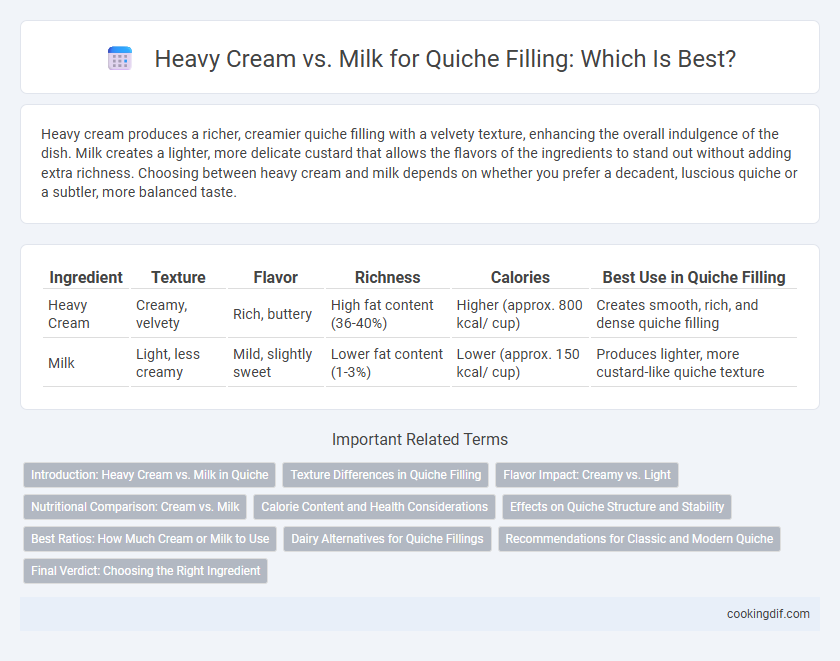
Heavy cream produces a richer, creamier quiche filling with a velvety texture, enhancing the overall indulgence of the dish. Milk creates a lighter, more delicate custard that allows the flavors of the ingredients to stand out without adding extra richness. Choosing between heavy cream and milk depends on whether you prefer a decadent, luscious quiche or a subtler, more balanced taste.
Table of Comparison
| Ingredient | Texture | Flavor | Richness | Calories | Best Use in Quiche Filling |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heavy Cream | Creamy, velvety | Rich, buttery | High fat content (36-40%) | Higher (approx. 800 kcal/ cup) | Creates smooth, rich, and dense quiche filling |
| Milk | Light, less creamy | Mild, slightly sweet | Lower fat content (1-3%) | Lower (approx. 150 kcal/ cup) | Produces lighter, more custard-like quiche texture |
Introduction: Heavy Cream vs. Milk in Quiche
Heavy cream creates a richer, velvety quiche filling with a higher fat content, enhancing flavor and texture. Milk produces a lighter, less dense custard, resulting in a more delicate quiche that allows other ingredients to shine. Choosing heavy cream or milk directly impacts the quiche's mouthfeel, moisture, and overall richness.
Texture Differences in Quiche Filling
Heavy cream creates a rich, velvety quiche filling with a dense, custard-like texture that holds its shape well after baking. Milk results in a lighter, softer filling that may be less firm and slightly more delicate in consistency. Choosing heavy cream over milk enhances the quiche's smoothness and creaminess, making a more luxurious mouthfeel.
Flavor Impact: Creamy vs. Light
Heavy cream in quiche filling delivers a rich, velvety texture with pronounced buttery flavors that enhance the overall indulgence of the dish. Milk produces a lighter, more delicate custard, allowing the fillings' ingredients like cheese, vegetables, or meats to stand out more prominently. Choosing heavy cream results in a decadent mouthfeel, while milk creates a fresher, less dense flavor profile.
Nutritional Comparison: Cream vs. Milk
Heavy cream contains significantly higher fat content, providing a rich, creamy texture that enhances the quiche filling's mouthfeel, while whole milk offers a lighter, lower-calorie alternative with less saturated fat. Nutritionally, heavy cream delivers approximately 5 grams of fat and 50 calories per tablespoon, compared to whole milk's 0.9 grams of fat and 9 calories per tablespoon, impacting the overall calorie density of the dish. Choosing between heavy cream and milk affects not only texture and flavor but also the nutritional profile, especially important for those managing fat intake or calorie consumption.
Calorie Content and Health Considerations
Heavy cream in quiche filling significantly increases calorie content due to its high fat percentage, typically around 36-40%, compared to milk's lower fat content of 1-3%, resulting in fewer calories. Choosing milk over heavy cream reduces saturated fat intake and overall calorie load, making the quiche a healthier option for heart health and weight management. However, heavy cream provides a richer texture and creamier mouthfeel, whereas milk yields a lighter, less indulgent filling.
Effects on Quiche Structure and Stability
Heavy cream produces a richer, creamier quiche filling with a denser texture and more stable structure due to its higher fat content, which helps bind ingredients and prevents water separation during baking. Milk results in a lighter, softer filling but can lead to a more fragile quiche with a less stable structure that may weep or become watery as the lower fat content offers less emulsification. For optimal quiche stability and a custard-like consistency, heavy cream or a combination of cream and milk is recommended over milk alone.
Best Ratios: How Much Cream or Milk to Use
Using heavy cream in quiche filling results in a richer, creamier texture, while milk produces a lighter, more custard-like consistency. The ideal ratio for a balanced quiche filling is typically one cup of dairy (heavy cream or milk) per three large eggs, with heavy cream preferred at about 1 cup for a dense, silky custard and milk at 1 to 1.5 cups for a lighter texture. Adjusting the ratio impacts firmness and richness, with 35-40% fat heavy cream yielding the creamiest results and 2% milk offering a subtler, less rich finish.
Dairy Alternatives for Quiche Fillings
Heavy cream provides a rich, velvety texture to quiche fillings, while milk yields a lighter, more delicate consistency. Dairy alternatives like coconut milk, almond milk, or cashew cream offer flavorful, lactose-free options but may alter the quiche's traditional custard structure. Choosing the right substitute depends on desired texture and dietary preferences, balancing creaminess with compatibility in baking.
Recommendations for Classic and Modern Quiche
Heavy cream yields a rich, custard-like filling ideal for classic quiche recipes such as Quiche Lorraine, providing a smooth texture and robust flavor. Milk offers a lighter alternative suited for modern quiches with vegetable or seafood fillings, resulting in a delicate consistency while reducing fat content. For balanced richness and creaminess, a mixture of half-and-half can be used, enhancing flavor without overwhelming the dish.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Right Ingredient
Heavy cream provides a rich, velvety texture and fuller flavor for quiche filling, enhancing its custard-like consistency and mouthfeel. Milk results in a lighter, less dense filling, offering a more subtle taste that allows other ingredients to shine. Choosing between heavy cream and milk depends on whether a rich indulgence or a lighter, more delicate quiche is desired.
heavy cream vs milk for filling Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com