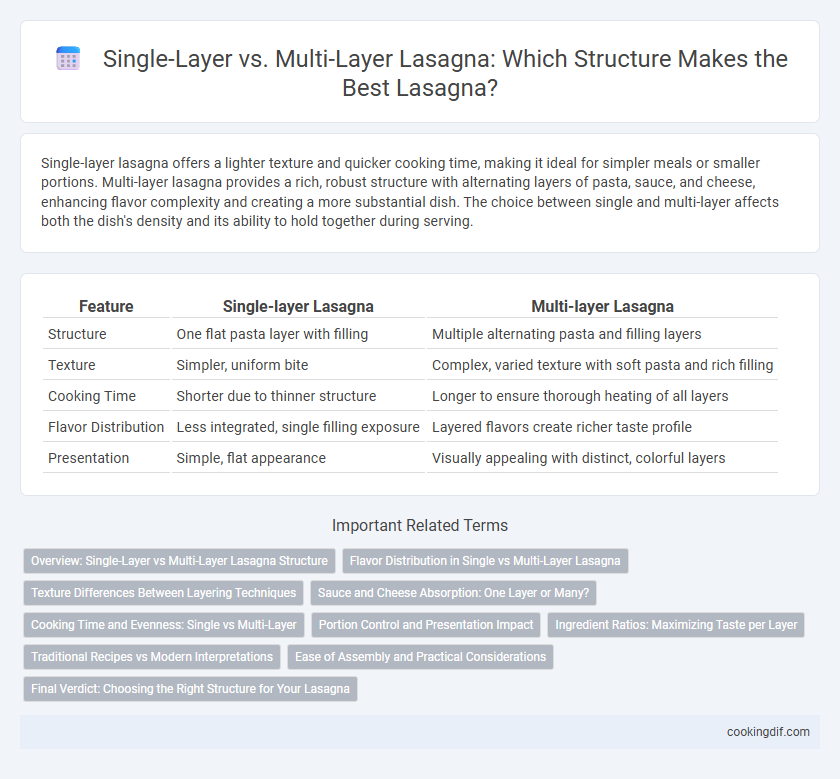
Single-layer lasagna offers a lighter texture and quicker cooking time, making it ideal for simpler meals or smaller portions. Multi-layer lasagna provides a rich, robust structure with alternating layers of pasta, sauce, and cheese, enhancing flavor complexity and creating a more substantial dish. The choice between single and multi-layer affects both the dish's density and its ability to hold together during serving.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Single-layer Lasagna | Multi-layer Lasagna |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | One flat pasta layer with filling | Multiple alternating pasta and filling layers |
| Texture | Simpler, uniform bite | Complex, varied texture with soft pasta and rich filling |
| Cooking Time | Shorter due to thinner structure | Longer to ensure thorough heating of all layers |
| Flavor Distribution | Less integrated, single filling exposure | Layered flavors create richer taste profile |
| Presentation | Simple, flat appearance | Visually appealing with distinct, colorful layers |
Overview: Single-Layer vs Multi-Layer Lasagna Structure
Single-layer lasagna features one continuous pasta sheet topped with sauce, cheese, and fillings, offering a simpler texture and quicker cooking time. Multi-layer lasagna alternates several pasta layers with rich fillings and sauce, creating a complex structure with enhanced flavors and a heartier bite. Both styles balance moisture and firmness differently, impacting the overall mouthfeel and presentation.
Flavor Distribution in Single vs Multi-Layer Lasagna
Single-layer lasagna offers a more uniform flavor distribution, allowing each bite to feature a balanced mix of sauce, cheese, and pasta. Multi-layer lasagna enhances complexity by layering diverse ingredients, creating a richer, more textured taste experience through varied flavor pockets. The choice between single and multi-layer directly impacts the intensity and harmony of flavors in each serving.
Texture Differences Between Layering Techniques
Single-layer lasagna offers a delicate texture, where each ingredient's distinct flavor and consistency are more pronounced, resulting in a lighter bite. Multi-layer lasagna creates a richer, more cohesive texture as the layers merge during baking, yielding a heartier and more indulgent mouthfeel. The layering technique significantly influences the balance between tenderness and density, with multi-layer structures providing a satisfying depth compared to the simpler, more breathable single-layer arrangement.
Sauce and Cheese Absorption: One Layer or Many?
Multi-layer lasagna offers superior sauce and cheese absorption as each layer provides more surface area for the flavors to meld, creating a rich and cohesive dish. Single-layer lasagna may result in uneven sauce distribution and less integrated textures, limiting the depth of flavor. Optimal absorption occurs when multiple layers are balanced with ample sauce and cheese between, enhancing moisture retention and taste complexity.
Cooking Time and Evenness: Single vs Multi-Layer
Single-layer lasagna cooks faster due to the even heat distribution across the entire dish, reducing overall cooking time significantly. Multi-layer lasagna requires longer baking to ensure heat penetrates through each layer, which can sometimes result in uneven cooking if not carefully monitored. Achieving consistent texture and flavor in multi-layer lasagna depends on properly balancing layer thickness and baking duration.
Portion Control and Presentation Impact
Single-layer lasagna offers precise portion control with evenly distributed ingredients, making it easier to serve consistent servings. Multi-layer lasagna creates a visually appealing, towering presentation that highlights varied textures and flavors between layers. Structurally, multi-layer versions provide a richer mouthfeel but can be harder to cut neatly compared to the simpler, more uniform single-layer format.
Ingredient Ratios: Maximizing Taste per Layer
Single-layer lasagna offers a balanced ratio of pasta, sauce, cheese, and fillings, maximizing flavor intensity in each bite without overwhelming textures. Multi-layer lasagna stacks these components to create complex depth and a richer taste experience, though proper ingredient distribution is crucial to prevent dryness or sogginess. Optimizing ingredient ratios per layer ensures even cooking and harmonious flavor blending, enhancing overall taste satisfaction.
Traditional Recipes vs Modern Interpretations
Traditional lasagna recipes emphasize multi-layer structures with alternating sheets of pasta, rich meat sauce, bechamel, and cheese, creating a complex texture and flavor profile. Modern interpretations often experiment with single-layer formats, using larger pasta sheets or alternative ingredients for a lighter, faster-to-serve dish. The multi-layer approach offers depth and authenticity, while single-layer versions cater to simplicity and contemporary dining preferences.
Ease of Assembly and Practical Considerations
Single-layer lasagna offers ease of assembly with fewer components, making it ideal for quick preparation and consistent cooking. Multi-layer lasagna provides a richer texture and complex flavor profile but requires more time and attention to assemble evenly and avoid sogginess. Practical considerations include oven size and serving requirements, where single-layer suits smaller portions and multi-layer fits larger gatherings.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Right Structure for Your Lasagna
Single-layer lasagna offers a simpler, quicker preparation with a lighter texture, ideal for smaller servings or delicate flavor profiles, while multi-layer lasagna delivers a rich, hearty experience with complex flavor integration and a denser, more satisfying bite. The final verdict depends on personal preference and occasion; multi-layered versions are best for traditional, indulgent meals, whereas single-layer suits quick, casual dining. Consider ingredient ratios, baking time, and desired texture to choose the right structure that complements your recipe and serving needs.
Single-layer vs Multi-layer for structure Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com