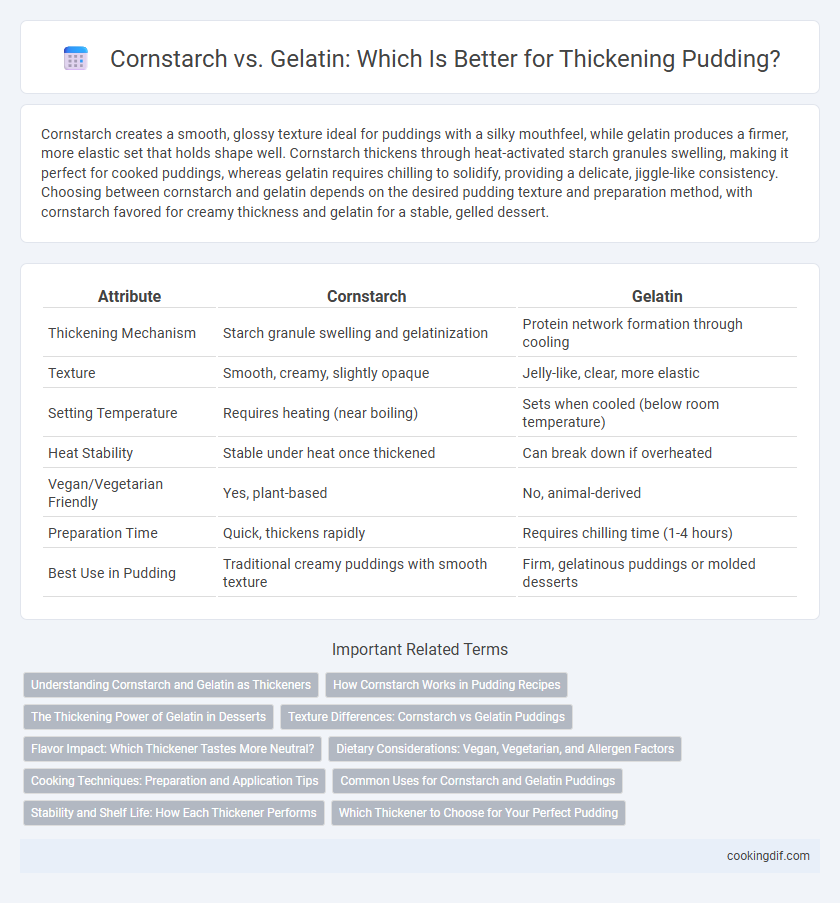
Cornstarch creates a smooth, glossy texture ideal for puddings with a silky mouthfeel, while gelatin produces a firmer, more elastic set that holds shape well. Cornstarch thickens through heat-activated starch granules swelling, making it perfect for cooked puddings, whereas gelatin requires chilling to solidify, providing a delicate, jiggle-like consistency. Choosing between cornstarch and gelatin depends on the desired pudding texture and preparation method, with cornstarch favored for creamy thickness and gelatin for a stable, gelled dessert.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Cornstarch | Gelatin |
|---|---|---|
| Thickening Mechanism | Starch granule swelling and gelatinization | Protein network formation through cooling |
| Texture | Smooth, creamy, slightly opaque | Jelly-like, clear, more elastic |
| Setting Temperature | Requires heating (near boiling) | Sets when cooled (below room temperature) |
| Heat Stability | Stable under heat once thickened | Can break down if overheated |
| Vegan/Vegetarian Friendly | Yes, plant-based | No, animal-derived |
| Preparation Time | Quick, thickens rapidly | Requires chilling time (1-4 hours) |
| Best Use in Pudding | Traditional creamy puddings with smooth texture | Firm, gelatinous puddings or molded desserts |
Understanding Cornstarch and Gelatin as Thickeners
Cornstarch and gelatin are both widely used thickeners in pudding, but they function differently at the molecular level. Cornstarch swells and gelatinizes when heated with liquid, creating a smooth, opaque texture ideal for creamy puddings, while gelatin sets as it cools, forming a clear, elastic gel perfect for molded or chilled desserts. Understanding these distinct thickening properties helps in choosing the right ingredient for desired pudding consistency and appearance.
