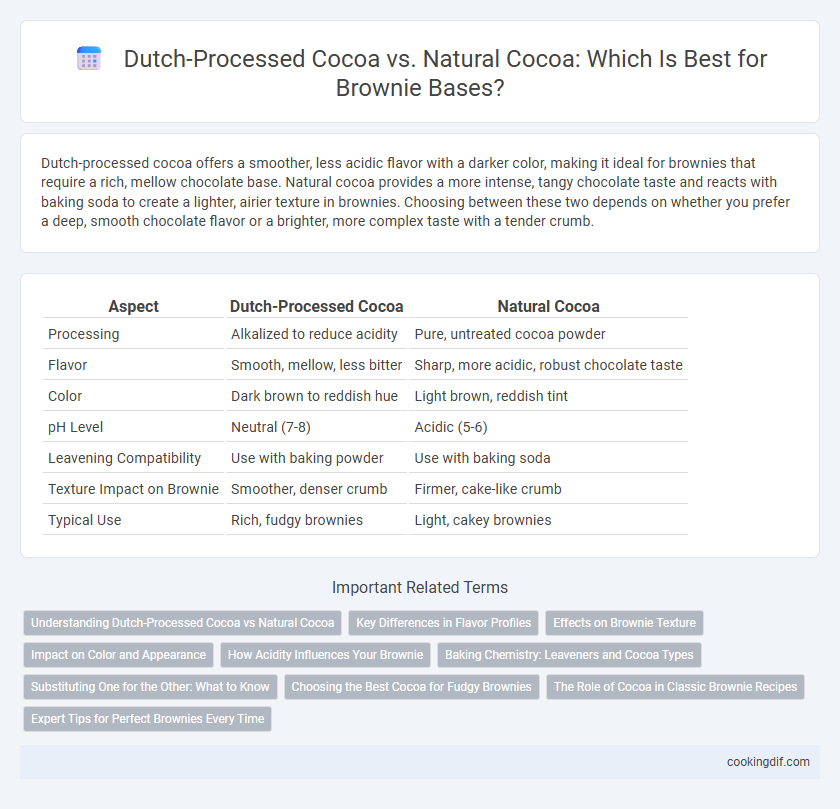
Dutch-processed cocoa offers a smoother, less acidic flavor with a darker color, making it ideal for brownies that require a rich, mellow chocolate base. Natural cocoa provides a more intense, tangy chocolate taste and reacts with baking soda to create a lighter, airier texture in brownies. Choosing between these two depends on whether you prefer a deep, smooth chocolate flavor or a brighter, more complex taste with a tender crumb.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Dutch-Processed Cocoa | Natural Cocoa |
|---|---|---|
| Processing | Alkalized to reduce acidity | Pure, untreated cocoa powder |
| Flavor | Smooth, mellow, less bitter | Sharp, more acidic, robust chocolate taste |
| Color | Dark brown to reddish hue | Light brown, reddish tint |
| pH Level | Neutral (7-8) | Acidic (5-6) |
| Leavening Compatibility | Use with baking powder | Use with baking soda |
| Texture Impact on Brownie | Smoother, denser crumb | Firmer, cake-like crumb |
| Typical Use | Rich, fudgy brownies | Light, cakey brownies |
Understanding Dutch-Processed Cocoa vs Natural Cocoa
Dutch-processed cocoa undergoes an alkalization process that neutralizes its acidity, resulting in a smoother, darker, and milder flavor ideal for brownies with a rich chocolate taste. Natural cocoa retains its natural acidity, offering a more robust, slightly bitter profile that reacts with baking soda to provide lift and texture in brownie recipes. Choosing between Dutch-processed and natural cocoa affects the overall flavor intensity, color depth, and chemical reactions during baking, making it essential to adjust leavening agents accordingly for perfect brownies.
Key Differences in Flavor Profiles
Dutch-processed cocoa offers a smooth, mellow flavor with reduced acidity, resulting in a rich, dark chocolate taste ideal for fudgy brownies. Natural cocoa maintains a bright, fruity, and slightly bitter profile with higher acidity, providing a more intense and tangy chocolate flavor that enhances cakey brownie textures. Understanding these key differences helps bakers tailor their brownie base to achieve either a velvety richness or a vibrant chocolate punch.
