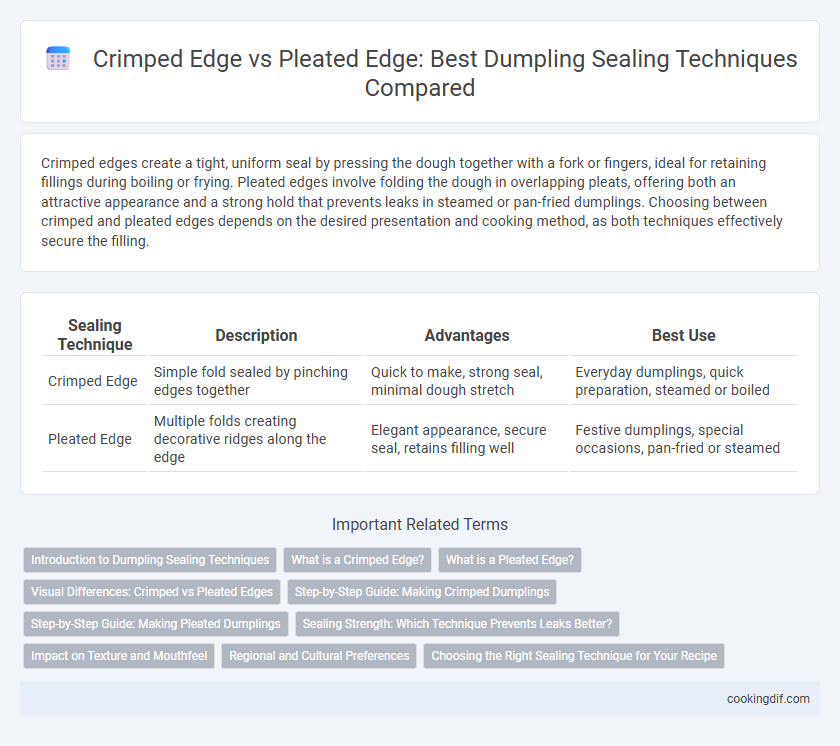
Crimped edges create a tight, uniform seal by pressing the dough together with a fork or fingers, ideal for retaining fillings during boiling or frying. Pleated edges involve folding the dough in overlapping pleats, offering both an attractive appearance and a strong hold that prevents leaks in steamed or pan-fried dumplings. Choosing between crimped and pleated edges depends on the desired presentation and cooking method, as both techniques effectively secure the filling.
Table of Comparison
| Sealing Technique | Description | Advantages | Best Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crimped Edge | Simple fold sealed by pinching edges together | Quick to make, strong seal, minimal dough stretch | Everyday dumplings, quick preparation, steamed or boiled |
| Pleated Edge | Multiple folds creating decorative ridges along the edge | Elegant appearance, secure seal, retains filling well | Festive dumplings, special occasions, pan-fried or steamed |
Introduction to Dumpling Sealing Techniques
Crimped edges create a tight, uniform seal with a simple fold that prevents filling leakage and enhances dumpling durability during cooking. Pleated edges involve intricate pleats that add decorative appeal and stronger grip, making them ideal for delicate fillings and boiling methods. Both techniques ensure effective sealing while contributing distinct textures and aesthetics to various types of dumplings.
What is a Crimped Edge?
A crimped edge in dumpling sealing involves pinching the dough together tightly to create a series of small, uniform ridges along the edge, ensuring a secure closure that prevents filling leakage during cooking. This technique enhances the dumpling's structural integrity and provides a rustic appearance that differs from the pleated edge's intricate folds. Crimped edges are particularly effective for thicker doughs and heartier fillings, offering a reliable seal and a satisfying texture.
What is a Pleated Edge?
A pleated edge on a dumpling sealing technique involves creating multiple small folds along the dumpling's dough edge, forming a decorative and secure seal that prevents filling leakage during cooking. This method enhances the dumpling's texture and visual appeal while providing structural integrity, especially for steamed or boiled varieties like Chinese jiaozi or Japanese gyoza. Pleating requires skillful folding and pinching, contributing to an even cooking process and an attractive finished product.
Visual Differences: Crimped vs Pleated Edges
Crimped edges on dumplings feature a simple, pinched seam creating a uniform, ridged pattern that is easy to recognize and produces a sturdy seal. Pleated edges display multiple folds pressed together, resulting in a decorative, fan-like appearance that enhances the dumpling's visual appeal. The distinction between these techniques lies in the texture and complexity of the edge, with crimped edges offering a more streamlined look and pleated edges providing intricate artistry.
Step-by-Step Guide: Making Crimped Dumplings
Creating crimped dumplings involves folding the dumpling wrapper in half, then pressing the edges firmly to seal while using your thumb and forefinger to create tight, decorative ridges along the edge. This technique ensures a secure seal that prevents filling leakage during cooking, especially for juicy fillings like pork or shrimp. Pressing the crimped edges evenly helps maintain the dumpling's structure, resulting in a uniform, appealing presentation ideal for boiling or steaming.
Step-by-Step Guide: Making Pleated Dumplings
To make pleated dumplings, start by placing a small amount of filling in the center of the wrapper. Fold the wrapper in half, pinching the edge to seal, then create pleats by folding and pinching small sections along the edge, ensuring even compression for a tight seal. This pleating technique enhances both the visual appeal and structural integrity, preventing filling leakage during cooking.
Sealing Strength: Which Technique Prevents Leaks Better?
The crimped edge sealing technique creates a rigid, compressed seal that provides strong resistance against leaks by tightly pressing the dough layers together. In contrast, the pleated edge involves folding the dough into overlapping ridges, enhancing flexibility but sometimes resulting in small gaps that can allow filling to escape during cooking. For maximum sealing strength and leak prevention, crimped edges are generally more reliable, especially for dumplings with juicy or liquid fillings.
Impact on Texture and Mouthfeel
Crimped edge sealing creates a firm, uniform closure that results in a slightly denser dumpling texture, enhancing the bite's solidity. Pleated edge sealing, characterized by overlapping folds, adds a delicate, layered effect that contributes to a lighter, more tender mouthfeel. The choice between crimped and pleated edges significantly influences dumpling texture, affecting consumer perception of softness and chewiness.
Regional and Cultural Preferences
Crimped edges are commonly associated with Eastern European dumplings such as pierogi, where a simple folding method ensures a sturdy seal that holds fillings like potatoes, cheese, or meat during boiling or frying. Pleated edges are a hallmark of Chinese dumplings like jiaozi, reflecting intricate craftsmanship that not only secures the filling but also symbolizes good luck and cultural identity during festive occasions. Regional variations in sealing techniques highlight the fusion of practical cooking methods with local traditions and cultural symbolism in dumpling preparation worldwide.
Choosing the Right Sealing Technique for Your Recipe
Crimped edges create a simple, strong seal ideal for thicker fillings like meat or vegetable dumplings, preventing leakage during cooking. Pleated edges offer an intricate seal, often used for delicate, moist fillings such as seafood or finely minced mixtures, enhancing both aesthetics and grip. Selecting the right sealing technique balances durability, cooking method, and filling texture to ensure optimal dumpling integrity and presentation.
Crimped edge vs Pleated edge for sealing technique Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com