Barley porridge offers a chewy texture with a nutty flavor and is rich in soluble fiber, promoting heart health and stable blood sugar levels. Millet porridge is lighter and slightly sweet, providing a gluten-free whole grain alternative packed with magnesium and antioxidants. Choosing between barley and millet porridge depends on dietary needs; barley supports digestion and cholesterol management, while millet suits gluten sensitivities and supports bone health.
Table of Comparison
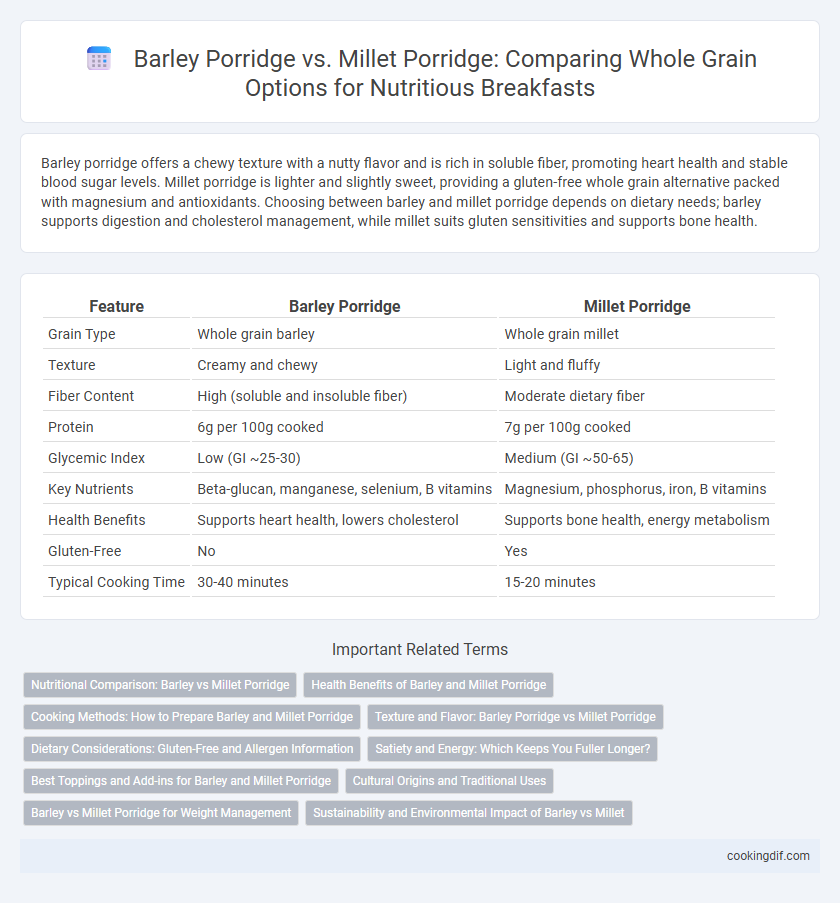
| Feature | Barley Porridge | Millet Porridge |
|---|---|---|
| Grain Type | Whole grain barley | Whole grain millet |
| Texture | Creamy and chewy | Light and fluffy |
| Fiber Content | High (soluble and insoluble fiber) | Moderate dietary fiber |
| Protein | 6g per 100g cooked | 7g per 100g cooked |
| Glycemic Index | Low (GI ~25-30) | Medium (GI ~50-65) |
| Key Nutrients | Beta-glucan, manganese, selenium, B vitamins | Magnesium, phosphorus, iron, B vitamins |
| Health Benefits | Supports heart health, lowers cholesterol | Supports bone health, energy metabolism |
| Gluten-Free | No | Yes |
| Typical Cooking Time | 30-40 minutes | 15-20 minutes |
Nutritional Comparison: Barley vs Millet Porridge
Barley porridge contains higher dietary fiber, particularly beta-glucan, which supports heart health and blood sugar regulation, whereas millet porridge is rich in magnesium, phosphorus, and antioxidants, promoting bone health and reducing inflammation. Both grains provide essential minerals and vitamins, but barley offers more protein and soluble fiber, making it beneficial for digestive health. Millet porridge, gluten-free and easily digestible, is a suitable option for those with gluten intolerance or sensitive stomachs.
