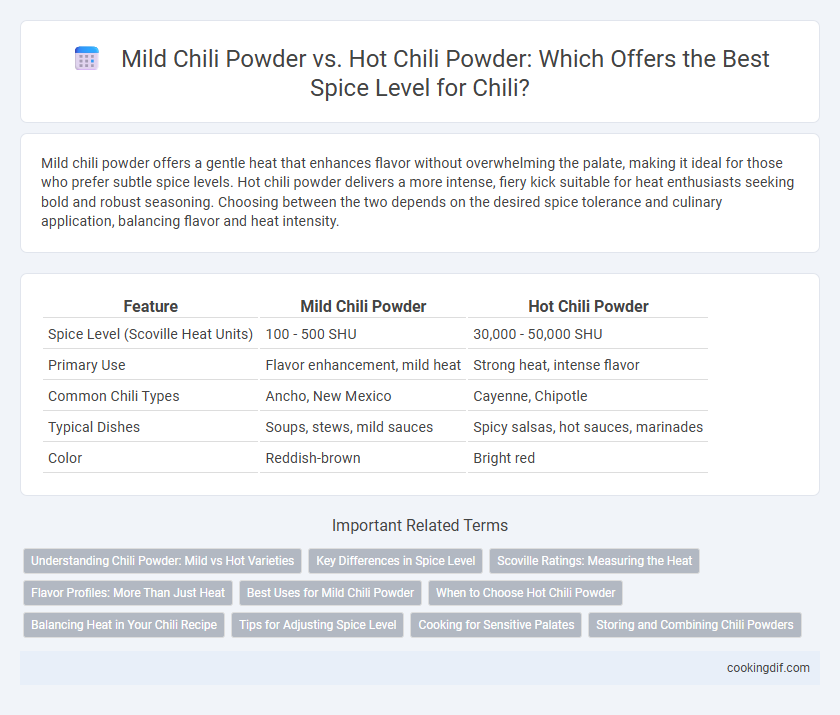
Mild chili powder offers a gentle heat that enhances flavor without overwhelming the palate, making it ideal for those who prefer subtle spice levels. Hot chili powder delivers a more intense, fiery kick suitable for heat enthusiasts seeking bold and robust seasoning. Choosing between the two depends on the desired spice tolerance and culinary application, balancing flavor and heat intensity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Mild Chili Powder | Hot Chili Powder |
|---|---|---|
| Spice Level (Scoville Heat Units) | 100 - 500 SHU | 30,000 - 50,000 SHU |
| Primary Use | Flavor enhancement, mild heat | Strong heat, intense flavor |
| Common Chili Types | Ancho, New Mexico | Cayenne, Chipotle |
| Typical Dishes | Soups, stews, mild sauces | Spicy salsas, hot sauces, marinades |
| Color | Reddish-brown | Bright red |
Understanding Chili Powder: Mild vs Hot Varieties
Mild chili powder typically contains less capsaicin, resulting in a gentler heat level suitable for those sensitive to spice, while hot chili powder has higher capsaicin content, delivering a more intense, fiery flavor. Varieties like ancho or paprika-based mild chili powders are often used for deeper color and subtle warmth, whereas cayenne or chipotle powders provide pronounced heat and smoky undertones. Understanding these differences helps chefs and cooks tailor dishes to desired spice levels and flavor profiles.
Key Differences in Spice Level
Mild chili powder typically contains fewer capsaicin compounds, resulting in a lower Scoville Heat Unit (SHU) rating, often ranging from 100 to 500 SHU, making it suitable for those seeking a gentle, flavorful spice without intense heat. Hot chili powder, on the other hand, is made from varieties of chili peppers with higher capsaicin content, such as cayenne or arbol, with SHU values that can exceed 30,000, delivering a significantly spicier experience. The key difference lies in their heat intensity and capsaicin concentration, affecting culinary use and heat tolerance preferences.
Scoville Ratings: Measuring the Heat
Mild chili powder typically ranges from 100 to 500 Scoville Heat Units (SHU), making it suitable for those who prefer subtle spiciness without overwhelming heat. Hot chili powder, on the other hand, often exceeds 30,000 SHU, delivering intense heat that significantly impacts the flavor profile of dishes. Understanding these Scoville Ratings helps chefs and home cooks adjust spice levels accurately to match desired heat intensity.
Flavor Profiles: More Than Just Heat
Mild chili powder offers a subtle, earthy flavor with hints of sweetness and smokiness, allowing the natural ingredients like cumin and garlic to shine without overpowering dishes. Hot chili powder delivers a sharp, intense heat combined with bold, complex notes that enhance robust recipes such as chili con carne and spicy salsas. Choosing between mild and hot chili powder depends on the desired balance of heat and depth, as each brings unique flavor profiles that transform culinary experiences beyond mere spiciness.
Best Uses for Mild Chili Powder
Mild chili powder offers a gentle heat level ideal for seasoning dishes where a subtle spice is preferred, such as soups, stews, and enchiladas. It enhances flavor without overpowering the natural taste of ingredients, making it perfect for children's meals or those sensitive to heat. Best uses for mild chili powder include marinades, rubs for poultry, and flavoring beans or rice dishes.
When to Choose Hot Chili Powder
Hot chili powder is ideal for recipes requiring a pronounced heat level and robust flavor, enhancing dishes like spicy stews, barbecue rubs, and chili con carne. Choose hot chili powder when a fiery spice is needed to intensify the taste profile and complement bold ingredients such as cumin, garlic, and smoked paprika. Its higher capsaicin content delivers a strong heat that elevates Mexican, Tex-Mex, and Southwestern cuisine authentically.
Balancing Heat in Your Chili Recipe
Mild chili powder offers a subtle warmth that enhances the flavor without overwhelming heat, making it ideal for those seeking a balanced chili recipe. Hot chili powder intensifies spice levels with capsaicin-rich peppers, adding depth and a fiery kick to dishes for heat lovers. Adjusting the ratio of mild to hot chili powder allows precise control over spice intensity, ensuring the perfect balance of flavor and heat in your chili.
Tips for Adjusting Spice Level
Mild chili powder offers a subtle heat, ideal for those who prefer gentle spice or want to preserve other flavors in their dishes, while hot chili powder provides intense heat for heat enthusiasts. To adjust spice level effectively, start by adding small amounts of chili powder and gradually increase to reach the desired heat, balancing with dairy or acidic ingredients to mellow spiciness if needed. Experimenting with blending mild and hot chili powders allows precise control over flavor and heat intensity in recipes.
Cooking for Sensitive Palates
Mild chili powder contains lower levels of capsaicin, making it ideal for cooking dishes suited to sensitive palates, as it imparts flavor without overwhelming heat. Hot chili powder has a higher concentration of capsaicin, delivering a significant spice level that can be too intense for those unaccustomed to fiery foods. Opting for mild chili powder ensures comfortable spice tolerance while preserving the rich, smoky notes essential in many recipes.
Storing and Combining Chili Powders
Mild chili powder retains its flavor best when stored in an airtight container away from heat and light, prolonging its shelf life and preserving its subtle spice level. Hot chili powder, with its more volatile capsaicin compounds, requires airtight storage in a cool, dark place to maintain potency and avoid degradation of heat intensity. Combining mild and hot chili powders allows precise control over spice levels, enabling tailored flavor profiles while keeping storage conditions optimal for each type.
Mild chili powder vs hot chili powder for spice level Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com