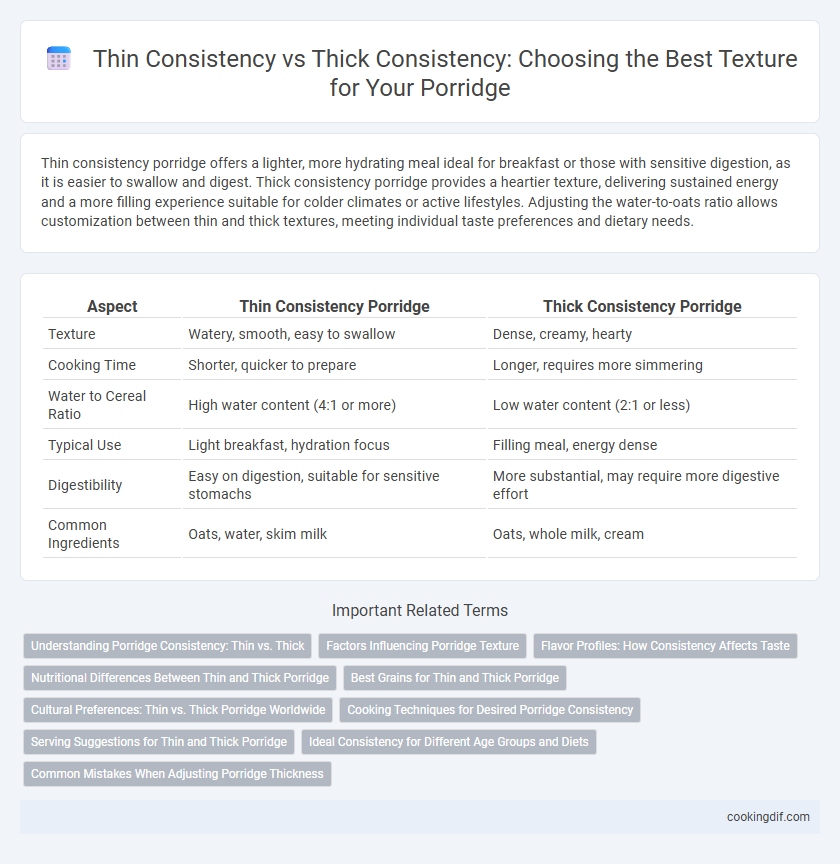
Thin consistency porridge offers a lighter, more hydrating meal ideal for breakfast or those with sensitive digestion, as it is easier to swallow and digest. Thick consistency porridge provides a heartier texture, delivering sustained energy and a more filling experience suitable for colder climates or active lifestyles. Adjusting the water-to-oats ratio allows customization between thin and thick textures, meeting individual taste preferences and dietary needs.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Thin Consistency Porridge | Thick Consistency Porridge |
|---|---|---|
| Texture | Watery, smooth, easy to swallow | Dense, creamy, hearty |
| Cooking Time | Shorter, quicker to prepare | Longer, requires more simmering |
| Water to Cereal Ratio | High water content (4:1 or more) | Low water content (2:1 or less) |
| Typical Use | Light breakfast, hydration focus | Filling meal, energy dense |
| Digestibility | Easy on digestion, suitable for sensitive stomachs | More substantial, may require more digestive effort |
| Common Ingredients | Oats, water, skim milk | Oats, whole milk, cream |
Understanding Porridge Consistency: Thin vs. Thick
Porridge consistency varies primarily between thin and thick textures, influenced by the ratio of liquid to grain and cooking duration. Thin porridge contains more water or milk, resulting in a smooth, soupy texture ideal for easier digestion and quick meals. Thick porridge, with less liquid and longer cooking, yields a dense, creamy, and hearty meal rich in fiber, perfect for sustained energy release.
Factors Influencing Porridge Texture
Porridge texture varies significantly between thin and thick consistencies, influenced primarily by the type of grain used, water-to-grain ratio, and cooking time. Grains like oats absorb water differently, where higher liquid ratios and shorter cooking yield thinner porridge, while lower water content with extended cooking results in thicker, creamier textures. Temperature control and stirring frequency also play critical roles in breaking down starches and proteins, directly affecting the porridge's viscosity.
Flavor Profiles: How Consistency Affects Taste
Thin porridge consistency delivers a lighter, more refreshing flavor profile where subtle grain notes and natural sweetness are prominent, enhancing delicate spices and fruits. Thick porridge offers a richer, creamier taste with intensified grain flavors, providing a hearty, comforting experience often complemented by bold toppings like nuts, seeds, or savory ingredients. The consistency directly influences the flavor release and texture perception, shaping the overall taste appeal and mouthfeel of the porridge.
Nutritional Differences Between Thin and Thick Porridge
Thin porridge typically contains a higher water-to-grain ratio, resulting in fewer calories and reduced carbohydrate density per serving compared to thick porridge. Thick porridge, being more concentrated, delivers greater amounts of protein, fiber, and essential micronutrients such as iron and B vitamins due to the larger proportion of grains per volume. The nutrient density in thick porridge supports better satiety and sustained energy release, making it more beneficial for individuals requiring higher caloric and nutrient intake.
Best Grains for Thin and Thick Porridge
Oats and millet are ideal grains for thin porridge due to their ability to absorb water quickly and create a smooth, flowing texture. For thick porridge, cornmeal and semolina are preferred as they swell and thicken more, providing a hearty, dense consistency. Choosing the right grain directly influences porridge viscosity, affecting digestion and nutrient absorption.
Cultural Preferences: Thin vs. Thick Porridge Worldwide
Cultural preferences for porridge consistency vary widely, with East African and Scandinavian countries favoring thin, soupy textures that are easy to sip or drink. In contrast, many Western and Asian cultures prefer thick porridge with a creamy, spoonable density, often enriched with grains like oats or rice. The choice between thin and thick porridge often reflects traditional eating habits and regional staple ingredients.
Cooking Techniques for Desired Porridge Consistency
Adjusting the water-to-grain ratio is crucial for achieving the desired porridge consistency, with higher liquid amounts yielding a thinner texture and lower liquid producing a thicker result. Prolonged simmering and stirring allow starches to gelatinize fully, thickening the porridge naturally without added thickeners. Using techniques like pre-soaking grains can also influence consistency by reducing cooking time and affecting the final porridge texture.
Serving Suggestions for Thin and Thick Porridge
Thin porridge is often served with a splash of milk or cream to enhance its smooth, easily drinkable texture, making it ideal for breakfast or light snacks. Thick porridge pairs well with toppings such as fresh fruits, nuts, honey, or yogurt, providing a hearty and filling meal. Each consistency caters to different preferences and meal occasions, with thin porridge favored for quick consumption and thick porridge preferred for sustained energy and satiety.
Ideal Consistency for Different Age Groups and Diets
Thin porridge consistency suits infants and elderly individuals who require easily digestible, liquid-like texture for safe swallowing and nutrient absorption. Thick porridge appeals to toddlers and adults needing higher energy density and prolonged satiety, supporting developmental stages and active lifestyles. Nutritionists recommend adjusting porridge thickness according to age-specific digestive capacity, hydration needs, and dietary restrictions to optimize health benefits.
Common Mistakes When Adjusting Porridge Thickness
Common mistakes when adjusting porridge thickness include adding too much water too quickly or not stirring consistently, leading to uneven texture and watery spots. Overcooking porridge can result in a thick, gluey consistency that is difficult to remedy without diluting and reheating. Properly balancing liquid ratios and gradual adjustments during cooking ensures smooth, creamy porridge with desired thin or thick consistency.
Thin consistency vs Thick consistency for porridge Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com