Hand-cut pasta offers irregular shapes with varied thickness, enhancing sauce absorption and providing a rustic texture. Extruded pasta is produced by forcing dough through shaped dies, resulting in consistent, uniform shapes ideal for holding thicker sauces. Choosing between hand-cut and extruded techniques depends on desired texture, sauce pairing, and visual appeal.
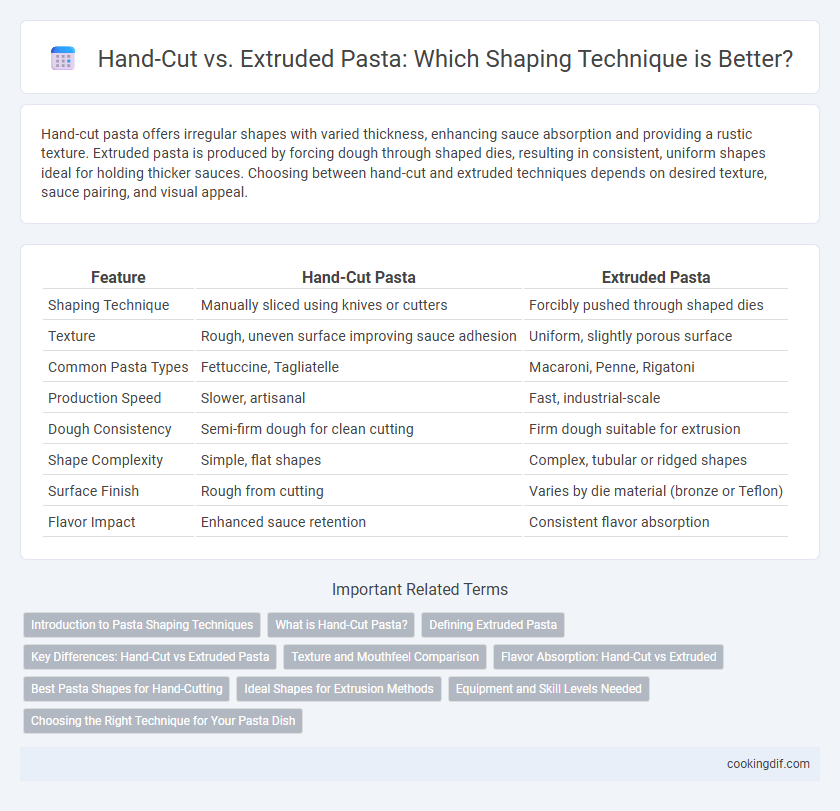
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hand-Cut Pasta | Extruded Pasta |
|---|---|---|
| Shaping Technique | Manually sliced using knives or cutters | Forcibly pushed through shaped dies |
| Texture | Rough, uneven surface improving sauce adhesion | Uniform, slightly porous surface |
| Common Pasta Types | Fettuccine, Tagliatelle | Macaroni, Penne, Rigatoni |
| Production Speed | Slower, artisanal | Fast, industrial-scale |
| Dough Consistency | Semi-firm dough for clean cutting | Firm dough suitable for extrusion |
| Shape Complexity | Simple, flat shapes | Complex, tubular or ridged shapes |
| Surface Finish | Rough from cutting | Varies by die material (bronze or Teflon) |
| Flavor Impact | Enhanced sauce retention | Consistent flavor absorption |
Introduction to Pasta Shaping Techniques
Hand-cut pasta offers a traditional, artisanal appeal with irregular textures that enhance sauce absorption, while extruded pasta, created by forcing dough through specialized dies, produces uniform shapes ideal for consistent cooking. Techniques like hand-cut fettuccine emphasize craftsmanship and varied thickness, contrasting with extruded varieties such as penne or rigatoni that provide precise ridges and hollow centers to trap sauce. Understanding these shaping methods highlights the balance between rustic authenticity and industrial efficiency in pasta production.
What is Hand-Cut Pasta?
