Egg pasta offers a rich flavor and a tender texture thanks to the inclusion of eggs, which also contribute to higher protein content and a golden hue. Eggless pasta, typically made from flour and water, provides a lighter, more neutral base that caters to vegan diets and those with egg allergies. Both types can be crafted into various shapes and cooked to al dente perfection, but their ingredient bases influence taste, texture, and dietary suitability significantly.
Table of Comparison
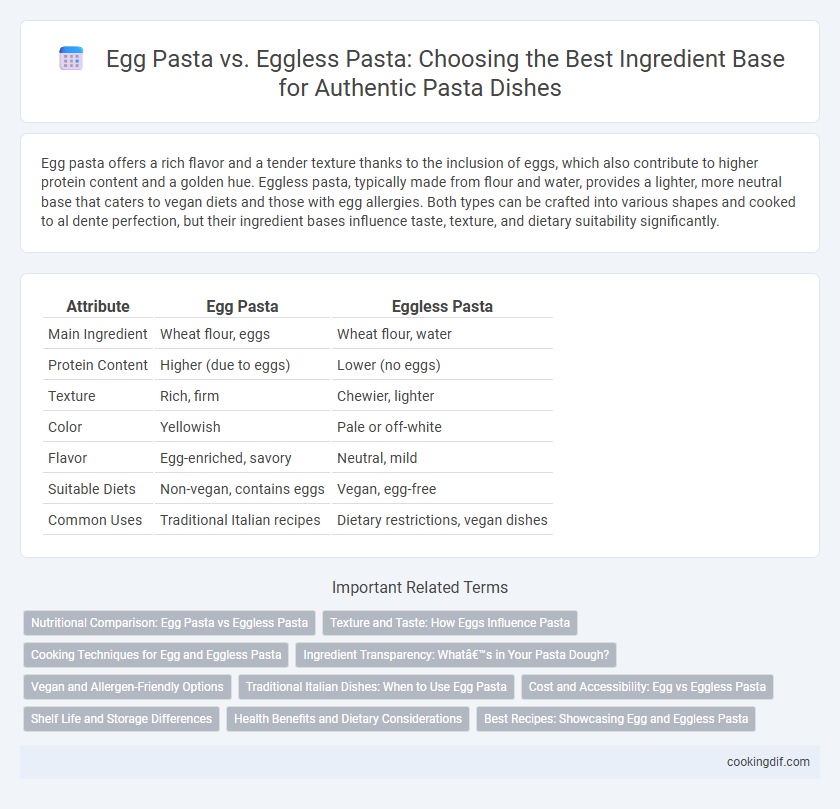
| Attribute | Egg Pasta | Eggless Pasta |
|---|---|---|
| Main Ingredient | Wheat flour, eggs | Wheat flour, water |
| Protein Content | Higher (due to eggs) | Lower (no eggs) |
| Texture | Rich, firm | Chewier, lighter |
| Color | Yellowish | Pale or off-white |
| Flavor | Egg-enriched, savory | Neutral, mild |
| Suitable Diets | Non-vegan, contains eggs | Vegan, egg-free |
| Common Uses | Traditional Italian recipes | Dietary restrictions, vegan dishes |
Nutritional Comparison: Egg Pasta vs Eggless Pasta
Egg pasta contains higher protein and vitamin B12 levels due to the inclusion of eggs, which contribute to improved muscle repair and energy metabolism. Eggless pasta, typically made from durum wheat semolina and water, offers lower fat content and is often suitable for vegan diets while providing complex carbohydrates for sustained energy. The choice between egg and eggless pasta impacts nutrient intake, with egg pasta delivering more essential amino acids and eggless pasta favoring lower cholesterol and allergen concerns.
Texture and Taste: How Eggs Influence Pasta
Egg pasta delivers a richer, silkier texture and a more complex flavor profile due to the protein and fat content of eggs, creating a tender yet firm bite. Eggless pasta, typically made with just flour and water, tends to have a firmer, chewier texture and a more neutral taste, making it versatile for various sauces. The presence of eggs enhances the pasta's golden color, elasticity, and ability to absorb flavors, distinguishing it from eggless varieties.
