Gluten-free pasta offers a vital alternative for individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, providing a safe option without compromising taste or texture. Regular pasta, made from wheat, contains gluten, which can cause adverse reactions for those with specific dietary restrictions. Choosing the right pasta depends on personal health requirements and nutritional goals, ensuring each meal supports overall well-being.
Table of Comparison
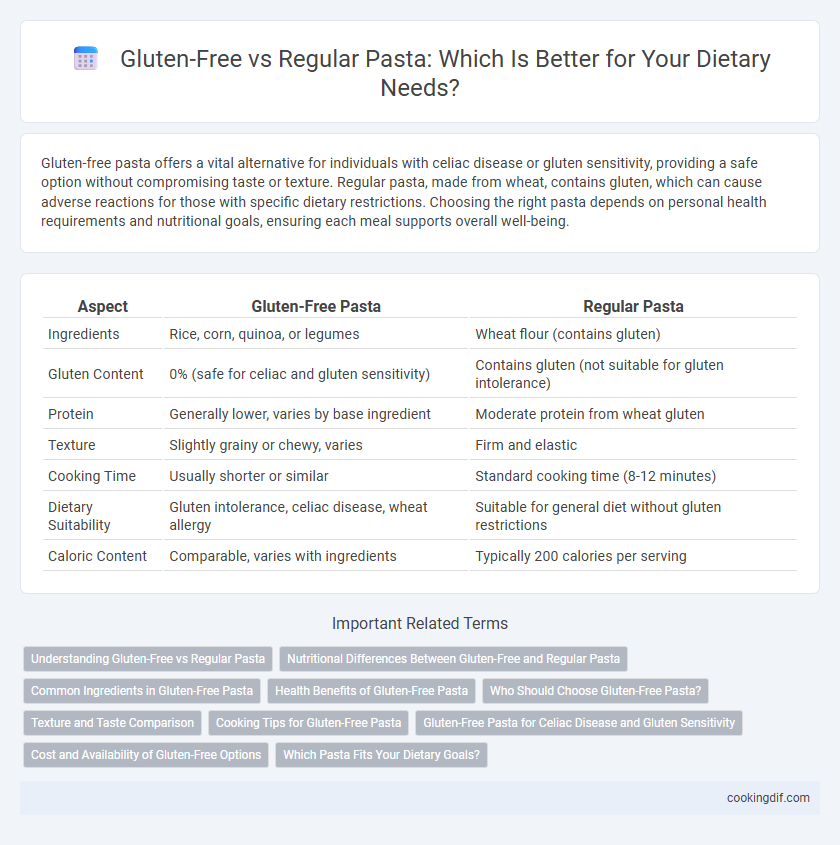
| Aspect | Gluten-Free Pasta | Regular Pasta |
|---|---|---|
| Ingredients | Rice, corn, quinoa, or legumes | Wheat flour (contains gluten) |
| Gluten Content | 0% (safe for celiac and gluten sensitivity) | Contains gluten (not suitable for gluten intolerance) |
| Protein | Generally lower, varies by base ingredient | Moderate protein from wheat gluten |
| Texture | Slightly grainy or chewy, varies | Firm and elastic |
| Cooking Time | Usually shorter or similar | Standard cooking time (8-12 minutes) |
| Dietary Suitability | Gluten intolerance, celiac disease, wheat allergy | Suitable for general diet without gluten restrictions |
| Caloric Content | Comparable, varies with ingredients | Typically 200 calories per serving |
Understanding Gluten-Free vs Regular Pasta
Gluten-free pasta is made from alternative flours such as rice, corn, or quinoa, designed to accommodate individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity by eliminating wheat-based gluten. Regular pasta typically contains durum wheat, which provides a distinct texture and taste but can trigger digestive issues in sensitive individuals. Choosing between gluten-free and regular pasta depends on dietary restrictions and nutritional goals, with gluten-free options often offering lower protein content but suitable for maintaining gluten-free diets.
