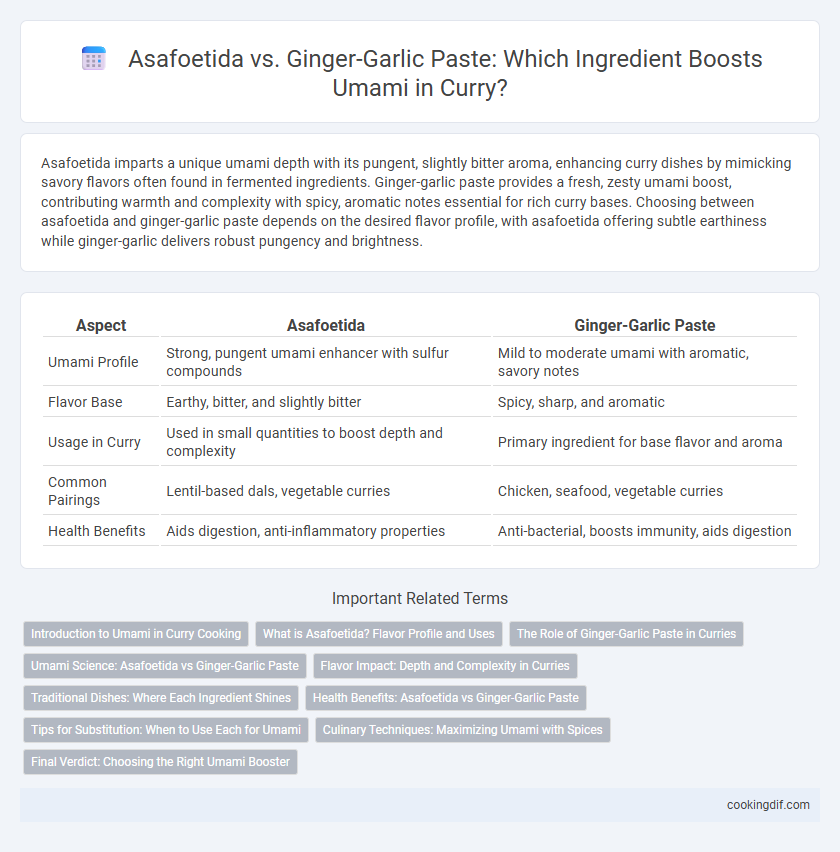
Asafoetida imparts a unique umami depth with its pungent, slightly bitter aroma, enhancing curry dishes by mimicking savory flavors often found in fermented ingredients. Ginger-garlic paste provides a fresh, zesty umami boost, contributing warmth and complexity with spicy, aromatic notes essential for rich curry bases. Choosing between asafoetida and ginger-garlic paste depends on the desired flavor profile, with asafoetida offering subtle earthiness while ginger-garlic delivers robust pungency and brightness.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Asafoetida | Ginger-Garlic Paste |
|---|---|---|
| Umami Profile | Strong, pungent umami enhancer with sulfur compounds | Mild to moderate umami with aromatic, savory notes |
| Flavor Base | Earthy, bitter, and slightly bitter | Spicy, sharp, and aromatic |
| Usage in Curry | Used in small quantities to boost depth and complexity | Primary ingredient for base flavor and aroma |
| Common Pairings | Lentil-based dals, vegetable curries | Chicken, seafood, vegetable curries |
| Health Benefits | Aids digestion, anti-inflammatory properties | Anti-bacterial, boosts immunity, aids digestion |
Introduction to Umami in Curry Cooking
Asafoetida and ginger-garlic paste both enhance umami in curry cooking, but their flavor profiles differ significantly; asafoetida adds a pungent, savory depth often compared to garlic and onion, while ginger-garlic paste delivers a fresh, aromatic sharpness that intensifies the curry's complexity. Umami, known as the fifth taste, enriches curry by boosting savory notes and balancing spices, making these ingredients essential for achieving a full-bodied flavor. Incorporating either asafoetida or ginger-garlic paste allows cooks to layer umami elements that elevate the overall taste experience in diverse curry recipes.
