Convection ovens circulate hot air with a fan, promoting even baking and reducing cooking time for cakes, resulting in a consistently golden crust and moist interior. Conventional ovens rely on radiant heat without air circulation, which may cause uneven rising and browning, often requiring adjustments in baking time or temperature. Choosing a convection oven can enhance cake texture and appearance, but lowering the temperature by 25 degrees Fahrenheit is recommended to prevent overbaking.
Table of Comparison
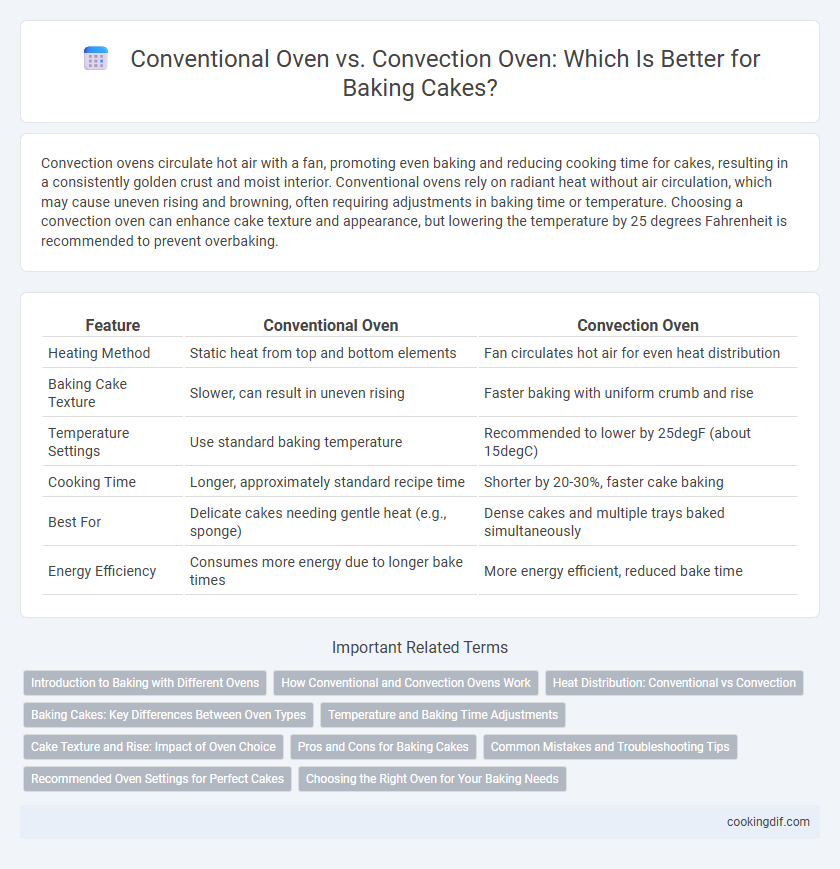
| Feature | Conventional Oven | Convection Oven |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Static heat from top and bottom elements | Fan circulates hot air for even heat distribution |
| Baking Cake Texture | Slower, can result in uneven rising | Faster baking with uniform crumb and rise |
| Temperature Settings | Use standard baking temperature | Recommended to lower by 25degF (about 15degC) |
| Cooking Time | Longer, approximately standard recipe time | Shorter by 20-30%, faster cake baking |
| Best For | Delicate cakes needing gentle heat (e.g., sponge) | Dense cakes and multiple trays baked simultaneously |
| Energy Efficiency | Consumes more energy due to longer bake times | More energy efficient, reduced bake time |
Introduction to Baking with Different Ovens
Baking cakes in a conventional oven provides consistent, radiant heat ideal for delicate, even rising, while a convection oven uses a fan to circulate hot air, promoting faster, more uniform baking and browning. Understanding the heat distribution of each oven type helps bakers adjust temperatures and baking times to prevent overbaking or uneven textures. Mastery of these ovens enhances the quality and appearance of cakes, ensuring moist interiors and crisp, golden crusts.
