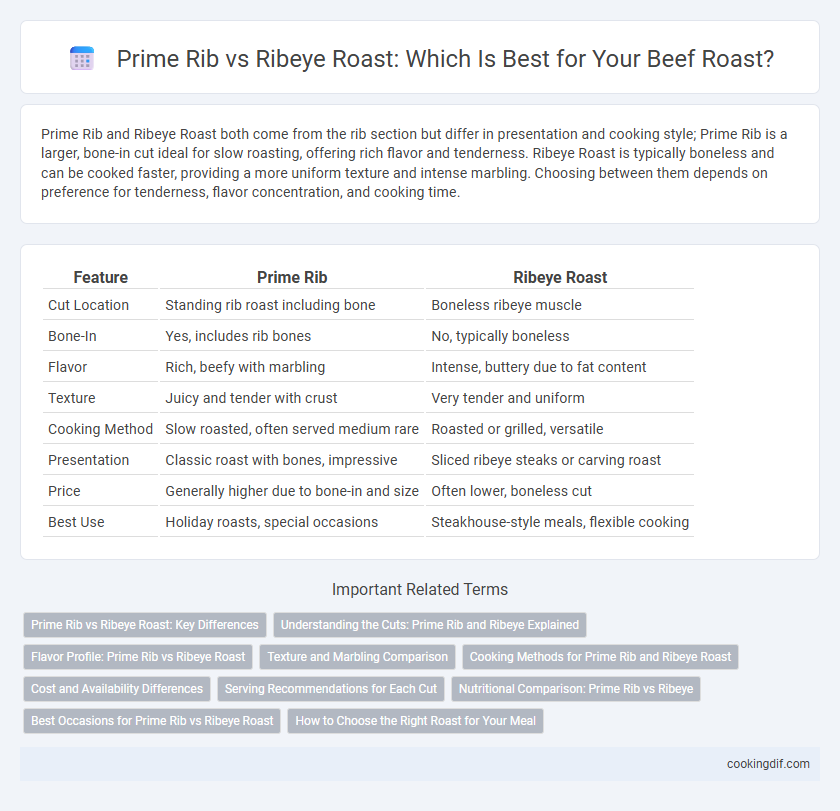
Prime Rib and Ribeye Roast both come from the rib section but differ in presentation and cooking style; Prime Rib is a larger, bone-in cut ideal for slow roasting, offering rich flavor and tenderness. Ribeye Roast is typically boneless and can be cooked faster, providing a more uniform texture and intense marbling. Choosing between them depends on preference for tenderness, flavor concentration, and cooking time.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Prime Rib | Ribeye Roast |
|---|---|---|
| Cut Location | Standing rib roast including bone | Boneless ribeye muscle |
| Bone-In | Yes, includes rib bones | No, typically boneless |
| Flavor | Rich, beefy with marbling | Intense, buttery due to fat content |
| Texture | Juicy and tender with crust | Very tender and uniform |
| Cooking Method | Slow roasted, often served medium rare | Roasted or grilled, versatile |
| Presentation | Classic roast with bones, impressive | Sliced ribeye steaks or carving roast |
| Price | Generally higher due to bone-in and size | Often lower, boneless cut |
| Best Use | Holiday roasts, special occasions | Steakhouse-style meals, flexible cooking |
Prime Rib vs Ribeye Roast: Key Differences
Prime Rib and Ribeye Roast originate from the same primal cut but differ in bone-in presentation, with Prime Rib typically roasted with the bone and Ribeye Roast boneless. Prime Rib offers a juicier, more flavorful experience due to the bone and marbling, while Ribeye Roast provides easier carving and uniform thickness. Choosing between them depends on preference for presentation and cooking style, as both deliver tender, rich beef roast results.
Understanding the Cuts: Prime Rib and Ribeye Explained
Prime Rib and Ribeye roast both come from the same section of the cow, specifically the rib primal, but differ in presentation and bone-in vs. boneless preparation. Prime Rib roast is a whole rib section, typically cooked with the bone in, which enhances flavor and moisture retention, while Ribeye roast is a boneless cut trimmed from the prime rib, offering easier carving and a slightly leaner profile. Understanding these distinctions helps in selecting the ideal beef roast for tenderness, juiciness, and preferred cooking method.
Flavor Profile: Prime Rib vs Ribeye Roast
Prime Rib offers a rich, juicy flavor with a tender, marbled texture that enhances its savory beefiness, ideal for a luxurious roast experience. Ribeye Roast, while similar due to its marbling and fat content, tends to have a slightly more intense, beef-forward taste with a crispier outer crust when roasted. Both cuts deliver exceptional flavor, but Prime Rib is often favored for its balance of tenderness and robust, buttery notes.
Texture and Marbling Comparison
Prime Rib offers a tender, juicy texture with abundant marbling that melts into the meat during roasting, enhancing its rich flavor and succulence. Ribeye Roast features a similar marbling level but tends to be denser and more uniform in texture, delivering a slightly firmer bite with concentrated beefy taste. Both cuts excel in marbling, yet prime rib is often preferred for its superior tenderness and moisture retention in slow roasting.
Cooking Methods for Prime Rib and Ribeye Roast
Prime rib is best cooked using slow roasting techniques at low temperatures to maintain its tenderness and juiciness, often finished with a high-heat sear to develop a flavorful crust. Ribeye roast, with its marbled fat, benefits from roasting at higher temperatures or reverse searing to render fat evenly and enhance rich beef flavors. Both cuts require resting after cooking to redistribute juices and achieve optimal texture and succulence.
Cost and Availability Differences
Prime rib typically commands a higher price due to its premium cut from the standing rib roast, featuring a balance of tenderness and marbling ideal for special occasions. Ribeye roast, often more readily available in grocery stores, provides a cost-effective alternative with rich flavor and less fat trim compared to prime rib. Availability varies regionally, with prime rib favored in upscale markets while ribeye roast remains accessible in both retail and wholesale outlets.
Serving Recommendations for Each Cut
Prime rib is best served medium-rare to medium to maintain its tender, juicy texture and rich flavor, often presented as an impressive centerpiece for special occasions. Ribeye roast, known for its marbling and robust beefy taste, is ideal when cooked medium to medium-well to enhance its savory crust and melt-in-your-mouth consistency. Both cuts pair excellently with horseradish sauce or au jus and benefit from resting before slicing to preserve moisture and tenderness.
Nutritional Comparison: Prime Rib vs Ribeye
Prime rib contains slightly higher fat content than ribeye roast, contributing to its richer flavor and increased calorie count. Ribeye roast offers a balanced profile with more protein per serving, making it a leaner option for those focused on muscle maintenance. Both cuts provide essential nutrients such as iron, zinc, and B vitamins, supporting overall health in beef roast selections.
Best Occasions for Prime Rib vs Ribeye Roast
Prime rib is best suited for special occasions and holiday feasts due to its rich marbling and impressive presentation. Ribeye roast, with its tender texture and uniform shape, is ideal for intimate gatherings and casual dinners. Choosing prime rib elevates celebratory meals, while ribeye roast offers a flavorful alternative for everyday roasting.
How to Choose the Right Roast for Your Meal
Prime Rib offers a tender, flavorful cut with a higher fat content, ideal for special occasions demanding rich, juicy slices with a crispy crust. Ribeye Roast, while similar, tends to be more marbled and slightly smaller, making it perfect for those seeking intense beef flavor and a more manageable portion size. Choose Prime Rib for an impressive centerpiece roast or Ribeye for a flavorful yet versatile option suitable for smaller gatherings.
Prime Rib vs Ribeye Roast for Beef Roast Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com