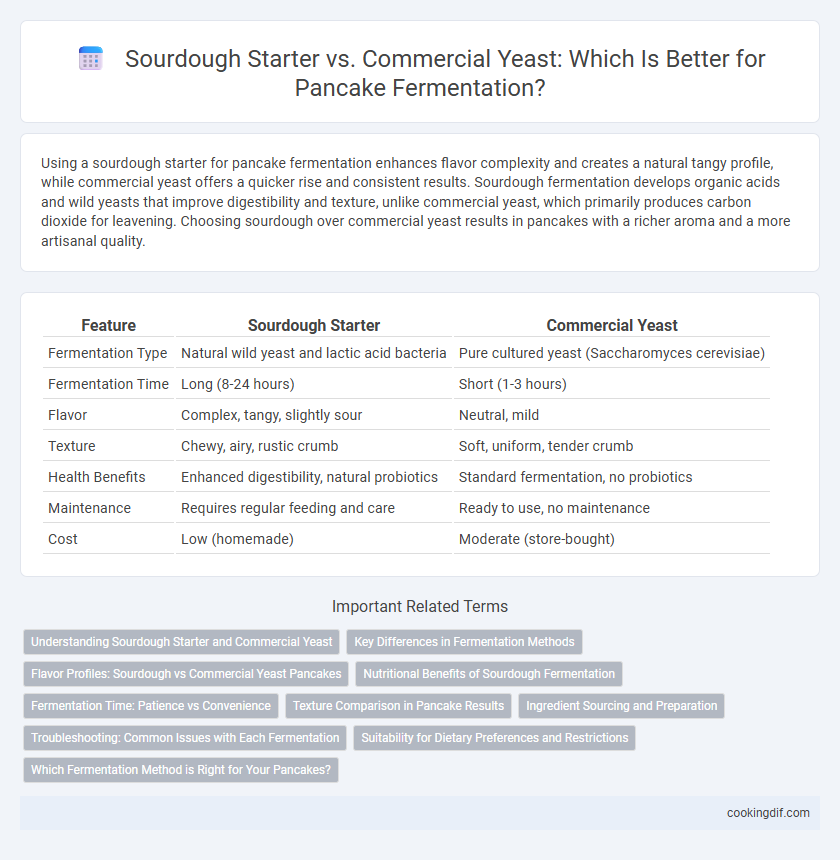
Using a sourdough starter for pancake fermentation enhances flavor complexity and creates a natural tangy profile, while commercial yeast offers a quicker rise and consistent results. Sourdough fermentation develops organic acids and wild yeasts that improve digestibility and texture, unlike commercial yeast, which primarily produces carbon dioxide for leavening. Choosing sourdough over commercial yeast results in pancakes with a richer aroma and a more artisanal quality.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sourdough Starter | Commercial Yeast |
|---|---|---|
| Fermentation Type | Natural wild yeast and lactic acid bacteria | Pure cultured yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) |
| Fermentation Time | Long (8-24 hours) | Short (1-3 hours) |
| Flavor | Complex, tangy, slightly sour | Neutral, mild |
| Texture | Chewy, airy, rustic crumb | Soft, uniform, tender crumb |
| Health Benefits | Enhanced digestibility, natural probiotics | Standard fermentation, no probiotics |
| Maintenance | Requires regular feeding and care | Ready to use, no maintenance |
| Cost | Low (homemade) | Moderate (store-bought) |
Understanding Sourdough Starter and Commercial Yeast
Sourdough starter is a natural fermentation culture made of wild yeast and lactic acid bacteria, offering complex flavors and longer fermentation times that enhance pancake texture and digestibility. Commercial yeast, typically Saccharomyces cerevisiae, provides fast, predictable fermentation, resulting in quicker rise but milder taste. Choosing between sourdough starter and commercial yeast affects the pancake's flavor depth, fermentation duration, and nutritional profile.
Key Differences in Fermentation Methods
Sourdough starter relies on wild yeast and lactic acid bacteria, producing a slower, natural fermentation that develops complex flavors and a tangy aroma in pancakes. Commercial yeast contains concentrated strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, leading to faster fermentation with more predictable rise and milder taste. The natural acidity and longer fermentation time in sourdough improve texture and digestibility, while commercial yeast offers convenience and consistent results.