How Conventional and Convection Ovens Work
Conventional ovens use radiant heat from heating elements at the top and bottom, creating a static cooking environment that bakes cakes through gradual heat transfer. Convection ovens feature an internal fan that circulates hot air evenly, promoting consistent temperature distribution and faster baking times for cakes. Understanding these heating mechanisms helps bakers choose the best oven type for even crumb texture and optimal rise in cakes.
Heat Distribution: Conventional vs Convection
Conventional ovens use radiant heat from stationary heating elements, resulting in uneven heat distribution that can cause hot spots and inconsistent cake baking. Convection ovens feature a fan that circulates hot air, ensuring even heat distribution and faster, more uniform cake baking. This improved air circulation helps cakes rise better and develop a consistent crust and texture.
Baking Cakes: Key Differences Between Oven Types
Baking cakes in a conventional oven provides steady, radiant heat ideal for recipes requiring slow, even rising and browning. Convection ovens use fans to circulate hot air, promoting faster, more uniform baking, which can lead to crisper edges but may dry out delicate cakes if baking time and temperature adjustments aren't made. Understanding these differences helps bakers optimize cake texture, moisture, and appearance based on oven type.
Temperature and Baking Time Adjustments
Convection ovens require lowering the baking temperature by about 25degF compared to conventional ovens due to their fan-assisted heat circulation, which promotes even cooking and prevents hot spots in cakes. Baking times in convection ovens are typically reduced by 25%, enhancing efficiency without compromising texture or moisture. Adjusting temperature and time properly ensures cakes rise evenly and develop a consistent crumb structure.
Cake Texture and Rise: Impact of Oven Choice
Convection ovens circulate hot air evenly, promoting consistent cake rise and a uniform, tender crumb texture, while conventional ovens rely on static heat that may cause uneven baking and denser cake centers. The constant airflow in convection ovens accelerates moisture evaporation, resulting in a slightly drier crust but a lighter, fluffier interior. Bakers aiming for optimal volume and delicate crumb often prefer convection baking for cakes due to superior heat distribution and rise control.
Pros and Cons for Baking Cakes
Conventional ovens provide consistent, even heat ideal for classic cake recipes, ensuring a uniform rise and moist crumb, but they often require longer baking times and can create hot spots. Convection ovens use a fan to circulate hot air, leading to faster, more even baking and browning, which benefits layered and sponge cakes, though they may cause delicate cakes to dry out or bake unevenly if not carefully monitored. Adjusting temperature settings and baking time is essential when using convection ovens to optimize cake texture and prevent over-baking.
Common Mistakes and Troubleshooting Tips
Baking cakes in a conventional oven often leads to uneven cooking and underbaked centers due to inconsistent heat distribution, while convection ovens provide more uniform heat but can cause cakes to dry out if baking times are not adjusted. A common mistake in convection baking is failing to reduce the temperature by 25degF or cut baking time by 25%, resulting in overbrowned edges and dry texture. To troubleshoot, use an oven thermometer to verify actual temperature, rotate pans in conventional ovens for even browning, and monitor cakes closely when using convection settings to avoid overbaking.
Recommended Oven Settings for Perfect Cakes
For baking perfect cakes, conventional ovens are best set to a temperature 25 degrees Fahrenheit higher than the recipe's suggested temperature because they rely on radiant heat for even cooking. Convection ovens require lowering the temperature by 20 to 25 degrees Fahrenheit and reducing baking time by about 25%, as the fan circulates hot air to promote uniform baking and browning. Optimal oven settings also include placing the cake rack in the center for even heat distribution and monitoring the cake closely to prevent overbaking.
Choosing the Right Oven for Your Baking Needs
Conventional ovens provide consistent heat from the top and bottom elements, making them ideal for traditional cakes that require even, gentle baking to avoid over-browning. Convection ovens use a fan to circulate hot air, resulting in faster baking times and more uniform heat distribution, perfect for layered or chiffon cakes needing precise temperature control. Choosing the right oven depends on the cake type and desired texture, with conventional ovens best for delicate crumb structures and convection ovens suited for quicker, evenly baked results.
Conventional oven vs Convection oven for baking Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com