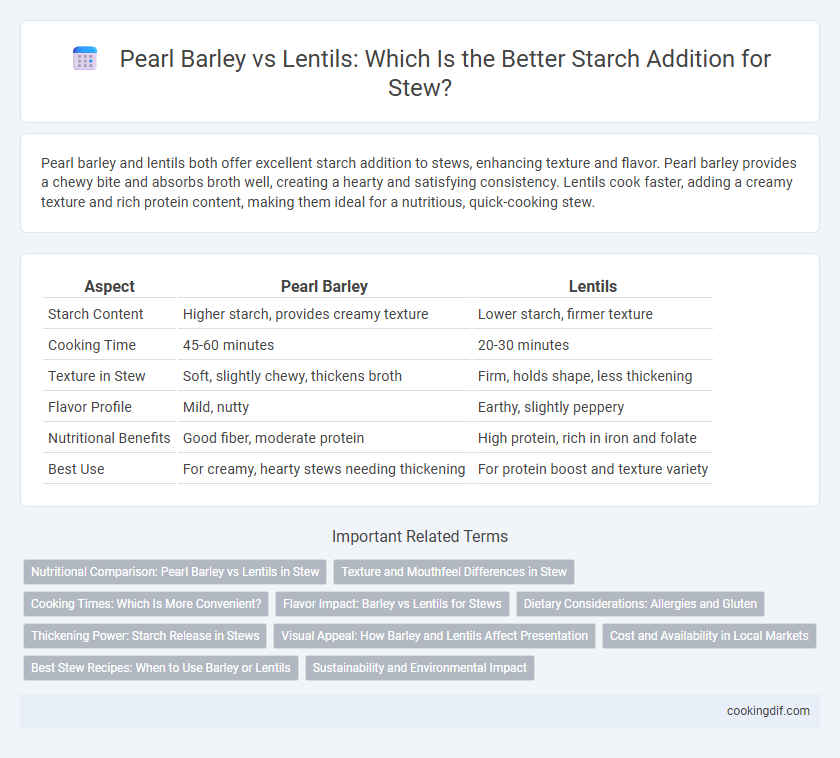
Pearl barley and lentils both offer excellent starch addition to stews, enhancing texture and flavor. Pearl barley provides a chewy bite and absorbs broth well, creating a hearty and satisfying consistency. Lentils cook faster, adding a creamy texture and rich protein content, making them ideal for a nutritious, quick-cooking stew.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Pearl Barley | Lentils |
|---|---|---|
| Starch Content | Higher starch, provides creamy texture | Lower starch, firmer texture |
| Cooking Time | 45-60 minutes | 20-30 minutes |
| Texture in Stew | Soft, slightly chewy, thickens broth | Firm, holds shape, less thickening |
| Flavor Profile | Mild, nutty | Earthy, slightly peppery |
| Nutritional Benefits | Good fiber, moderate protein | High protein, rich in iron and folate |
| Best Use | For creamy, hearty stews needing thickening | For protein boost and texture variety |
Nutritional Comparison: Pearl Barley vs Lentils in Stew
Pearl barley provides a rich source of dietary fiber, particularly beta-glucan, which supports heart health and aids digestion, containing around 6 grams of fiber per 100 grams cooked. Lentils offer a higher protein content, averaging 9 grams per 100 grams cooked, alongside essential minerals like iron and folate that contribute to muscle repair and energy metabolism. In stew recipes, choosing pearl barley enhances carbohydrate complexity and satiety, while lentils boost protein density and micronutrient diversity for a balanced meal.
Texture and Mouthfeel Differences in Stew
Pearl barley adds a chewy, slightly nutty texture to stew, enhancing its heartiness and providing a pleasant bite that contrasts with tender vegetables and meat. Lentils, on the other hand, soften significantly during cooking, contributing a creamy, smooth mouthfeel that thickens the stew and blends flavors seamlessly. Choosing between pearl barley and lentils depends on whether a stew benefits more from a firm, grainy texture or a silky, velvety consistency.
Cooking Times: Which Is More Convenient?
Pearl barley requires a longer cooking time, typically 45-60 minutes, making it less convenient for quick stews, while lentils cook much faster, usually within 20-30 minutes. Red and yellow lentils soften rapidly and integrate seamlessly, whereas pearl barley adds a chewy texture that suits slow-cooked recipes. For time-sensitive meals, lentils offer a more efficient starch addition without compromising flavor or consistency.
Flavor Impact: Barley vs Lentils for Stews
Pearl barley adds a nutty, earthy flavor to stews while providing a chewy texture that absorbs surrounding spices well, enhancing the overall depth of the dish. Lentils contribute a mild, slightly peppery taste with a softer texture, which thickens stews and blends seamlessly without overpowering other ingredients. Choosing between pearl barley and lentils depends on whether a heartier bite or smoother consistency best suits the desired stew profile.
Dietary Considerations: Allergies and Gluten
Pearl barley is a gluten-containing grain that can trigger allergic reactions or gluten intolerance in sensitive individuals, making it unsuitable for gluten-free diets. Lentils are naturally gluten-free and hypoallergenic, offering a safer starch addition for those with celiac disease or grain allergies. Choosing lentils over pearl barley supports dietary restrictions while providing rich fiber and protein content in stews.
Thickening Power: Starch Release in Stews
Pearl barley and lentils both contribute to thickening stews through starch release, but pearl barley has a higher starch content, resulting in a creamier, thicker texture. Lentils release less starch and tend to maintain a firmer consistency, contributing more to body and protein rather than viscosity. For a stew requiring substantial thickening, pearl barley is the preferred choice due to its superior gelatinization and starch expansion during simmering.
Visual Appeal: How Barley and Lentils Affect Presentation
Pearl barley adds a glossy, translucent appearance to stew, creating a visually appealing contrast with vibrant vegetables and tender meat. Lentils, with their matte finish and earthy tones, blend seamlessly into the stew, offering a uniform and rustic presentation. The choice between pearl barley and lentils influences the stew's texture and overall visual depth, enhancing either a polished or hearty look.
Cost and Availability in Local Markets
Pearl barley offers consistent availability in local markets and is generally priced lower than specialty lentil varieties, making it an economical choice for starch addition in stew. Lentils, while slightly more expensive, provide diverse options such as red, green, and brown types, whose prices and availability fluctuate based on regional demand and seasonality. Choosing between pearl barley and lentils depends on balancing cost-efficiency with desired texture and flavor profiles in stew preparation.
Best Stew Recipes: When to Use Barley or Lentils
Pearl barley adds a chewy texture and nutty flavor to stew, making it ideal for hearty recipes that benefit from a slow-cooked, barley-rich base. Lentils, especially red or green varieties, offer a creamy consistency and faster cooking time, perfect for lighter, protein-packed stews. Use pearl barley for thickening and robust mouthfeel, while lentils enhance stews with their protein content and smoother texture.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Pearl barley offers a lower environmental footprint compared to lentils due to its lower water usage and reduced greenhouse gas emissions during cultivation. While lentils fix nitrogen and improve soil health, their production often requires more water and longer growth periods, impacting sustainability. Choosing pearl barley as a starch addition in stew enhances eco-friendly cooking by minimizing resource consumption and supporting less intensive agricultural practices.
Pearl Barley vs Lentils for starch addition Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com