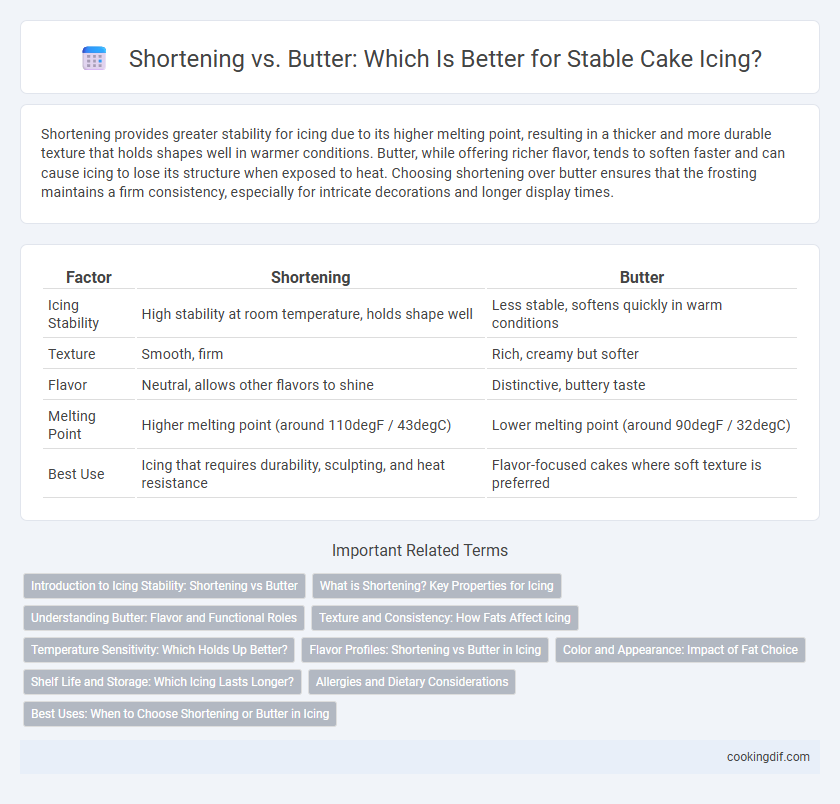
Shortening provides greater stability for icing due to its higher melting point, resulting in a thicker and more durable texture that holds shapes well in warmer conditions. Butter, while offering richer flavor, tends to soften faster and can cause icing to lose its structure when exposed to heat. Choosing shortening over butter ensures that the frosting maintains a firm consistency, especially for intricate decorations and longer display times.
Table of Comparison
| Factor | Shortening | Butter |
|---|---|---|
| Icing Stability | High stability at room temperature, holds shape well | Less stable, softens quickly in warm conditions |
| Texture | Smooth, firm | Rich, creamy but softer |
| Flavor | Neutral, allows other flavors to shine | Distinctive, buttery taste |
| Melting Point | Higher melting point (around 110degF / 43degC) | Lower melting point (around 90degF / 32degC) |
| Best Use | Icing that requires durability, sculpting, and heat resistance | Flavor-focused cakes where soft texture is preferred |
Introduction to Icing Stability: Shortening vs Butter
Icing stability is crucial for maintaining texture and appearance, with shortening and butter being the primary fats influencing these qualities. Shortening offers superior stability due to its higher melting point and less natural water content, resulting in icings that hold shape longer at room temperature. Butter provides rich flavor but melts more quickly, which can cause icings to soften or lose structure in warmer conditions.
What is Shortening? Key Properties for Icing
Shortening is a solid fat made from vegetable oils, primarily designed to provide a smooth, stable texture in icings due to its high melting point and lack of water content. Its key properties for icing include superior stability, resistance to melting at room temperature, and the ability to hold shape for extended periods, which prevents icings from becoming greasy or runny. Unlike butter, shortening creates a more consistent and firm frosting ideal for intricate cake decorating and lasting freshness.
Understanding Butter: Flavor and Functional Roles
Butter enhances icing stability by providing a rich flavor and creamy texture that complements other ingredients. Its natural fats contribute to a smooth consistency while adding moisture retention, which prevents cracking and improves mouthfeel. Butter's unique properties support aeration and structure, making it essential for stable, flavorful icings in cake decoration.
Texture and Consistency: How Fats Affect Icing
Shortening provides a smooth, stable texture in icing due to its higher melting point, resulting in a consistent and firm finish that holds up well in warm conditions. Butter imparts a rich flavor but melts faster, often causing icings to be creamier yet softer and more prone to melting or losing shape. The choice between shortening and butter significantly impacts the firmness and spreadability of icing, influencing overall cake decoration durability.
Temperature Sensitivity: Which Holds Up Better?
Shortening offers superior temperature stability compared to butter, maintaining a smooth texture in icings even in warmer conditions above 70degF (21degC). Butter-based icings are more temperature-sensitive, prone to melting or becoming greasy when exposed to heat. Choosing shortening for icing ensures better structural integrity and a consistent finish in variable climates.
Flavor Profiles: Shortening vs Butter in Icing
Shortening provides a neutral flavor that allows other ingredients' tastes to shine in icing, offering a stable texture with minimal melt. Butter delivers a rich, creamy flavor that enhances the overall taste profile but can affect icing stability due to its lower melting point. Choosing between shortening and butter depends on balancing desired flavor intensity with the need for firm, stable icings.
Color and Appearance: Impact of Fat Choice
Shortening provides a consistently white base that enhances the brightness and vibrancy of icing colors, making it ideal for pastel and bold hues. Butter contributes a naturally yellow tint, which can warm the overall appearance but may alter the intended color palette. The choice of fat directly influences the visual appeal and clarity of icing, impacting presentation quality.
Shelf Life and Storage: Which Icing Lasts Longer?
Shortening-based icings exhibit superior shelf life and stability compared to butter-based icings due to their higher melting point and resistance to spoilage. Butter icings, while rich in flavor, tend to soften and degrade faster, especially under warm conditions, limiting their storage duration to a few days in refrigeration. For extended shelf life, shortening icings maintain texture and freshness for up to several weeks when stored in airtight containers at cool temperatures.
Allergies and Dietary Considerations
Shortening provides greater icing stability due to its higher melting point, making it ideal for warm environments and intricate decorations. Butter offers a rich flavor but can be problematic for those with dairy allergies or lactose intolerance, requiring alternatives like dairy-free spreads. Choosing between shortening and butter depends on dietary restrictions and the desired texture and taste of the icing.
Best Uses: When to Choose Shortening or Butter in Icing
Shortening offers superior stability and a higher melting point, making it ideal for icings that need to withstand heat or hold intricate decorations, such as in warmer climates or elaborate cake designs. Butter imparts richer flavor and a creamy texture, best suited for icings consumed immediately or in cooler environments where flavor is prioritized over durability. Choose shortening for structural reliability and butter for taste-focused applications in cake decorating.
Shortening vs Butter for Icing Stability Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com