Gelatin provides a smooth, creamy texture to pudding and sets at a lower temperature, creating a tender gel that melts in the mouth. Agar-agar, a plant-based alternative, sets more firmly and remains stable at higher temperatures, making it ideal for vegan or vegetarian puddings. While gelatin yields a silkier finish, agar-agar offers a slightly firmer consistency and is better suited for recipes requiring a robust set.
Table of Comparison
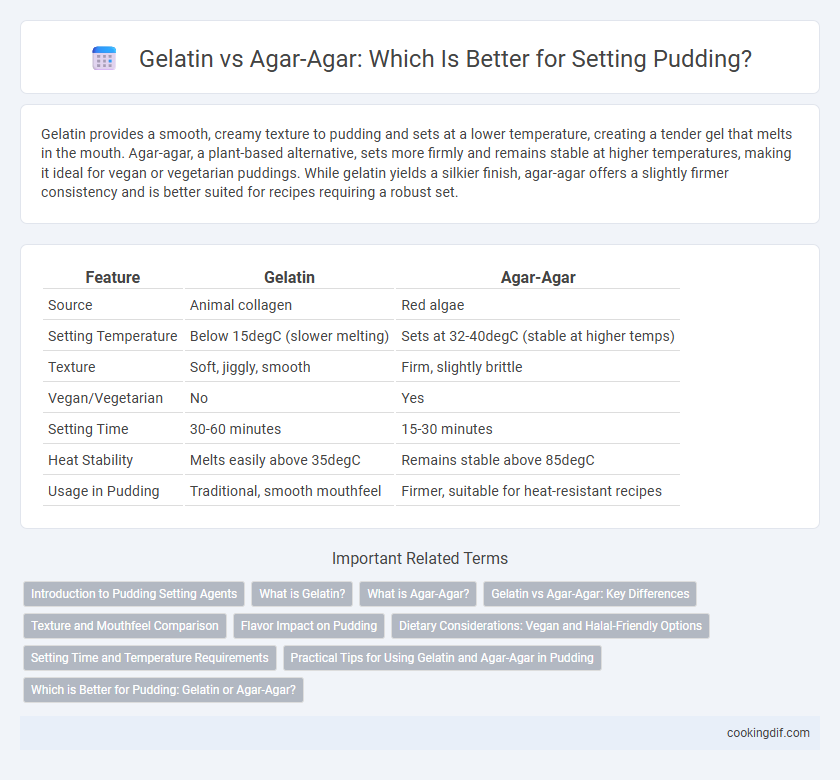
| Feature | Gelatin | Agar-Agar |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Animal collagen | Red algae |
| Setting Temperature | Below 15degC (slower melting) | Sets at 32-40degC (stable at higher temps) |
| Texture | Soft, jiggly, smooth | Firm, slightly brittle |
| Vegan/Vegetarian | No | Yes |
| Setting Time | 30-60 minutes | 15-30 minutes |
| Heat Stability | Melts easily above 35degC | Remains stable above 85degC |
| Usage in Pudding | Traditional, smooth mouthfeel | Firmer, suitable for heat-resistant recipes |
Introduction to Pudding Setting Agents
Gelatin and agar-agar are popular setting agents used to achieve the desired texture in puddings, with gelatin derived from animal collagen and agar-agar sourced from red algae. Gelatin creates a smooth, creamy consistency and melts at body temperature, making it ideal for soft, delicate puddings. Agar-agar sets firmer and remains stable at higher temperatures, providing a vegan alternative that produces a resilient, slightly brittle pudding texture.
What is Gelatin?
Gelatin is a protein derived from collagen found in animal bones and skin, commonly used as a gelling agent in pudding to create a smooth, creamy texture. It melts at body temperature, providing a soft, melt-in-the-mouth consistency that distinguishes it from plant-based alternatives like agar-agar. Gelatin requires refrigeration to set properly and is favored for its clear, glossy finish and stable gel structure in desserts.
