Bone broth is rich in collagen, amino acids, and minerals like calcium and magnesium, promoting joint health and skin elasticity. Vegetable broth offers a high concentration of vitamins, antioxidants, and fiber, supporting immune function and digestion. Choosing between bone broth and vegetable broth depends on dietary preferences and specific nutritional needs, as both provide unique health benefits.
Table of Comparison
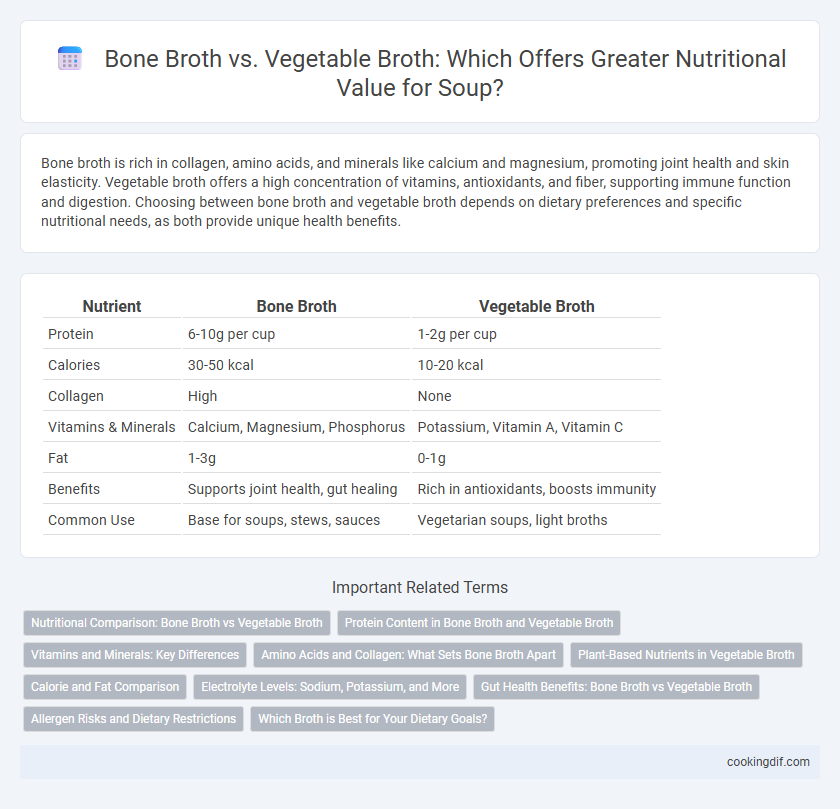
| Nutrient | Bone Broth | Vegetable Broth |
|---|---|---|
| Protein | 6-10g per cup | 1-2g per cup |
| Calories | 30-50 kcal | 10-20 kcal |
| Collagen | High | None |
| Vitamins & Minerals | Calcium, Magnesium, Phosphorus | Potassium, Vitamin A, Vitamin C |
| Fat | 1-3g | 0-1g |
| Benefits | Supports joint health, gut healing | Rich in antioxidants, boosts immunity |
| Common Use | Base for soups, stews, sauces | Vegetarian soups, light broths |
Nutritional Comparison: Bone Broth vs Vegetable Broth
Bone broth is rich in collagen, amino acids like glycine and proline, and minerals such as calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus, supporting joint health and skin elasticity. Vegetable broth contains higher levels of antioxidants, fiber, vitamins A, C, and K, and phytochemicals that promote immune function and reduce inflammation. While bone broth excels in protein and mineral content, vegetable broth offers a broader range of vitamins and plant-based nutrients crucial for overall wellness.
Protein Content in Bone Broth and Vegetable Broth
Bone broth typically contains higher protein content due to the collagen and amino acids extracted from simmered bones, providing essential nutrients like glycine and proline. Vegetable broth generally has lower protein levels since it is primarily composed of water infused with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants from vegetables. For those prioritizing protein intake and joint health, bone broth offers a more nutrient-dense option compared to vegetable broth.
