient due to longer baking times | More efficient, circulates heat effectively |
Introduction to Baking Ovens
Electric ovens provide consistent heat through exposed heating elements, ideal for stable temperature control during delicate cake baking. Convection ovens utilize a fan to circulate hot air evenly, reducing baking time and promoting uniform browning for cakes. Selecting between electric and convection ovens depends on desired cake texture and baking speed preferences.
How Electric Ovens Work
Electric ovens use heating elements, typically located at the top and bottom, to generate consistent radiant heat essential for baking cakes. The heating elements convert electrical energy into heat, creating a stable temperature environment that ensures even cooking of the batter. Precise temperature control in electric ovens helps maintain uniformity in texture and rise, crucial for achieving moist and well-baked cakes.
How Convection Ovens Work
Convection ovens use a built-in fan and exhaust system to circulate hot air evenly around the cake, promoting uniform baking and a consistent rise. This method reduces hot spots common in electric ovens, ensuring the cake cooks faster and more evenly, with a golden crust and moist interior. The continuous air circulation enhances heat transfer, improving texture and preventing sogginess often encountered in standard electric oven baking.
Heat Distribution: Electric vs Convection Ovens
Electric ovens provide consistent, radiant heat that bakes cakes evenly but can create hot spots requiring careful rack placement. Convection ovens use an internal fan to circulate hot air, promoting uniform heat distribution which results in faster, more even baking and a superior crumb texture. The fan-driven airflow in convection ovens also helps maintain moisture balance, preventing dry cake edges compared to static heat in electric ovens.
Baking Cakes: Which Oven Delivers Better Results?
Electric ovens provide consistent, even heating suitable for baking cakes but can create hot spots that may cause uneven rising or browning. Convection ovens use a fan to circulate hot air, promoting faster and more uniform baking, ideal for cakes requiring a tender crumb and even texture. Bakers often prefer convection ovens for complex cakes since they reduce baking time and deliver a moist interior with a golden, crisp exterior.
Temperature and Baking Times Compared
Electric ovens maintain a steady temperature through radiant heat, often requiring longer baking times to ensure even cooking, typically around 350degF for 25-35 minutes for cakes. Convection ovens circulate hot air with a fan, allowing for a lower temperature setting, usually around 325degF, and reducing baking times by 20-25%, resulting in faster, more evenly baked cakes. Adjusting temperature and time is crucial in each oven type to prevent overbaking or undercooking, optimizing moisture and texture in cakes.
Energy Efficiency: Electric vs Convection
Electric ovens consume more energy due to longer preheating and baking times, whereas convection ovens use fans to circulate hot air, reducing cooking duration and overall energy consumption. The enhanced air circulation in convection ovens ensures even heat distribution, leading to faster baking and lower electricity usage. Consequently, convection ovens offer superior energy efficiency compared to traditional electric ovens when baking cakes.
Pros and Cons of Electric Ovens for Cakes
Electric ovens provide consistent, even heat essential for baking cakes evenly without hot spots, which helps achieve a uniform crumb and texture. However, they may take longer to preheat compared to convection ovens, potentially slowing down the baking process. The lack of built-in fans in electric ovens can result in less efficient heat circulation, sometimes causing uneven browning on cakes.
Pros and Cons of Convection Ovens for Cakes
Convection ovens use a fan to circulate hot air, promoting even baking and reducing cooking time for cakes, which helps achieve a consistent texture and well-browned crust. However, the intense airflow can sometimes cause cakes to dry out or rise unevenly, requiring adjustments in temperature and baking time. These ovens are ideal for experienced bakers seeking efficiency but may pose challenges for delicate cake recipes sensitive to air movement.
Choosing the Right Oven for Perfect Cakes
Electric ovens provide consistent, even heating ideal for delicate cakes, while convection ovens circulate hot air to reduce baking time and create a golden crust. Choosing the right oven depends on the cake type and desired texture, with electric ovens preferred for soft, moist cakes and convection ovens suited for denser, evenly browned cakes. Precise temperature control and proper rack placement further enhance baking results, ensuring perfect cakes every time.
Electric oven vs Convection oven for baking method Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com