What is Agar-Agar?
Agar-agar is a natural gelling agent derived from red seaweed, commonly used as a vegetarian and vegan alternative to gelatin in pudding recipes. It sets more firmly than gelatin at room temperature and remains stable at higher temperatures, making it ideal for desserts requiring a sturdy texture. Rich in fiber and free from animal products, agar-agar enhances pudding with a smooth, slightly chewy consistency without altering flavor.
Gelatin vs Agar-Agar: Key Differences
Gelatin and agar-agar differ significantly in their setting properties and origins, with gelatin derived from animal collagen and agar-agar sourced from seaweed, making it suitable for vegetarian and vegan diets. Gelatin creates a smooth, elastic texture, setting at lower temperatures, while agar-agar produces a firmer, more brittle gel that sets quickly at room temperature. Agar-agar withstands higher temperatures without melting, offering greater heat stability for puddings served warm or stored ambiently.
Texture and Mouthfeel Comparison
Gelatin creates a smooth, creamy texture with a soft, melt-in-the-mouth mouthfeel ideal for classic pudding recipes. Agar-agar produces a firmer, slightly more brittle gel that holds its shape well but offers a less creamy and more jelly-like consistency. Choosing between gelatin and agar-agar directly impacts pudding texture, with gelatin delivering richer mouthfeel and agar-agar providing a vegetarian alternative with a springier bite.
Flavor Impact on Pudding
Gelatin provides a smooth, creamy texture with a subtle flavor that enhances the natural taste of pudding without overpowering it, maintaining a delicate balance ideal for dairy-based desserts. Agar-agar offers a firmer, slightly brittle texture and can impart a mild, vegetal taste that may alter the pudding's flavor profile, especially in delicate or fruit-flavored recipes. Choosing gelatin or agar-agar significantly influences the pudding's mouthfeel and taste, with gelatin preferred for richer flavors and agar-agar for vegetarian alternatives that allow more pronounced ingredient notes.
Dietary Considerations: Vegan and Halal-Friendly Options
Gelatin, derived from animal collagen, is unsuitable for vegan and some Halal diets, making agar-agar a preferred plant-based alternative that gels without animal products. Agar-agar, extracted from seaweed, sets pudding firmly and is naturally vegan and Halal-friendly, catering to diverse dietary restrictions. This seaweed-derived ingredient also offers a neutral flavor and higher heat stability compared to gelatin, enhancing pudding texture while respecting dietary preferences.
Setting Time and Temperature Requirements
Gelatin requires a setting temperature of around 2-5degC and typically sets within 2 to 4 hours, making it ideal for chilled puddings. Agar-agar sets at room temperature, around 25-30degC, and solidifies much faster, usually within 30 to 60 minutes, offering a quicker alternative. Agar-agar's higher melting point of 85degC allows puddings to remain stable at warmer temperatures compared to gelatin's melt point of 35degC.
Practical Tips for Using Gelatin and Agar-Agar in Pudding
Gelatin sets pudding with a smooth, tender texture and requires soaking in cold water before melting gently to dissolve completely. Agar-agar, a plant-based alternative derived from seaweed, sets more firmly and quickly without refrigeration, but must be boiled to activate its gelling properties effectively. When substituting agar-agar for gelatin, use about half the amount and dissolve it thoroughly in boiling liquid to avoid grainy texture and ensure proper setting.
Which is Better for Pudding: Gelatin or Agar-Agar?
Gelatin creates a smooth, creamy texture in pudding due to its protein-based composition, while agar-agar, derived from seaweed, provides a firmer, more brittle set ideal for vegan and vegetarian diets. Agar-agar sets at room temperature and withstands higher temperatures, making it a reliable choice for puddings exposed to heat, whereas gelatin requires refrigeration to maintain its gel structure. For traditional creamy puddings, gelatin is often preferred, but agar-agar offers a plant-based alternative with a distinctly different texture and setting behavior.
gelatin vs agar-agar for pudding setting Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com