Flavor Profiles: Sourdough vs Commercial Yeast Pancakes
Sourdough starter pancakes develop complex, tangy flavors and a slightly chewy texture due to natural wild yeast and lactic acid bacteria fermentation. Commercial yeast pancakes yield a mild, consistent taste with a soft, fluffy crumb because of rapid fermentation and pure yeast strains. The choice between sourdough and commercial yeast impacts the pancake's depth of flavor and texture, favoring sourdough for artisanal profiles and commercial yeast for quick, tender results.
Nutritional Benefits of Sourdough Fermentation
Sourdough starter fermentation enhances pancakes by increasing bioavailability of minerals like iron and zinc through natural phytic acid reduction, unlike commercial yeast which lacks this effect. This fermentation process promotes beneficial lactic acid bacteria growth, improving gut health and aiding digestion. Moreover, sourdough pancakes often feature lower glycemic index values, contributing to better blood sugar regulation compared to those made with commercial yeast.
Fermentation Time: Patience vs Convenience
Sourdough starter requires a longer fermentation time, often 12 to 24 hours, allowing natural wild yeasts and bacteria to develop complex flavors in pancake batter. In contrast, commercial yeast ferments much faster, typically within 1 to 2 hours, offering convenience for quick pancake preparation. The extended fermentation with sourdough enhances texture and aroma, while commercial yeast emphasizes speed and consistency.
Texture Comparison in Pancake Results
Sourdough starter fermentation produces pancakes with a complex, tangy flavor and a light, airy texture characterized by irregular crumb structure due to natural wild yeast and bacteria activity. In contrast, commercial yeast yields a more uniform rise and fine crumb, resulting in pancakes that are denser and less textured. The longer fermentation time of sourdough promotes gluten development and acidity that enhance chewiness and crisp edges, distinguishing it from the quicker, more predictable rise of commercial yeast.
Ingredient Sourcing and Preparation
Sourdough starter requires natural fermentation through wild yeast and lactic acid bacteria, often cultivated over several days from flour and water, offering complex flavors and improved digestibility. Commercial yeast provides a consistent, rapid rise due to its concentrated, selected Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains, simplifying ingredient sourcing and reducing preparation time. Choosing between these fermentation agents impacts not only flavor profiles but also ingredient freshness, availability, and overall preparation workflow in pancake making.
Troubleshooting: Common Issues with Each Fermentation
Sourdough starter fermentation in pancakes often faces issues like inconsistent rise due to variable wild yeast activity, requiring adjustments in feeding schedules and ambient temperature control. Commercial yeast fermentation typically encounters problems such as overproofing or underproofing, which can be resolved by precise timing and maintaining optimal dough temperature around 75-80degF (24-27degC). Understanding the specific fermentation requirements of each--wild yeast viability for sourdough and controlled fermentation rates for commercial yeast--enables troubleshooting common problems and achieving consistent pancake texture and flavor.
Suitability for Dietary Preferences and Restrictions
Sourdough starter is naturally fermented and contains beneficial lactic acid bacteria, making it suitable for individuals with sensitivities to commercial yeast or those seeking a more natural fermentation process. Commercial yeast, typically Saccharomyces cerevisiae, offers a faster and more predictable rise but may not be ideal for people avoiding highly processed ingredients or those with yeast intolerances. Selecting sourdough over commercial yeast can enhance digestibility and align better with dietary preferences emphasizing whole, minimally processed foods.
Which Fermentation Method is Right for Your Pancakes?
Sourdough starter ferments pancake batter with wild yeast and lactobacilli, producing a tangy flavor and complex texture, while commercial yeast offers faster fermentation and a milder taste. Choosing sourdough enhances nutritional benefits and digestibility through natural fermentation, whereas commercial yeast provides consistent rise and quick preparation. Your decision depends on whether you prioritize flavor complexity and health benefits or speed and simplicity in pancake making.
Sourdough starter vs commercial yeast for fermentation Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com