Hand-cut pasta refers to dough sheets sliced manually into various shapes like fettuccine and pappardelle using a knife or pizza cutter, offering a rustic texture and thickness variation. This technique allows for greater control over the pasta's thickness, resulting in a chewier bite compared to uniform extruded shapes such as penne or rigatoni produced by forcing dough through molds. Artisanal hand-cut pasta maintains traditional craftsmanship, enhancing sauce absorption and providing a handcrafted eating experience.
Defining Extruded Pasta
Extruded pasta is created by forcing dough through a die to produce various shapes with intricate surfaces, such as penne or fusilli, that capture sauces effectively. This shaping technique allows for consistent texture and thickness, enhancing cooking uniformity and sauce adherence. Unlike hand-cut pasta, extruded pasta offers precision and scalability suitable for industrial production.
Key Differences: Hand-Cut vs Extruded Pasta
Hand-cut pasta features irregular thickness and rough edges, enhancing sauce adhesion and providing a rustic texture, while extruded pasta is shaped by pushing dough through molds, resulting in uniform shapes like penne or rigatoni. The hand-cut method allows for traditional shapes such as pappardelle and tagliatelle, emphasizing artisanal quality, whereas extrusion produces consistent pasta ideal for mass production and shapes with hollow centers. Texture differences affect cooking times and sauce pairing, with hand-cut pasta often offering a chewier bite compared to the smoother surface of extruded varieties.
Texture and Mouthfeel Comparison
Hand-cut pasta boasts a rustic texture with irregular edges that enhance sauce adherence, creating a tender yet slightly chewy mouthfeel. Extruded pasta, produced by forcing dough through shaped dies, delivers consistent thickness and smooth surfaces, resulting in a firmer bite and uniform cooking. Texture variations directly influence the sensory experience, with hand-cut styles offering artisan appeal while extruded shapes ensure precision and durability.
Flavor Absorption: Hand-Cut vs Extruded
Hand-cut pasta features irregular surfaces and rough edges that enhance flavor absorption by trapping sauces more effectively compared to the smoother, uniform texture of extruded pasta. The porous nature of hand-cut noodles allows for deeper sauce penetration, intensifying taste with each bite. Extruded pasta, while consistent in shape, tends to offer less surface area for sauce adhesion, resulting in a milder flavor experience.
Best Pasta Shapes for Hand-Cutting
Hand-cut pasta offers unparalleled texture and artisanal appeal, making shapes like pappardelle, tagliatelle, and fettuccine ideal for showcasing its rustic charm. These broad, flat noodles benefit from the uneven edges and thickness variations achieved by hand-cutting, enhancing sauce absorption and mouthfeel. Unlike extruded pasta, which excels in creating hollow or intricate shapes, hand-cut pasta best suits traditional flat ribbons and sheets that emphasize simplicity and texture.
Ideal Shapes for Extrusion Methods
Extrusion methods are ideal for creating pasta shapes with intricate patterns and consistent thickness, such as penne, rigatoni, and ziti, which benefit from the method's ability to produce hollow tubes and ridged surfaces. The uniformity afforded by extrusion enhances sauce adhesion and cooking performance, making it perfect for robust, baked, or sauced pasta dishes. Hand-cut pasta, in contrast, typically results in flatter, less uniform shapes like fettuccine or pappardelle, which suit lighter sauces or delicate presentations.
Equipment and Skill Levels Needed
Hand-cut pasta requires minimal equipment such as a rolling pin and knife, making it accessible for home cooks with basic culinary skills. Extruded pasta demands specialized machinery that forces dough through shaped dies, necessitating a higher level of technical knowledge and often industrial-scale equipment. Skill levels vary as hand-cutting emphasizes precision and manual dexterity, while extrusion relies more on equipment handling and consistency in dough preparation.
Choosing the Right Technique for Your Pasta Dish
Hand-cut pasta offers a rustic texture and irregular shapes that hold thick, chunky sauces well, making it ideal for hearty dishes like pappardelle with meat ragu. Extruded pasta, created by forcing dough through molds, produces uniform shapes such as penne or rigatoni, providing consistent cooking and better sauce adhesion for lighter, oil-based sauces. Selecting the right shaping technique enhances the overall mouthfeel and sauce compatibility, ensuring the pasta complements the dish's flavor profile perfectly.
Hand-cut vs Extruded for shaping technique Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com