Cooking Techniques for Egg and Eggless Pasta
Egg pasta requires gentle handling and shorter cooking times to prevent overcooking, as the proteins in eggs coagulate quickly during boiling, resulting in a tender yet firm texture. Eggless pasta benefits from longer boiling due to its higher starch content and lack of emulsifying eggs, often requiring more frequent stirring to avoid sticking and ensure even cooking. Adjusting water temperature and cooking duration is essential to achieve optimal texture in both egg and eggless pasta varieties, with egg pasta demanding faster attention and eggless pasta needing gradual hydration.
Ingredient Transparency: What’s in Your Pasta Dough?
Egg pasta contains eggs as a primary ingredient, lending a richer texture and deeper flavor due to the protein and fats, while eggless pasta relies on flour and water, making it suitable for vegan diets and those with egg allergies. Ingredient transparency is crucial, as egg pastas highlight whole eggs or egg yolks on labels, whereas eggless varieties emphasize plant-based components, ensuring clarity for consumers with dietary restrictions. Understanding these differences helps in selecting pasta that aligns with nutritional needs and culinary preferences.
Vegan and Allergen-Friendly Options
Eggless pasta offers a vegan and allergen-friendly alternative by eliminating eggs, making it suitable for individuals with egg allergies or dietary restrictions. Traditional egg pasta typically contains high-protein eggs that enhance texture and flavor but may trigger allergic reactions and exclude vegan consumers. Choosing eggless pasta supports diverse dietary needs while maintaining essential nutrients derived from wheat or alternative gluten-free grains.
Traditional Italian Dishes: When to Use Egg Pasta
Egg pasta, rich in protein and moisture from fresh eggs, is essential for traditional Italian dishes like tagliatelle alla Bolognese and tortellini, where a tender yet elastic texture enhances the sauce absorption and overall mouthfeel. Eggless pasta, typically made from durum wheat semolina and water, suits lighter preparations such as seafood-based pasta or vegetable primavera, offering a firmer bite that holds well in brothy or olive oil-based sauces. The choice between egg and eggless pasta fundamentally influences the dish's texture, flavor integration, and authenticity in replicating regional Italian culinary traditions.
Cost and Accessibility: Egg vs Eggless Pasta
Eggless pasta often costs less to produce due to the absence of eggs, making it a budget-friendly option for consumers and manufacturers. The ingredients for eggless pasta, such as semolina or wheat flour and water, are more accessible and stable in price compared to eggs, which can fluctuate due to supply and demand or seasonal constraints. Egg pasta, while richer in flavor and texture, typically incurs higher production costs and may be less accessible in regions with limited egg availability or higher egg prices.
Shelf Life and Storage Differences
Egg pasta contains fresh eggs, which shorten its shelf life and require refrigeration to prevent spoilage, typically lasting 2-3 days when fresh. Eggless pasta, made primarily from semolina and water, has a longer shelf life and can be stored in a cool, dry place for several months without refrigeration. The absence of eggs reduces moisture content, minimizing bacterial growth and making eggless pasta ideal for extended storage.
Health Benefits and Dietary Considerations
Egg pasta contains higher protein and essential amino acids, supporting muscle repair and satiety, while also providing vitamins A and D. Eggless pasta, often made from semolina or whole wheat, is lower in cholesterol and suitable for vegan and cholesterol-conscious diets. Both types offer complex carbohydrates for sustained energy, but eggless pasta is preferable for those with egg allergies or seeking plant-based options.
Best Recipes: Showcasing Egg and Eggless Pasta
Egg pasta delivers a rich, tender texture with a deep golden hue, perfect for classic Italian dishes like fresh tagliatelle or tortellini that highlight its silky bite. Eggless pasta, often made from semolina or whole wheat flour and water, offers a lighter, firmer alternative ideal for recipes such as vegan spaghetti or gluten-sensitive penne. Both varieties serve as versatile bases, allowing chefs to craft diverse culinary experiences that accommodate dietary preferences without compromising authentic flavor profiles.
Egg pasta vs eggless pasta for ingredient base Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com