What is Asafoetida? Flavor Profile and Uses
Asafoetida is a pungent, sulfurous resin derived from the root of the Ferula plant, commonly used in Indian cuisine to enhance umami and add depth to curries. Its flavor profile includes a strong onion-garlic aroma when raw, which mellows into a smooth, savory taste upon cooking, making it a potent umami booster especially useful in vegetarian dishes. Replacing ginger-garlic paste with asafoetida alters the flavor complexity by providing a unique tangy and slightly bitter note that complements legumes and vegetables, intensifying savory richness in curry preparations.
The Role of Ginger-Garlic Paste in Curries
Ginger-garlic paste is a fundamental ingredient in curries, providing a robust umami depth that enhances the overall flavor profile. Its blend of pungent ginger and aromatic garlic creates a savory base that intensifies the spice complexity and richness. Unlike asafoetida, which offers a sharp, sulfurous aroma, ginger-garlic paste contributes a balanced, warm umami that supports the melding of other spices.
Umami Science: Asafoetida vs Ginger-Garlic Paste
Asafoetida and ginger-garlic paste both contribute to umami in curry, but their profiles differ significantly. Asafoetida contains sulfur compounds that mimic the savoriness of glutamates, enhancing depth and mouthfeel without overpowering other spices. Ginger-garlic paste, rich in allicin and zingiberene, provides a pungent, aromatic umami that balances sweetness and spice, creating a multidimensional taste experience.
Flavor Impact: Depth and Complexity in Curries
Asafoetida delivers a pungent, umami-rich depth that enhances the savory foundation of curries, imparting subtle onion-garlic nuances without overpowering other spices. Ginger-garlic paste contributes a fresh, aromatic sharpness that brightens flavors while adding warmth and complexity. Combining both ingredients can create a multidimensional flavor profile, balancing the intense earthiness of asafoetida with the vibrant zest of ginger-garlic paste for richer curry depth.
Traditional Dishes: Where Each Ingredient Shines
Asafoetida imparts a distinct umami depth essential in Indian lentil dishes like dal and sambar, enhancing their earthy flavors with its pungent, savory profile. Ginger-garlic paste is a cornerstone in North Indian curries and masalas, providing a robust, aromatic base that intensifies meat and vegetable stews. Traditional cuisines leverage asafoetida for its digestive and flavor-boosting properties, while ginger-garlic paste offers a complex, spicy warmth crucial to layered curry dishes.
Health Benefits: Asafoetida vs Ginger-Garlic Paste
Asafoetida contains potent antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds that support digestive health and reduce bloating, making it beneficial in curry preparations. Ginger-garlic paste offers strong antimicrobial and immune-boosting properties, along with enhanced cardiovascular benefits due to gingerol and allicin content. Both ingredients contribute unique umami profiles while providing complementary health benefits such as improved digestion, immune defense, and anti-inflammatory effects.
Tips for Substitution: When to Use Each for Umami
Asafoetida offers a potent umami depth ideal for vegetarian or lentil-based curries, adding a subtle onion-garlic aroma without overpowering flavors. Ginger-garlic paste provides a balanced umami foundation perfect for meat or vegetable curries, enhancing richness and warmth with its natural pungency. Use asafoetida sparingly in dishes requiring umami without strong garlic notes, while ginger-garlic paste suits recipes needing a pronounced savory base for complex flavor layering.
Culinary Techniques: Maximizing Umami with Spices
Asafoetida enhances umami in curry by releasing sulfur compounds that deepen savory flavors when sauteed in hot oil, creating a rich base for the dish. Ginger-garlic paste contributes both pungency and subtle sweetness, intensifying umami through its natural glutamates and allicin released during cooking. Combining these spices in culinary techniques like tempering can maximize umami by layering complex taste profiles that elevate the overall flavor depth in curries.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Right Umami Booster
Asafoetida delivers a potent, sulfurous umami depth that enhances savory curries with a unique, slightly bitter undertone, ideal for vegetarian dishes craving complexity. Ginger-garlic paste offers a fresher, aromatic umami profile, balancing heat and sweetness, perfect for rich, meat-based curries seeking robust flavor layering. Choosing the right umami booster depends on the desired flavor intensity and dish type; use asafoetida for subtle, lingering umami in legume or vegetable curries, and ginger-garlic paste for vibrant, bold umami in hearty, protein-rich recipes.
Asafoetida vs Ginger-garlic paste for umami Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com