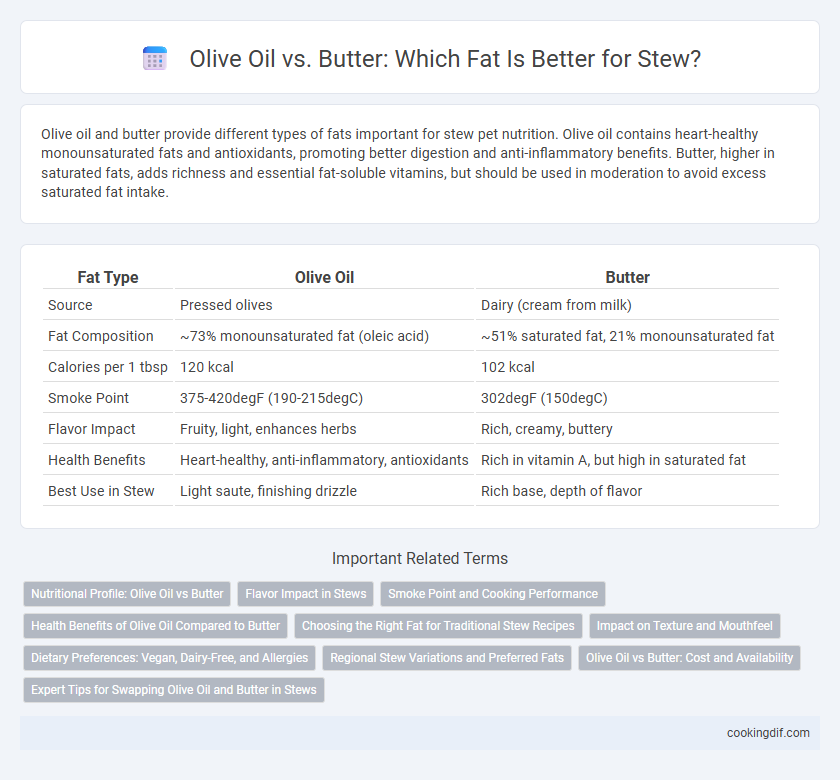
Olive oil and butter provide different types of fats important for stew pet nutrition. Olive oil contains heart-healthy monounsaturated fats and antioxidants, promoting better digestion and anti-inflammatory benefits. Butter, higher in saturated fats, adds richness and essential fat-soluble vitamins, but should be used in moderation to avoid excess saturated fat intake.
Table of Comparison
| Fat Type | Olive Oil | Butter |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Pressed olives | Dairy (cream from milk) |
| Fat Composition | ~73% monounsaturated fat (oleic acid) | ~51% saturated fat, 21% monounsaturated fat |
| Calories per 1 tbsp | 120 kcal | 102 kcal |
| Smoke Point | 375-420degF (190-215degC) | 302degF (150degC) |
| Flavor Impact | Fruity, light, enhances herbs | Rich, creamy, buttery |
| Health Benefits | Heart-healthy, anti-inflammatory, antioxidants | Rich in vitamin A, but high in saturated fat |
| Best Use in Stew | Light saute, finishing drizzle | Rich base, depth of flavor |
Nutritional Profile: Olive Oil vs Butter
Olive oil is rich in monounsaturated fats, particularly oleic acid, which supports heart health and reduces inflammation, while butter contains higher levels of saturated fat linked to increased LDL cholesterol. Olive oil also provides antioxidants such as vitamin E and polyphenols that contribute to cellular protection and overall wellness. Butter offers fat-soluble vitamins like A and K2 but lacks the beneficial plant compounds found in olive oil, making olive oil a nutritionally superior choice for cooking stews.
Flavor Impact in Stews
Olive oil imparts a fruity, slightly peppery flavor that enhances the aromatic herbs and vegetables in stews, creating a Mediterranean-inspired depth. Butter contributes a rich, creamy texture with nutty undertones that elevate the stew's mouthfeel and add a subtle sweetness. Choosing olive oil or butter influences the stew's overall taste profile, balancing between light, fresh notes and hearty, indulgent richness.
Smoke Point and Cooking Performance
Olive oil offers a higher smoke point around 375degF (190degC) compared to butter's lower smoke point of approximately 302degF (150degC), making it more suitable for sauteing and searing in stew preparation. Olive oil's monounsaturated fats provide a stable cooking performance at moderate heat, while butter's milk solids can burn easily, adding a rich flavor but requiring careful temperature control. Choosing olive oil enhances the stew's health profile and reduces the risk of burnt fats, optimizing both taste and nutrition.
Health Benefits of Olive Oil Compared to Butter
Olive oil contains high levels of monounsaturated fats, which are known to reduce inflammation and lower the risk of heart disease, unlike butter that is rich in saturated fats linked to increased cholesterol levels. Rich in antioxidants such as vitamin E and polyphenols, olive oil supports cellular health and provides anti-inflammatory effects that butter lacks. Incorporating olive oil into stews enhances nutrient absorption and promotes cardiovascular health by improving lipid profiles compared to butter.
Choosing the Right Fat for Traditional Stew Recipes
Olive oil offers a fruity, slightly peppery flavor and contains heart-healthy monounsaturated fats, making it ideal for Mediterranean-style stews. Butter provides richness with a creamy texture and contains saturated fats that enhance the depth of flavor in classic European stews. Selecting the right fat depends on the stew's regional origin and desired taste profile, balancing health benefits and authentic flavor.
Impact on Texture and Mouthfeel
Olive oil imparts a smoother, silkier texture to stew by coating ingredients with a light, fruity richness that enhances mouthfeel without heaviness. Butter contributes a creamy, velvety consistency and adds subtle sweetness, creating a richer, more indulgent stew with a fuller mouthfeel. Choosing olive oil yields a lighter, more aromatic stew, while butter offers a dense, luscious texture that thickens the broth and elevates savory depth.
Dietary Preferences: Vegan, Dairy-Free, and Allergies
Olive oil is preferred for vegan and dairy-free stews due to its plant-based origin and absence of allergens, making it safe for those with dairy allergies or lactose intolerance. Butter, derived from dairy, is unsuitable for vegans and individuals with dairy allergies, potentially causing adverse reactions. Choosing olive oil supports dietary restrictions while adding a fruity, rich flavor profile to stews.
Regional Stew Variations and Preferred Fats
Regional stew variations heavily influence the choice between olive oil and butter as the preferred fat, with Mediterranean stews favoring olive oil for its rich monounsaturated fats and fruity aroma. In contrast, Northern European and American stews often rely on butter, prized for its creamy texture and saturated fat content that enhances hearty flavors. These fat preferences significantly impact the stew's overall taste profile and cultural authenticity.
Olive Oil vs Butter: Cost and Availability
Olive oil generally costs more than butter but offers greater availability in most grocery stores, especially in Mediterranean and health-conscious markets. Butter prices can fluctuate seasonally and regionally due to dairy supply constraints, whereas olive oil prices are influenced by olive harvest yields and import tariffs. For cooking stews, olive oil provides a longer shelf life and remains liquid at room temperature, making it a convenient fat choice despite its higher price.
Expert Tips for Swapping Olive Oil and Butter in Stews
Expert tips for swapping olive oil and butter in stews emphasize olive oil's higher smoke point and heart-healthy monounsaturated fats, making it ideal for browning meats and sauteing vegetables without burning. Butter contributes rich flavor and creaminess but has a lower smoke point and higher saturated fat content, requiring careful temperature control to avoid scorching. For optimal results, combine both fats by starting with olive oil for searing and finishing with butter to enhance depth and texture in the stew.
Olive Oil vs Butter for fat Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com