Buttermilk creates a tangy flavor and tender texture in pancake batter due to its acidity, which reacts with baking soda to produce a fluffier rise. Regular milk results in a milder taste and a denser, less airy pancake because it lacks the acidic properties needed for optimal leavening. Choosing buttermilk enhances both the flavor depth and lightness of pancakes compared to using regular milk.
Table of Comparison
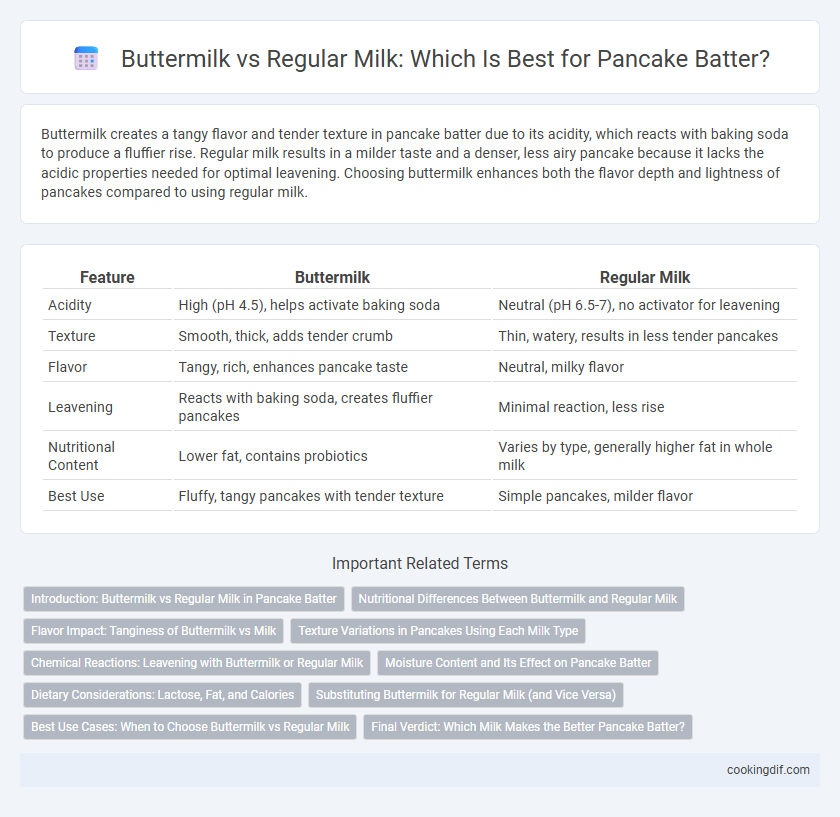
| Feature | Buttermilk | Regular Milk |
|---|---|---|
| Acidity | High (pH 4.5), helps activate baking soda | Neutral (pH 6.5-7), no activator for leavening |
| Texture | Smooth, thick, adds tender crumb | Thin, watery, results in less tender pancakes |
| Flavor | Tangy, rich, enhances pancake taste | Neutral, milky flavor |
| Leavening | Reacts with baking soda, creates fluffier pancakes | Minimal reaction, less rise |
| Nutritional Content | Lower fat, contains probiotics | Varies by type, generally higher fat in whole milk |
| Best Use | Fluffy, tangy pancakes with tender texture | Simple pancakes, milder flavor |
Introduction: Buttermilk vs Regular Milk in Pancake Batter
Buttermilk creates a tangy flavor and tender texture in pancake batter due to its acidity, which reacts with baking soda to produce a light, fluffy pancake. Regular milk offers a neutral taste and denser consistency, resulting in a thicker batter and slightly heavier pancakes. The choice between buttermilk and regular milk significantly influences the pancake's rise, moisture, and overall flavor profile.