Health Benefits of Barley and Millet Porridge
Barley porridge is rich in beta-glucan fiber, which supports heart health by lowering cholesterol levels and stabilizing blood sugar, making it ideal for diabetes management. Millet porridge offers high magnesium and antioxidant content, promoting bone health and reducing inflammation. Both whole grain porridges provide essential nutrients and fiber that aid digestion and contribute to sustained energy release.
Cooking Methods: How to Prepare Barley and Millet Porridge
Barley porridge requires simmering pearl or hulled barley in water or broth for approximately 40-50 minutes until soft, often with periodic stirring to achieve a creamy texture. Millet porridge cooks faster, typically boiling millet grains in water for about 20 minutes, stirring occasionally to prevent clumping and then allowing it to rest off heat for thicker consistency. Incorporating techniques like pre-soaking barley or toasting millet can enhance flavor profiles and improve absorption of nutrients in whole grain porridge dishes.
Texture and Flavor: Barley Porridge vs Millet Porridge
Barley porridge offers a chewy, slightly nutty texture with a robust flavor profile, making it a hearty whole grain option rich in fiber and beta-glucans. Millet porridge provides a smoother, creamier consistency with a mild, subtly sweet taste, favored for its lightness and easy digestibility. Both grains deliver distinct textures and flavors, catering to different dietary preferences and culinary uses.
Dietary Considerations: Gluten-Free and Allergen Information
Barley porridge contains gluten, making it unsuitable for individuals with gluten intolerance or celiac disease, whereas millet porridge is naturally gluten-free and a safe option for those with gluten sensitivities. Millet is also hypoallergenic and less likely to cause allergic reactions compared to barley, which may trigger issues in people with grain allergies. Choosing millet porridge offers a whole grain option that accommodates various dietary restrictions while supporting digestive health.
Satiety and Energy: Which Keeps You Fuller Longer?
Barley porridge offers higher fiber content and beta-glucans that promote prolonged satiety and sustained energy release, making it a superior whole grain option for keeping you fuller longer. Millet porridge, while rich in magnesium and antioxidants, digests more quickly, resulting in shorter satiety compared to barley. Choosing barley porridge enhances appetite control and stabilizes blood sugar levels, supporting longer-lasting energy throughout the day.
Best Toppings and Add-ins for Barley and Millet Porridge
Barley porridge pairs well with hearty toppings like toasted nuts, dried cranberries, and a drizzle of honey, enhancing its chewy texture and nutty flavor. Millet porridge benefits from creamy add-ins such as coconut milk, fresh berries, and a sprinkle of cinnamon to complement its naturally mild and slightly sweet taste. Both porridges can be enriched with seeds like chia or flax for added fiber and omega-3 fatty acids, optimizing their nutritional profile.
Cultural Origins and Traditional Uses
Barley porridge, rooted in European and Middle Eastern traditions, is celebrated for its nutty flavor and high dietary fiber, often used as a savory staple or breakfast cereal. Millet porridge holds significant cultural importance in African and Asian cuisines, known for its subtle sweetness and versatility in both sweet and savory dishes. Both whole grains offer diverse nutritional benefits, reflecting their regional agricultural practices and culinary heritage.
Barley vs Millet Porridge for Weight Management
Barley porridge contains more soluble fiber than millet porridge, promoting satiety and aiding in appetite control for effective weight management. Millet porridge is lower in calories and carbohydrates but offers fewer benefits for blood sugar regulation compared to barley. Choosing barley porridge supports steady digestion and prolonged fullness, making it a preferred whole grain option for weight control diets.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact of Barley vs Millet
Barley porridge offers a sustainable choice due to barley's low water requirements and ability to thrive in cool, arid climates, reducing environmental strain compared to millet. Millet, while drought-resistant and beneficial for semi-arid regions, often requires more intensive land use and can contribute to soil degradation if improperly managed. Choosing barley promotes soil health and biodiversity, making it a preferable whole grain option for eco-conscious consumers.
Barley Porridge vs Millet Porridge for Whole Grain Options Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com