Effects on Brownie Texture
Dutch-processed cocoa produces a smoother, more tender brownie texture because its alkalized properties reduce acidity and enhance cocoa solubility, leading to better fat incorporation and a finer crumb. Natural cocoa, being more acidic, reacts strongly with baking soda, creating more rise and a coarser, cakier texture with a pronounced chocolate flavor. Choosing Dutch-processed cocoa results in denser, fudgier brownies, while natural cocoa yields lighter, airier consistency.
Impact on Color and Appearance
Dutch-processed cocoa produces a darker, richer color in brownies due to its alkalizing treatment, which neutralizes acidity and enhances deep brown tones. Natural cocoa results in a lighter, reddish-brown hue, as its higher acidity reacts with baking soda causing a brighter appearance. Choosing Dutch-processed cocoa ensures a more uniform and visually intense chocolate color in brownies compared to the lighter and more varied shades from natural cocoa.
How Acidity Influences Your Brownie
Dutch-processed cocoa is alkalized to neutralize acidity, resulting in a smoother, milder flavor and darker color that can affect the texture of brownies, making them more tender and less bitter. Natural cocoa retains its acidic profile, which reacts with baking soda to produce lift and a slightly tangy taste, contributing to a fudgier, denser brownie crumb. Understanding the acidity difference helps bakers choose the right cocoa to control the balance between rise, moisture, and flavor depth in their brownies.
Baking Chemistry: Leaveners and Cocoa Types
Dutch-processed cocoa, treated with an alkalizing agent, has a neutral pH that requires baking soda as a leavener to properly activate and produce a tender brownie texture. Natural cocoa, being acidic, reacts with baking soda to create carbon dioxide, contributing to the rise and crumb structure of brownies. Choosing the correct leavener based on cocoa type is essential for achieving the desired balance between chewiness and lift in brownie baking chemistry.
Substituting One for the Other: What to Know
Dutch-processed cocoa has a milder, less acidic flavor compared to the sharper, more bitter natural cocoa, impacting the overall taste of brownies. Natural cocoa reacts with baking soda to provide rise and a lighter texture, while Dutch-processed cocoa requires baking powder for proper leavening. When substituting Dutch-processed for natural cocoa or vice versa, adjusting the leavening agents ensures the desired crumb and height in the brownie base.
Choosing the Best Cocoa for Fudgy Brownies
Dutch-processed cocoa offers a smooth, mellow flavor and darker color, ideal for creating rich, fudgy brownies with a velvety texture. Natural cocoa tends to be more acidic and intense, resulting in a lighter color and slightly tangier taste that can affect leavening and moisture balance in your brownie batter. For the ultimate fudgy brownie base, Dutch-processed cocoa is preferred due to its lower acidity and ability to blend seamlessly with butter and sugar, producing a dense, chewy bite.
The Role of Cocoa in Classic Brownie Recipes
Dutch-processed cocoa, treated with alkaline to neutralize acidity, creates a smoother, mellower flavor and darker color in classic brownie recipes, making it ideal for rich, fudgy textures. Natural cocoa retains its acidic properties, offering a sharper, more robust chocolate taste that reacts with baking soda for a lighter, more cake-like crumb. Choosing between Dutch-processed and natural cocoa determines the brownie's flavor profile, texture, and overall mouthfeel in traditional chocolate desserts.
Expert Tips for Perfect Brownies Every Time
Dutch-processed cocoa offers a smoother, less acidic flavor that enhances the rich chocolate taste in brownies, while natural cocoa provides a more robust, tangy profile ideal for a traditional brownie base. Experts recommend adjusting leavening agents accordingly: baking soda pairs well with natural cocoa's acidity, whereas baking powder complements the neutral pH of Dutch-processed cocoa for optimal rise and texture. For perfect brownies every time, select cocoa based on desired flavor and balance ingredients to achieve the ideal moistness and crumb structure.
Dutch-processed cocoa vs Natural cocoa for brownie base Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com