Nutritional Differences Between Gluten-Free and Regular Pasta
Gluten-free pasta is typically made from rice, corn, or legumes and often contains higher amounts of protein and fiber compared to regular pasta made from durum wheat. While regular pasta provides more iron and B vitamins, gluten-free options may lack these nutrients unless fortified. Choosing between gluten-free and regular pasta depends on individual dietary needs, especially for those with gluten intolerance or celiac disease seeking to avoid gluten while maintaining balanced nutrition.
Common Ingredients in Gluten-Free Pasta
Gluten-free pasta commonly features ingredients such as rice flour, corn flour, quinoa, and chickpea flour, which provide alternatives for those with gluten sensitivities or celiac disease. These grains and legumes offer diverse nutrient profiles, including higher protein and fiber content compared to traditional wheat-based pasta. Choosing gluten-free options can accommodate dietary restrictions while maintaining texture and taste close to regular pasta.
Health Benefits of Gluten-Free Pasta
Gluten-free pasta, often made from rice, quinoa, or legumes, provides a vital alternative for individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, preventing adverse immune reactions and promoting digestive health. It is typically lower in carbohydrates and higher in fiber and protein compared to traditional wheat pasta, supporting blood sugar regulation and satiety. Choosing gluten-free pasta can reduce inflammation and improve nutrient absorption for those with gluten-related disorders, enhancing overall well-being.
Who Should Choose Gluten-Free Pasta?
Gluten-free pasta is essential for individuals with celiac disease or non-celiac gluten sensitivity, as it prevents adverse autoimmune reactions and digestive discomfort. Those with wheat allergies also benefit from gluten-free options to avoid allergic responses. Consumers seeking to reduce gluten intake for digestive health or lifestyle preferences may choose gluten-free pasta, but regular pasta remains suitable for those without gluten-related conditions.
Texture and Taste Comparison
Gluten-free pasta, typically made from rice, corn, or quinoa flour, offers a slightly different texture that is often firmer or more brittle compared to the tender, chewy consistency of regular wheat-based pasta. Taste profiles vary, with gluten-free options presenting a milder, sometimes nuttier flavor, while regular pasta delivers a traditional wheat flavor favored in classic Italian cuisine. Individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity benefit from gluten-free pasta without compromising significantly on taste or mouthfeel.
Cooking Tips for Gluten-Free Pasta
Gluten-free pasta requires careful cooking to maintain an ideal texture, typically needing less stirring and a slightly shorter boiling time than regular pasta to prevent breaking apart. Using plenty of water and thoroughly salting it enhances flavor, while rinsing gluten-free pasta after cooking can help remove excess starch and reduce stickiness. Choosing varieties made from brown rice, quinoa, or corn offers diverse nutritional benefits, catering to celiac disease or gluten sensitivity dietary needs.
Gluten-Free Pasta for Celiac Disease and Gluten Sensitivity
Gluten-free pasta is specifically formulated to exclude wheat, barley, and rye, making it safe for individuals with celiac disease and gluten sensitivity. Common gluten-free pasta varieties include those made from rice, corn, quinoa, and legumes, providing essential nutrients without triggering autoimmune responses. Choosing gluten-free pasta supports digestive health and prevents symptoms such as inflammation, abdominal pain, and nutrient malabsorption associated with gluten intolerance.
Cost and Availability of Gluten-Free Options
Gluten-free pasta often costs significantly more than regular pasta due to specialized ingredients like rice, corn, or quinoa flour and smaller production scales. Availability of gluten-free options has expanded in many supermarkets, yet they remain less common and typically stocked in smaller quantities compared to traditional pasta varieties. Consumers with dietary restrictions should expect higher prices and may need to seek specialty stores or online retailers to access a wider range of gluten-free pasta products.
Which Pasta Fits Your Dietary Goals?
Gluten-free pasta, made from rice, corn, or quinoa, caters to individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, offering a safe alternative without compromising texture or taste. Regular pasta, typically crafted from durum wheat, provides higher protein and fiber content, supporting muscle growth and digestive health for those without gluten restrictions. Choosing between gluten-free and regular pasta depends on dietary needs such as gluten tolerance, nutritional goals, and personal health conditions.
Gluten-free vs regular pasta for dietary needs Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com