Nutritional Differences Between Buttermilk and Regular Milk
Buttermilk contains fewer calories and less fat compared to regular milk, making it a leaner choice for pancake batter. It is richer in lactic acid bacteria, which aids digestion and improves gut health, unlike regular milk. The higher acidity in buttermilk helps activate baking soda, resulting in fluffier and more tender pancakes with enhanced flavor.
Flavor Impact: Tanginess of Buttermilk vs Milk
Buttermilk imparts a distinct tangy flavor to pancake batter that enhances the overall taste with a subtle acidity, creating a richer and more complex profile compared to regular milk. The lactic acid in buttermilk also reacts with baking soda, producing a fluffier texture while balancing the sweetness of the batter. In contrast, regular milk provides a milder, creamier flavor that results in pancakes with a more neutral taste and softer crumb.
Texture Variations in Pancakes Using Each Milk Type
Buttermilk creates pancakes with a tender, moist texture due to its acidity reacting with baking soda, which helps to produce a light and fluffy crumb. Regular milk results in a denser, sturdier pancake with a subtle sweetness, lacking the tangy depth that buttermilk provides. The choice between buttermilk and regular milk significantly influences the final pancake texture, making buttermilk ideal for soft, airy pancakes and regular milk suited for thicker, more substantial cakes.
Chemical Reactions: Leavening with Buttermilk or Regular Milk
Buttermilk's acidity reacts with baking soda in pancake batter, producing carbon dioxide bubbles that create a lighter, fluffier texture compared to regular milk, which lacks this acidic component and relies solely on baking powder for leavening. The lactic acid in buttermilk enhances gluten development and tenderizes the batter, resulting in pancakes with a delicate crumb and slight tang. Regular milk-based batters often yield denser pancakes without the pronounced rise and flavor produced by the synergy of buttermilk and alkaline leavening agents.
Moisture Content and Its Effect on Pancake Batter
Buttermilk contains higher acidity and a slightly lower moisture content compared to regular milk, which enhances the batter's texture by breaking down gluten and creating tender, fluffy pancakes. The acidity in buttermilk also reacts with baking soda, producing carbon dioxide that increases leavening and results in a lighter, softer pancake. In contrast, regular milk's higher moisture content can lead to a thinner batter, affecting the overall fluffiness and height of the pancakes.
Dietary Considerations: Lactose, Fat, and Calories
Buttermilk contains less lactose than regular milk, making it a better choice for those with mild lactose intolerance. It is also lower in fat and calories compared to whole milk, contributing to a lighter batter texture and fewer calories per serving. Choosing buttermilk enhances pancake flavor while supporting dietary goals related to fat and calorie intake.
Substituting Buttermilk for Regular Milk (and Vice Versa)
Using buttermilk instead of regular milk in pancake batter enhances the texture and flavor due to its acidity, which reacts with baking soda to create fluffier pancakes. When substituting buttermilk for regular milk, reduce or omit baking powder to avoid excessive leavening. Alternatively, if regular milk is used instead of buttermilk, adding 1 tablespoon of lemon juice or vinegar per cup of milk replicates the acidity, ensuring a tender and slightly tangy pancake.
Best Use Cases: When to Choose Buttermilk vs Regular Milk
Buttermilk is ideal for pancake batter when aiming for a tender texture and a slight tangy flavor, as its acidity reacts with baking soda to create extra fluffiness and rise. Regular milk works best for a neutral taste and a denser, more straightforward pancake, suitable when leavening agents like baking powder are used instead of baking soda. Choose buttermilk for richer, fluffier pancakes with a subtle tang, and opt for regular milk when a lighter, milder flavor is preferred or when buttermilk is unavailable.
Final Verdict: Which Milk Makes the Better Pancake Batter?
Buttermilk creates a thicker, tangier pancake batter that produces fluffier, more tender pancakes due to its acidity reacting with baking soda for better rise. Regular milk results in a thinner batter with a milder flavor and denser texture but offers a more neutral base for added ingredients. For superior fluffiness and richer taste, buttermilk is the preferred choice in pancake batter.
Buttermilk vs regular milk for batter Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com