Vitamins and Minerals: Key Differences
Bone broth is rich in minerals such as calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, and potassium, along with collagen, gelatin, and amino acids that support joint and gut health. Vegetable broth offers a diverse range of vitamins like vitamin C, vitamin A, and various B vitamins, alongside antioxidants and fiber from the vegetables used. Choosing between bone broth and vegetable broth depends on the specific nutritional needs, with bone broth excelling in mineral content and protein-related benefits, while vegetable broth provides more vitamins and plant-based nutrients.
Amino Acids and Collagen: What Sets Bone Broth Apart
Bone broth contains a higher concentration of amino acids like glycine, proline, and glutamine, which support joint health and digestion, unlike vegetable broth that lacks collagen entirely. Collagen in bone broth provides vital peptides that promote skin elasticity and bone strength, benefits not present in vegetable broth. While vegetable broth offers vitamins and antioxidants, bone broth's unique collagen and amino acid profile distinctly elevates its nutritional value.
Plant-Based Nutrients in Vegetable Broth
Vegetable broth offers a rich source of plant-based nutrients such as antioxidants, vitamins A, C, and K, along with minerals like potassium and magnesium essential for immune support and hydration. The presence of phytonutrients and dietary fiber in vegetable broth enhances digestive health and provides anti-inflammatory benefits. Unlike bone broth, vegetable broth is cholesterol-free and suitable for vegan diets, making it a nutrient-dense choice for overall wellness.
Calorie and Fat Comparison
Bone broth typically contains 30-50 calories per cup with 1-3 grams of fat, providing essential amino acids and collagen that support joint health. Vegetable broth usually has fewer calories, around 10-20 per cup, and less than 1 gram of fat, making it lower in calories and fat but lacking the protein and collagen benefits of bone broth. For those prioritizing calorie control and fat reduction, vegetable broth is preferable, while bone broth offers superior nutritional value in terms of protein and healthy fats.
Electrolyte Levels: Sodium, Potassium, and More
Bone broth offers higher electrolyte levels, particularly sodium and potassium, compared to vegetable broth, aiding in better hydration and muscle function. It contains minerals like calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus from simmered bones, which enhance electrolyte balance. Vegetable broth provides modest electrolytes primarily from potassium-rich vegetables, but generally lacks the comprehensive mineral profile found in bone broth.
Gut Health Benefits: Bone Broth vs Vegetable Broth
Bone broth is rich in collagen, gelatin, and amino acids like glycine and proline that support gut lining repair and reduce inflammation, promoting improved digestion and gut health. Vegetable broth provides dietary fiber and antioxidants that nourish gut microbiota, aiding in digestion and reducing oxidative stress. Both broths offer unique gut health benefits, with bone broth focusing on tissue repair and vegetable broth enhancing microbial diversity.
Allergen Risks and Dietary Restrictions
Bone broth provides high levels of collagen, amino acids, and minerals like calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus, supporting joint health and immune function, but it may pose allergen risks for individuals with bone or meat allergies. Vegetable broth is plant-based and generally free from common allergens such as dairy, gluten, and nuts, making it suitable for vegan, vegetarian, and gluten-free diets while offering antioxidants and vitamins from diverse vegetables. Choosing between bone broth and vegetable broth depends on specific dietary restrictions and allergen sensitivities, with bone broth often richer in protein but vegetable broth safer for those with common food allergies.
Which Broth is Best for Your Dietary Goals?
Bone broth offers a higher protein content and essential minerals like collagen, calcium, and magnesium, making it ideal for muscle repair and joint health. Vegetable broth is rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and fiber, supporting digestive health and providing low-calorie hydration for plant-based diets. Choosing the best broth depends on your dietary goals: bone broth for increased protein and minerals, or vegetable broth for vitamins and antioxidants.
Bone Broth vs Vegetable Broth for nutritional value Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com