How Cornstarch Works in Pudding Recipes
Cornstarch thickens pudding by absorbing water and swelling when heated, forming a smooth, gel-like consistency that stabilizes the mixture. Its starch molecules gelatinize at around 203degF (95degC), creating a creamy texture without altering the flavor. Unlike gelatin, cornstarch provides a plant-based, stable thickening agent suited for vegetarian and vegan pudding recipes.
The Thickening Power of Gelatin in Desserts
Gelatin provides a unique thickening power in desserts by forming a smooth, glossy gel that sets firmly at lower temperatures compared to cornstarch. Unlike cornstarch, which thickens through starch granule swelling and can result in a cloudy texture, gelatin creates a clear and elastic consistency ideal for delicate puddings and mousse. This protein-based thickener also stabilizes the structure, ensuring desserts maintain their shape and creamy mouthfeel.
Texture Differences: Cornstarch vs Gelatin Puddings
Cornstarch creates a creamy, smooth texture in puddings due to its ability to swell and gelatinize when heated, resulting in a dense and velvety consistency. Gelatin produces a firmer, more elastic set with a clear, slightly jiggly texture that melts softly on the palate. The choice between cornstarch and gelatin significantly affects the mouthfeel and structural integrity, with cornstarch offering a richer mouth-coating sensation and gelatin providing a lighter, more delicate gel.
Flavor Impact: Which Thickener Tastes More Neutral?
Cornstarch provides a neutral taste that allows the pudding's original flavors to shine without alteration, making it ideal for delicate or fruit-based desserts. Gelatin can impart a slightly savory taste and a unique texture, which may influence the overall flavor profile of the pudding. For recipes prioritizing flavor purity, cornstarch is generally preferred as a thickening agent due to its minimal impact on taste.
Dietary Considerations: Vegan, Vegetarian, and Allergen Factors
Cornstarch is a plant-based thickening agent suitable for vegan and vegetarian diets, making it free from animal-derived ingredients and common allergens. Gelatin, derived from animal collagen, is unsuitable for vegans and vegetarians and may trigger allergies in sensitive individuals. Choosing cornstarch ensures a neutral allergen profile and aligns with dietary restrictions while providing an effective pudding thickener.
Cooking Techniques: Preparation and Application Tips
Cornstarch provides a smooth, glossy texture by thickening through gelatinization when heated with liquid, requiring constant stirring and careful temperature control to avoid clumping or becoming too thick. Gelatin creates a gel-like consistency by setting as it cools, ideal for no-cook or chilled puddings, but must be dissolved in cold water before being heated gently to prevent losing its gelling properties. For optimal pudding texture, use cornstarch when a creamy, stovetop thickening method is desired, and gelatin for a firmer, set pudding that holds shape after refrigeration.
Common Uses for Cornstarch and Gelatin Puddings
Cornstarch is commonly used in puddings for its ability to create a smooth, creamy texture and is ideal for stovetop cooking where quick thickening is required. Gelatin, on the other hand, is preferred for refrigerated or molded puddings due to its unique gelling properties that provide a firm, jiggly consistency. Both thickeners serve distinct purposes: cornstarch for creamy, spoonable desserts and gelatin for structured, sliceable or shaped puddings.
Stability and Shelf Life: How Each Thickener Performs
Cornstarch provides a stable gel structure in puddings but tends to weep or separate over extended storage, limiting shelf life. Gelatin creates a more elastic and resilient texture, maintaining stability and preventing syneresis, which enhances pudding shelf life significantly. For prolonged freshness and texture retention, gelatin outperforms cornstarch as a thickening agent in pudding recipes.
Which Thickener to Choose for Your Perfect Pudding
Cornstarch creates a smooth, creamy pudding with a slightly opaque finish and a mild, neutral taste, perfect for traditional custard-style desserts. Gelatin produces a clear, firm, and jiggly pudding with a delicate mouthfeel, ideal for molded or layered desserts requiring a more stable set. Choose cornstarch for classic, rich textures and gelatin for a lighter, more elastic consistency in your perfect pudding.
Cornstarch vs gelatin for thickening Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com