Clarified butter provides a rich, nutty flavor that enhances the depth of soups while offering a higher smoke point ideal for cooking at elevated temperatures. Olive oil contributes a lighter, fruity taste and contains heart-healthy monounsaturated fats, making it a nutritious choice for light soups and finishing touches. Choosing clarified butter or olive oil depends on the desired flavor profile and cooking method for the soup pet recipe.
Table of Comparison
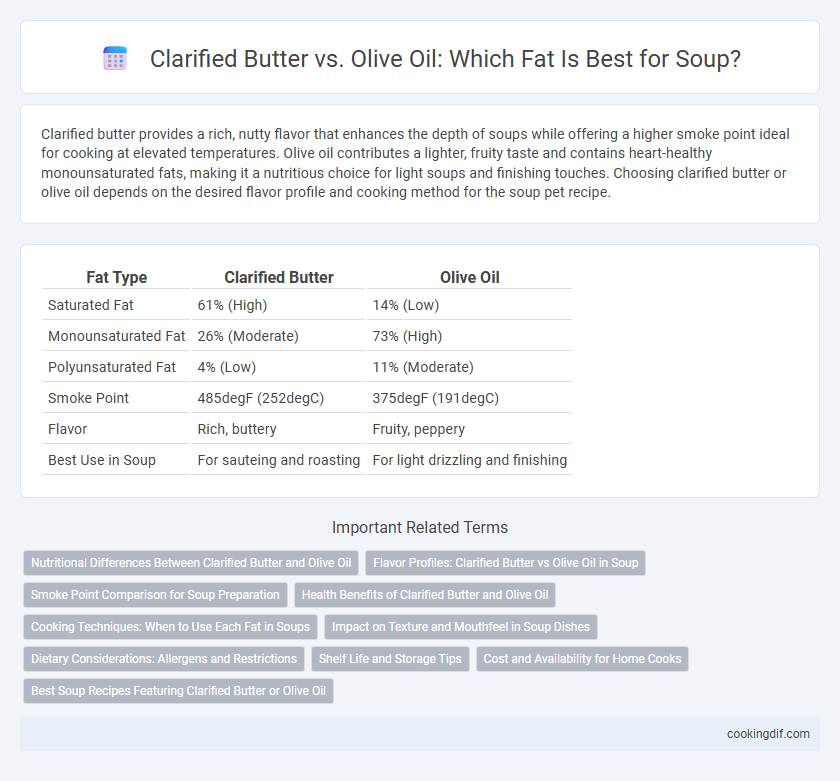
| Fat Type | Clarified Butter | Olive Oil |
|---|---|---|
| Saturated Fat | 61% (High) | 14% (Low) |
| Monounsaturated Fat | 26% (Moderate) | 73% (High) |
| Polyunsaturated Fat | 4% (Low) | 11% (Moderate) |
| Smoke Point | 485degF (252degC) | 375degF (191degC) |
| Flavor | Rich, buttery | Fruity, peppery |
| Best Use in Soup | For sauteing and roasting | For light drizzling and finishing |
Nutritional Differences Between Clarified Butter and Olive Oil
Clarified butter, or ghee, contains higher saturated fat levels, which can raise LDL cholesterol, whereas olive oil is rich in monounsaturated fats that promote heart health by improving HDL cholesterol. Olive oil provides significant amounts of antioxidants like vitamin E and polyphenols, offering anti-inflammatory properties absent in clarified butter. The calorie content of both fats is similar, but olive oil's fat profile supports better cardiovascular outcomes when used in soup preparation.
Flavor Profiles: Clarified Butter vs Olive Oil in Soup
Clarified butter imparts a rich, nutty flavor and smooth texture to soups, enhancing savory depth without overpowering other ingredients. Olive oil offers a fruitier, peppery taste that adds brightness and complexity, especially in Mediterranean or vegetable-based soups. Choosing between clarified butter and olive oil depends on the desired flavor profile and the soup's regional style or ingredient harmony.
Smoke Point Comparison for Soup Preparation
Clarified butter has a higher smoke point of around 485degF (252degC) compared to olive oil's 375degF (190degC), making it more suitable for high-heat soup preparation techniques like sauteing aromatics. Olive oil, while flavorful and rich in antioxidants, may break down and produce harmful compounds at higher temperatures during soup making. Using clarified butter in soups ensures stable fat content and a clean taste without the risk of burning, enhancing both the texture and flavor profile.
Health Benefits of Clarified Butter and Olive Oil
Clarified butter, rich in fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K, offers a high smoke point that preserves nutrient content during high-heat cooking, promoting heart health through its conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) content. Olive oil is abundant in monounsaturated fats and antioxidants like polyphenols, which reduce inflammation and lower the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Both fats contribute essential nutrients and support metabolic functions, but clarified butter provides fat-soluble vitamins, while olive oil enhances heart and brain health with its potent antioxidants.
Cooking Techniques: When to Use Each Fat in Soups
Clarified butter enhances soups by adding rich, nutty flavors and tolerates high heat without burning, making it ideal for sauteing vegetables or starting a roux. Olive oil, especially extra virgin, imparts a fruity, peppery taste and is best used for low to medium-heat cooking or finishing soups to preserve its delicate aroma. Choosing between clarified butter and olive oil depends on desired flavor profiles and cooking temperatures in soup preparation.
Impact on Texture and Mouthfeel in Soup Dishes
Clarified butter imparts a rich, velvety texture and smooth mouthfeel to soup dishes due to its creamy consistency and high smoke point, allowing for deeper flavor development without burning. Olive oil contributes a lighter, slightly fruitier mouthfeel with a silky texture that can vary depending on its quality and type, providing a fresh, Mediterranean nuance. The choice between clarified butter and olive oil significantly influences the soup's overall richness and tactile experience, impacting how flavors are perceived on the palate.
Dietary Considerations: Allergens and Restrictions
Clarified butter, also known as ghee, is a suitable fat for those with lactose intolerance due to its minimal milk solids, but it is not vegan or suitable for dairy allergies. Olive oil, a plant-based fat rich in monounsaturated fats and antioxidants, is ideal for vegan, dairy-free, and nut-free diets with fewer allergen concerns. Choosing between clarified butter and olive oil for soup depends on individual dietary restrictions, including allergen sensitivities and lifestyle choices such as veganism or lactose intolerance.
Shelf Life and Storage Tips
Clarified butter has a longer shelf life than olive oil due to its low moisture content and absence of milk solids, allowing it to be stored at room temperature for several months without spoiling. Olive oil should be kept in a cool, dark place and used within six months after opening to prevent oxidation and rancidity. For optimal storage, clarified butter can be refrigerated to extend its freshness, while olive oil benefits from airtight containers to maintain its quality.
Cost and Availability for Home Cooks
Clarified butter, known as ghee, tends to be more expensive and less readily available in regular grocery stores compared to olive oil, which is widely affordable and accessible. Home cooks often prefer olive oil for its versatility and easy shelf stability, while clarified butter offers a richer flavor but may require specialty stores or higher cost. Choosing between the two depends on budget constraints and ingredient availability within local markets.
Best Soup Recipes Featuring Clarified Butter or Olive Oil
Clarified butter enhances soup recipes with a rich, nutty flavor and high smoke point, making it ideal for sauteing aromatic vegetables in creamy bisques or veloute bases. Olive oil offers a lighter, fruitier taste perfect for Mediterranean-style soups like minestrone or gazpacho, providing heart-healthy monounsaturated fats. Selecting clarified butter or olive oil depends on desired flavor profiles and cooking techniques to elevate the soup's texture and nutritional value.
Clarified Butter vs Olive Oil for fat Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com