Black pepper and white pepper both offer distinct flavors for seasoning dishes, with black pepper providing a sharp, pungent heat and white pepper delivering a milder, earthier taste. Black pepper is harvested from unripe peppercorns, which are dried with their outer skin intact, while white pepper comes from fully ripe peppercorns with the outer layer removed, resulting in a less intense flavor. Choosing between them depends on the desired spice level and visual appearance in recipes like chili, where black pepper enhances boldness and white pepper subtly complements without altering color.
Table of Comparison
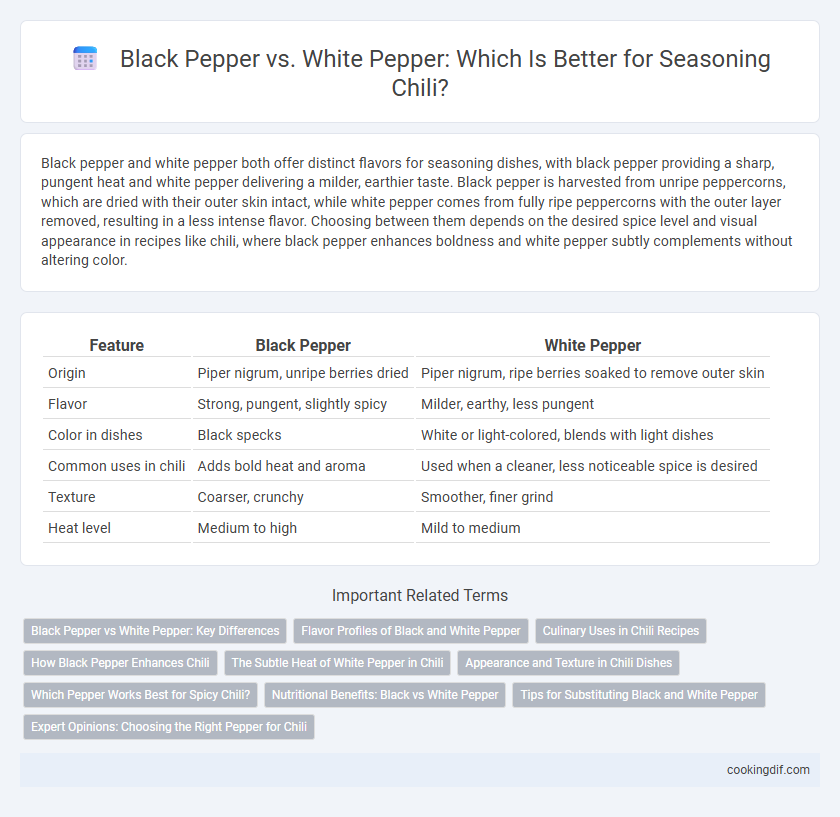
| Feature | Black Pepper | White Pepper |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Piper nigrum, unripe berries dried | Piper nigrum, ripe berries soaked to remove outer skin |
| Flavor | Strong, pungent, slightly spicy | Milder, earthy, less pungent |
| Color in dishes | Black specks | White or light-colored, blends with light dishes |
| Common uses in chili | Adds bold heat and aroma | Used when a cleaner, less noticeable spice is desired |
| Texture | Coarser, crunchy | Smoother, finer grind |
| Heat level | Medium to high | Mild to medium |
Black Pepper vs White Pepper: Key Differences
Black pepper and white pepper both originate from the same plant, Piper nigrum, but differ significantly in flavor and processing. Black pepper is harvested when green, then dried with the outer skin intact, offering a strong, pungent, and aromatic taste ideal for robust dishes. White pepper, produced by removing the outer layer after ripening, has a milder, earthier flavor, making it suitable for light-colored sauces and subtle seasoning without dark specks.
Flavor Profiles of Black and White Pepper
Black pepper offers a bold, pungent flavor with sharp, earthy undertones that enhance the complexity of chili dishes. White pepper provides a more subdued, slightly fermented taste with subtle heat, allowing chili's other spices to shine without overpowering. Both peppers contribute distinctive spice profiles, making black pepper ideal for robust flavors and white pepper suitable for smoother, milder seasoning in chili recipes.
Culinary Uses in Chili Recipes
Black pepper enhances chili recipes with its robust, pungent flavor and slight heat, complementing rich meats and smoky spices commonly used in traditional chili dishes. White pepper offers a milder, earthier taste that blends seamlessly into lighter chili preparations or creamy chili-based sauces without altering the dish's color. Chefs often choose black pepper for bold seasoning and white pepper for subtle heat in diverse chili variations.
How Black Pepper Enhances Chili
Black pepper adds a robust, earthy heat to chili, enhancing the dish's complex flavors with its bold, pungent notes. Its aromatic compounds intensify the savory spices typically found in chili, such as cumin and paprika, creating a layered taste experience. The subtle heat of black pepper also balances the chili's richness without overpowering the other ingredients.
The Subtle Heat of White Pepper in Chili
White pepper offers a more delicate and nuanced heat compared to the sharper intensity of black pepper, making it ideal for enhancing chili without overpowering other flavors. Its subtle warmth allows the complex spices and savory ingredients of chili to shine through, creating a balanced and smooth taste profile. Using white pepper in chili seasoning can elevate the dish by adding gentle heat and a slightly earthy undertone that complements chili's rich, robust character.
Appearance and Texture in Chili Dishes
Black pepper adds a coarse, grainy texture with visible dark specks that stand out against chili's vibrant colors, enhancing its rustic presentation. White pepper, being finely ground and pale, blends seamlessly into the chili, providing subtle heat without altering the dish's visual appearance. Choosing between black and white pepper affects not only the chili's flavor profile but also its aesthetic and mouthfeel.
Which Pepper Works Best for Spicy Chili?
Black pepper enhances spicy chili with its robust, sharp flavor and subtle heat, complementing the dish's bold spices without overwhelming them. White pepper offers a milder, earthier taste and is preferred for a smoother, less intrusive seasoning that maintains chili's vibrant aroma. Chefs often choose black pepper for a richer spice profile, while white pepper suits lighter chili variations where a delicate peppery touch is desired.
Nutritional Benefits: Black vs White Pepper
Black pepper contains higher levels of piperine, which enhances nutrient absorption and offers potent antioxidant properties, supporting digestion and reducing inflammation. White pepper, while milder in flavor, delivers comparable amounts of calcium and iron, contributing to bone health and oxygen transport. Both varieties provide essential vitamins like vitamin K, but black pepper generally offers superior nutritional benefits due to its less processed form.
Tips for Substituting Black and White Pepper
Black pepper offers a sharper, more complex flavor compared to the milder, earthier taste of white pepper often used in lighter dishes and sauces. When substituting black pepper with white pepper in chili recipes, use slightly less white pepper to avoid overpowering the dish, as it can be more pungent and has a distinct fermented note. For the reverse substitution, increase the quantity of black pepper moderately to achieve a similar heat and aroma, maintaining the chili's rich seasoning balance.
Expert Opinions: Choosing the Right Pepper for Chili
Experts emphasize that black pepper, with its robust and pungent flavor, enhances the depth and heat of chili, making it ideal for hearty, spicy recipes. White pepper, sourced from the same fruit but with the outer skin removed, offers a milder, earthy taste that blends seamlessly without overpowering other spices in chili. Chefs recommend selecting black pepper for bold seasoning or white pepper when aiming for subtlety and a smoother heat profile in chili dishes.
Black pepper vs white pepper for seasoning Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com