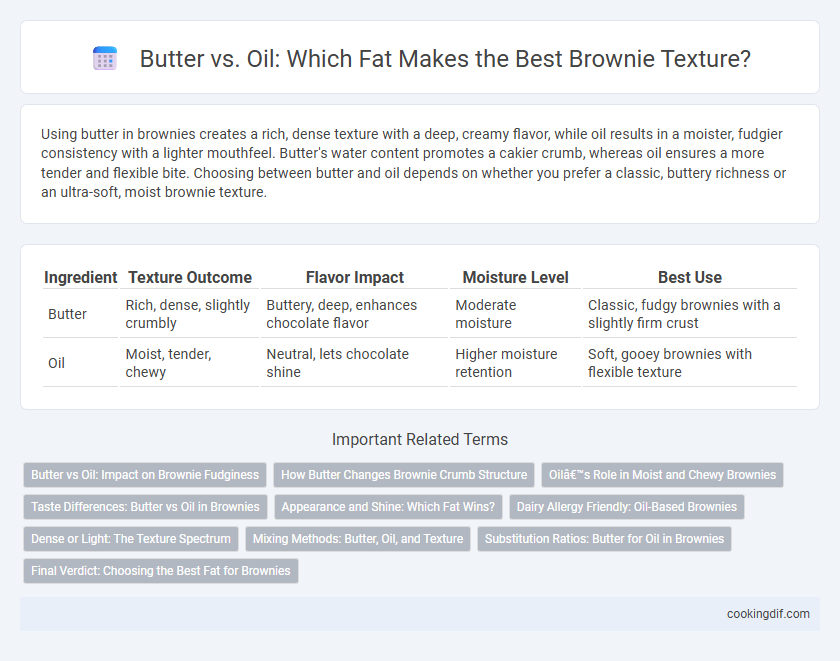
Using butter in brownies creates a rich, dense texture with a deep, creamy flavor, while oil results in a moister, fudgier consistency with a lighter mouthfeel. Butter's water content promotes a cakier crumb, whereas oil ensures a more tender and flexible bite. Choosing between butter and oil depends on whether you prefer a classic, buttery richness or an ultra-soft, moist brownie texture.
Table of Comparison
| Ingredient | Texture Outcome | Flavor Impact | Moisture Level | Best Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Butter | Rich, dense, slightly crumbly | Buttery, deep, enhances chocolate flavor | Moderate moisture | Classic, fudgy brownies with a slightly firm crust |
| Oil | Moist, tender, chewy | Neutral, lets chocolate shine | Higher moisture retention | Soft, gooey brownies with flexible texture |
Butter vs Oil: Impact on Brownie Fudginess
Butter contributes to a rich, dense texture in brownies due to its milk solids and water content, which promote a fudgy consistency. Oil, on the other hand, adds moisture and creates a softer, more tender crumb without firming up the structure. Choosing between butter and oil significantly affects the fudginess, with butter-based brownies typically being denser and oil-based ones often more moist and cake-like.
How Butter Changes Brownie Crumb Structure
Butter contributes to a denser, fudgier brownie crumb by solidifying as it cools, which traps air and moisture more effectively than oil. Its milk solids caramelize during baking, enhancing flavor and creating a slightly firmer texture with tender edges. In contrast, oil yields a moister but softer and more cake-like crumb due to its liquid fat properties that lack the structure-building characteristics of butter.
Oil’s Role in Moist and Chewy Brownies
Oil enhances brownie texture by creating a moist and chewy crumb due to its liquid fat composition that coats flour proteins, limiting gluten formation. Unlike butter, oil remains liquid at room temperature, contributing to a denser and fudgier consistency. This results in brownies that retain moisture longer and offer a supple bite, preferred in many rich brownie recipes.
Taste Differences: Butter vs Oil in Brownies
Butter in brownies enhances flavor with a rich, creamy taste and adds a slightly caramelized note due to milk solids, resulting in a dense, fudgy texture. Oil contributes to a moist, tender crumb but lacks the depth of flavor that butter provides, creating a lighter, more neutral brownie. Choosing butter over oil elevates the taste complexity, making brownies more flavorful and indulgent.
Appearance and Shine: Which Fat Wins?
Butter imparts a glossy, rich shine to brownies due to its milk solids caramelizing during baking, resulting in an appealing, crackly top crust. Oil-based brownies generally have a matte appearance and softer texture, lacking the distinct shine that butter provides. For a visually striking, shiny surface with a classic brownie look, butter emerges as the superior fat choice.
Dairy Allergy Friendly: Oil-Based Brownies
Oil-based brownies provide a dairy allergy-friendly alternative by eliminating butter, which contains milk proteins that can trigger allergic reactions. Using vegetable or canola oil maintains a moist, fudgy texture without compromising flavor, making these brownies safe for individuals with dairy sensitivities. This substitution ensures a tender crumb while accommodating dairy-free dietary needs effectively.
Dense or Light: The Texture Spectrum
Butter creates a dense, fudgy texture in brownies due to its solid fat content and water, which helps develop structure and richness. Oil, being liquid at room temperature, yields lighter, moister brownies with a tender crumb but less firm structure. Choosing butter results in a chewy bite, while oil produces a softer, cake-like tenderness ideal for lighter brownies.
Mixing Methods: Butter, Oil, and Texture
Butter in brownie recipes contributes to a denser, fudgier texture due to its solid fat content that traps air during creaming, enhancing crumb structure. Oil, being liquid at room temperature, yields a moister, softer brownie with a more uniform crumb by coating flour proteins evenly and preventing gluten overdevelopment. Mixing methods that incorporate melted butter create a rich, chewy texture, while using oil with minimal mixing preserves tenderness and promotes a moist, cakey brownie.
Substitution Ratios: Butter for Oil in Brownies
Substituting butter for oil in brownies typically requires a 1:1 ratio, but adjustments may be necessary depending on the desired texture. Butter contributes a richer flavor and denser crumb due to its milk solids, whereas oil creates a more moist and fudgy consistency. For optimal results, use equal amounts of melted butter when replacing oil, but expect a slightly firmer texture and enhanced buttery aroma in the final brownie.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Best Fat for Brownies
Butter delivers a rich, dense texture with a slightly crisp edge, enhancing the chocolate flavor and providing a traditional brownie experience. Oil creates a moister, softer crumb and yields a fudgier bite, ideal for those preferring extra moistness without firmness. For the best results, choose butter for a classic, rich taste and oil when a tender, melt-in-your-mouth brownie is desired.
Butter vs oil for brownie texture Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com