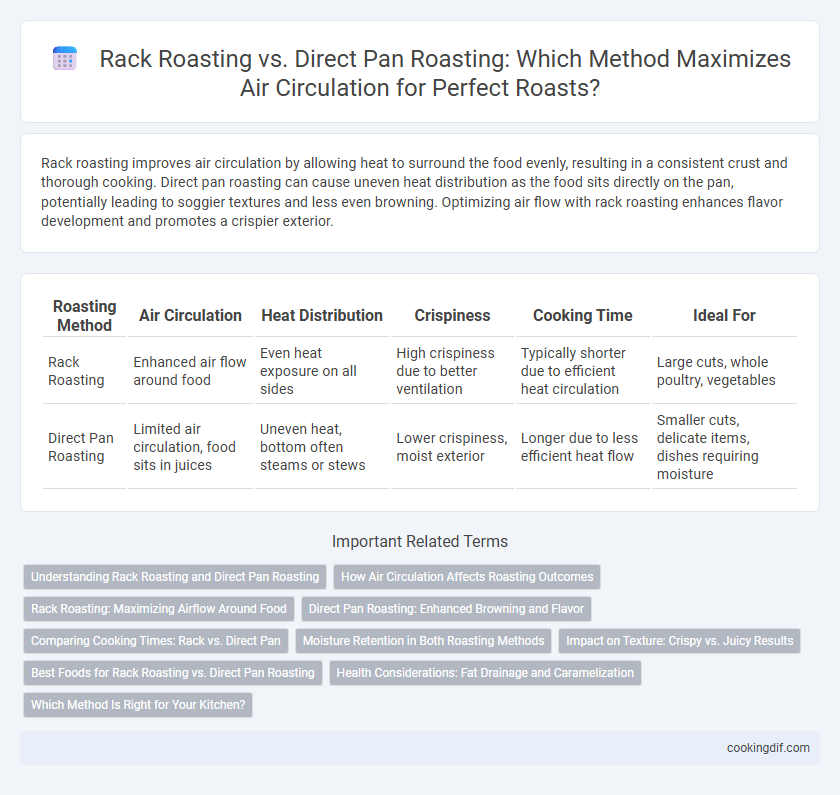
Rack roasting improves air circulation by allowing heat to surround the food evenly, resulting in a consistent crust and thorough cooking. Direct pan roasting can cause uneven heat distribution as the food sits directly on the pan, potentially leading to soggier textures and less even browning. Optimizing air flow with rack roasting enhances flavor development and promotes a crispier exterior.
Table of Comparison
| Roasting Method | Air Circulation | Heat Distribution | Crispiness | Cooking Time | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rack Roasting | Enhanced air flow around food | Even heat exposure on all sides | High crispiness due to better ventilation | Typically shorter due to efficient heat circulation | Large cuts, whole poultry, vegetables |
| Direct Pan Roasting | Limited air circulation, food sits in juices | Uneven heat, bottom often steams or stews | Lower crispiness, moist exterior | Longer due to less efficient heat flow | Smaller cuts, delicate items, dishes requiring moisture |
Understanding Rack Roasting and Direct Pan Roasting
Rack roasting enhances air circulation by allowing heat to surround the entire surface of the food, promoting even cooking and browning. Direct pan roasting limits airflow as the food sits directly on the pan, which can result in uneven heat distribution and potential moisture retention. Optimal roast quality depends on choosing rack roasting for crisp textures and direct pan roasting when a browned crust or sear is desired.
How Air Circulation Affects Roasting Outcomes
Rack roasting enhances air circulation by allowing heat to envelop the food evenly, leading to consistent browning and crisp textures. Direct pan roasting restricts airflow, which can cause uneven cooking and moisture trapping, resulting in less crispy surfaces. Air circulation is critical for Maillard reactions, impacting flavor development and achieving a uniform roast.
Rack Roasting: Maximizing Airflow Around Food
Rack roasting enhances air circulation by elevating food above the pan, allowing hot air to envelop all sides evenly, which promotes uniform cooking and browning. This method prevents moisture buildup under the food, resulting in a crispier texture and improved flavor development. Efficient airflow during rack roasting maximizes heat exposure, reducing cooking time and ensuring consistent roast quality.
Direct Pan Roasting: Enhanced Browning and Flavor
Direct pan roasting offers superior heat contact that promotes enhanced browning on the food's surface, intensifying Maillard reactions and deepening flavor complexity. The consistent heat distribution in direct pan roasting facilitates an even crust, locking in juices while creating a rich, caramelized exterior. This method's ability to maintain precise temperature control optimizes air circulation around the pan, improving overall roast quality and taste development.
Comparing Cooking Times: Rack vs. Direct Pan
Rack roasting enhances air circulation by elevating the food, resulting in more even heat distribution and generally shorter cooking times compared to direct pan roasting. Direct pan roasting traps heat and moisture underneath, often leading to longer cooking durations and uneven browning. Choosing rack roasting can improve overall efficiency and texture by promoting consistent heat exposure around the food.
Moisture Retention in Both Roasting Methods
Rack roasting enhances air circulation around the food, promoting even heat distribution while allowing excess moisture to escape, resulting in a crisper exterior but less moisture retention inside. Direct pan roasting limits airflow, trapping steam and retaining more moisture within the food, which creates a juicier texture but can reduce the crispness of the outer layer. Understanding the balance between airflow and moisture retention is essential for selecting the optimal roasting technique based on desired texture and flavor outcomes.
Impact on Texture: Crispy vs. Juicy Results
Rack roasting allows hot air to circulate evenly around the food, promoting a crispy exterior by rendering fat away from the surface. Direct pan roasting traps moisture beneath the food, resulting in juicier textures but less crispiness. The choice between rack and pan roasting directly influences the balance between a crunchy crust and tender interior in meats and vegetables.
Best Foods for Rack Roasting vs. Direct Pan Roasting
Rack roasting promotes even air circulation around the food, making it ideal for whole chickens, roasts, and vegetables that benefit from uniform browning and crisp textures. Direct pan roasting is better suited for foods releasing moisture or juices, such as fish fillets or smaller cuts of meat, as it allows the food to cook in its own drippings, enhancing flavor and tenderness. Proper selection between rack and pan roasting optimizes cooking efficiency and final dish quality based on moisture content and desired texture.
Health Considerations: Fat Drainage and Caramelization
Rack roasting promotes better air circulation around the meat, allowing excess fat to drain away and reducing grease accumulation, which supports healthier cooking by minimizing fat retention. Direct pan roasting traps fat beneath the meat, increasing the risk of reabsorbing rendered fat and potentially leading to higher calorie content and greasier texture. Enhanced caramelization occurs with improved airflow during rack roasting, resulting in more even browning and complex flavor development without excessive fat exposure.
Which Method Is Right for Your Kitchen?
Rack roasting allows for optimal air circulation around the food, promoting even cooking and browning due to heat exposure on all sides. Direct pan roasting limits airflow, causing the bottom to cook faster and potentially leading to uneven heat distribution. Choosing between rack and direct pan roasting depends on your kitchen's ventilation, desired crust texture, and ease of cleanup.
Rack Roasting vs Direct Pan Roasting for Air Circulation Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com