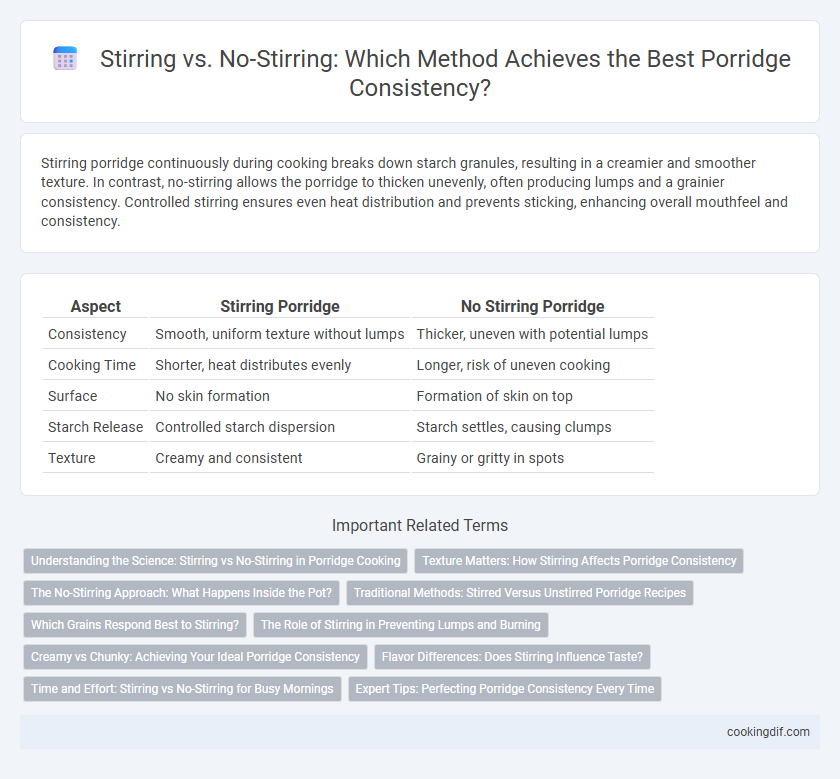
Stirring porridge continuously during cooking breaks down starch granules, resulting in a creamier and smoother texture. In contrast, no-stirring allows the porridge to thicken unevenly, often producing lumps and a grainier consistency. Controlled stirring ensures even heat distribution and prevents sticking, enhancing overall mouthfeel and consistency.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Stirring Porridge | No Stirring Porridge |
|---|---|---|
| Consistency | Smooth, uniform texture without lumps | Thicker, uneven with potential lumps |
| Cooking Time | Shorter, heat distributes evenly | Longer, risk of uneven cooking |
| Surface | No skin formation | Formation of skin on top |
| Starch Release | Controlled starch dispersion | Starch settles, causing clumps |
| Texture | Creamy and consistent | Grainy or gritty in spots |
Understanding the Science: Stirring vs No-Stirring in Porridge Cooking
Stirring porridge during cooking disrupts starch granules, promoting even heat distribution and preventing clumping, resulting in a smoother, creamier texture. Conversely, no-stirring allows starches to gelatinize undisturbed, which can create a thicker, chunkier consistency with more varied texture. Understanding the balance between these techniques helps tailor porridge consistency to preference, optimizing both mouthfeel and cooking efficiency.
Texture Matters: How Stirring Affects Porridge Consistency
Stirring porridge continuously during cooking breaks down starch molecules, resulting in a creamier and smoother texture that many prefer for a comforting meal. Conversely, avoiding stirring helps maintain a thicker, more rustic consistency with distinct grains, appealing to those who enjoy a heartier bite. The choice between stirring and no-stirring significantly influences the final mouthfeel and overall sensory experience of porridge.
The No-Stirring Approach: What Happens Inside the Pot?
The no-stirring approach to porridge allows the grains to absorb water slowly and swell evenly, resulting in a creamier and less sticky texture. Without disturbance, the starch granules gelatinize uniformly, promoting a smooth consistency and preventing clumping. This method also minimizes the risk of breaking grains, preserving the porridge's structural integrity and enhancing its natural creaminess.
Traditional Methods: Stirred Versus Unstirred Porridge Recipes
Stirring porridge during cooking promotes even heat distribution and prevents lumps, resulting in a smoother, creamier texture favored in traditional recipes like Scottish oats or rice-based congees. Unstirred porridge methods, common in some African and Asian culinary traditions, allow grains to cook gently in undisturbed liquid, producing a thicker, denser consistency with distinct grain separation. The choice between stirred and unstirred preparation directly impacts moisture retention, starch gelatinization, and ultimately the mouthfeel and digestibility of porridge.
Which Grains Respond Best to Stirring?
Oat-based porridge, especially steel-cut oats, benefits significantly from regular stirring, which helps release starches and creates a creamier, smoother texture. In contrast, grains like quinoa and millet maintain distinct, separate kernels when cooked without stirring, preserving a fluffier, less sticky consistency. Barley and rice varieties respond well to occasional stirring to prevent clumping while retaining a tender bite.
The Role of Stirring in Preventing Lumps and Burning
Stirring porridge continuously during cooking plays a crucial role in preventing lumps by evenly distributing heat and breaking down starch granules, resulting in a smooth, creamy texture. It also helps to prevent burning by keeping the porridge from sticking to the bottom of the pot where localized overheating can occur. Without stirring, porridge is more prone to developing uneven consistency and scorching, which affects both taste and quality.
Creamy vs Chunky: Achieving Your Ideal Porridge Consistency
Stirring porridge continuously helps break down oats, releasing starches that create a creamy, smooth texture ideal for a comforting bowl. In contrast, minimal or no stirring preserves oat structure, resulting in a chunkier consistency with distinct, chewy oat pieces. Adjusting stirring frequency allows precise control over porridge creaminess versus chunkiness to suit individual texture preferences.
Flavor Differences: Does Stirring Influence Taste?
Stirring porridge continuously during cooking helps develop a creamier texture and intensifies the natural starches, enhancing its rich, buttery flavor. In contrast, no-stir porridge often has a grainier consistency and a milder taste, as the starches do not fully gelatinize. The choice between stirring and no-stirring impacts not only texture but also the depth and balance of flavors in the finished dish.
Time and Effort: Stirring vs No-Stirring for Busy Mornings
Stirring porridge continuously during cooking requires more active time and effort but delivers a smoother, creamier texture by evenly distributing heat and preventing lumps. No-stirring methods save time and allow for a hands-off approach ideal for busy mornings, though the consistency may be slightly less uniform with occasional clumps. Choosing between stirring and no-stirring depends on balancing desired texture against the need for convenience and minimal cooking supervision.
Expert Tips: Perfecting Porridge Consistency Every Time
Stirring porridge during cooking breaks down starch granules, resulting in a creamier, smoother texture preferred by many chefs. Avoiding stirring retains more distinct grains, offering a thicker, chunkier consistency favored in traditional recipes. Expert tips suggest gentle, intermittent stirring for balance, ensuring optimal porridge consistency tailored to personal taste and ingredient type.
stirring vs no-stirring for porridge consistency Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com