Viennoiserie and patisserie are two distinct categories within the world of pastry, each offering unique textures and flavors. Viennoiserie includes yeast-leavened baked goods like croissants and brioche, characterized by their flaky, airy structure and buttery taste. In contrast, patisserie encompasses a wider variety of pastries such as eclairs, tarts, and mille-feuille, often focusing on intricate techniques and rich, creamy fillings.
Table of Comparison
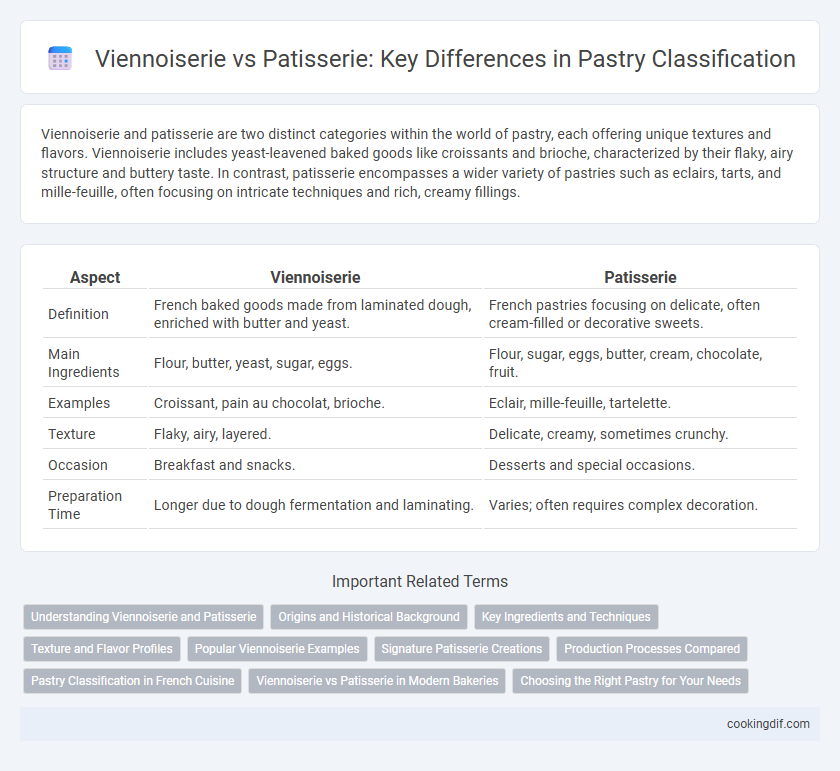
| Aspect | Viennoiserie | Patisserie |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | French baked goods made from laminated dough, enriched with butter and yeast. | French pastries focusing on delicate, often cream-filled or decorative sweets. |
| Main Ingredients | Flour, butter, yeast, sugar, eggs. | Flour, sugar, eggs, butter, cream, chocolate, fruit. |
| Examples | Croissant, pain au chocolat, brioche. | Eclair, mille-feuille, tartelette. |
| Texture | Flaky, airy, layered. | Delicate, creamy, sometimes crunchy. |
| Occasion | Breakfast and snacks. | Desserts and special occasions. |
| Preparation Time | Longer due to dough fermentation and laminating. | Varies; often requires complex decoration. |
Understanding Viennoiserie and Patisserie
Viennoiserie and patisserie represent two distinct categories within French pastry, each defined by unique ingredients and techniques. Viennoiserie, such as croissants and brioche, involves laminated dough enriched with butter and yeast, resulting in a flaky and airy texture. Patisserie encompasses delicate, often non-laminated creations like eclairs and tarts, highlighting intricate decoration and diverse fillings for refined sweetness.
Origins and Historical Background
Viennoiserie originated in Vienna during the 19th century, characterized by its enriched doughs such as croissants and brioche, which blend bread and pastry techniques. Patisserie, rooted in French baking traditions dating back to the Middle Ages, emphasizes elaborate pastries like tarts, eclairs, and choux-based desserts crafted primarily from pate a choux and puff pastry. Both categories reflect unique culinary heritages that shaped European pastry arts through distinct methods and ingredient profiles.
Key Ingredients and Techniques
Viennoiserie relies on laminated dough enriched with butter, sugar, and eggs, creating a flaky, buttery texture through repeated folding and rolling techniques. Patisserie centers on a broader range of pastries using ingredients such as flour, butter, sugar, and eggs, often incorporating creams, custards, and fruit fillings with techniques like baking, glazing, and piping. Key distinctions lie in Viennoiserie's emphasis on yeast-leavened dough and lamination versus patisserie's diverse methods and components in crafting delicate desserts.
Texture and Flavor Profiles
Viennoiserie features laminated doughs like croissants and pain au chocolat, creating a flaky, buttery texture with a rich, slightly sweet flavor enhanced by yeast fermentation. Patisserie encompasses a broader range of pastries including tarts, eclairs, and mousses, characterized by diverse textures from crisp to creamy and complex flavor profiles often combining fruit, chocolate, and custard. The distinction lies in Viennoiserie's emphasis on layered, airy dough contrasted with patisserie's varied use of dough and fillings delivering a balance of sweetness and richness.
Popular Viennoiserie Examples
Popular Viennoiserie examples include croissants, pain au chocolat, and brioche, distinguished by their flaky, buttery layers created through laminated dough techniques. Unlike patisserie, which emphasizes intricate cakes and desserts like eclairs and macarons, viennoiserie offers enriched bread varieties often enjoyed for breakfast or snacks. The use of yeast and butter differentiates viennoiserie pastries, giving them their signature airy texture and golden crust.
Signature Patisserie Creations
Signature patisserie creations emphasize delicate artistry and refined techniques, often featuring rich fillings, intricate designs, and a balance of sweetness and texture. Viennoiserie includes buttery, laminated dough pastries like croissants and pain au chocolat, characterized by their flaky layers and golden crusts, serving as breakfast staples. Both categories showcase unique traits within pastry classification, with patisserie highlighting confectionary finesse and viennoiserie delivering buttery, layered indulgence.
Production Processes Compared
Viennoiserie production involves yeast-leavened dough enriched with butter, eggs, and milk, creating a light, flaky texture through lamination and proofing, exemplified by croissants and brioche. Patisserie utilizes a broader range of techniques, often relying on shortcrust or sponge pastry foundations with fillings, creams, and delicate decorations, as seen in eclairs and tarts. The key distinction is Viennoiserie's fermentation and layering process versus Patisserie's emphasis on precise baking and intricate assembly methods.
Pastry Classification in French Cuisine
French pastry classification distinguishes Viennoiserie and Patisserie based on ingredients and preparation techniques. Viennoiserie includes enriched dough pastries like croissants and brioche, characterized by yeast-leavening and buttery layers, while Patisserie refers to a broader category of sweet pastries and desserts made from pate a choux, pate sablee, or pate sucree doughs. This classification reflects the diversity of French baking traditions, emphasizing texture, flavor, and culinary purpose.
Viennoiserie vs Patisserie in Modern Bakeries
Viennoiserie and patisserie represent two distinct categories of pastries in modern bakeries, with viennoiserie characterized by enriched doughs like croissants and brioche that emphasize flakiness and buttery layers. Patisserie focuses on more intricate, often cream-filled or fruit-based desserts such as eclairs, tarts, and macarons, highlighting delicate craftsmanship and decorative presentation. Contemporary bakeries prioritize viennoiserie for breakfast offerings and quick indulgences, while patisserie remains central to special occasion desserts and luxury pastry selections.
Choosing the Right Pastry for Your Needs
Viennoiserie includes buttery, flaky pastries like croissants and brioche, ideal for breakfast or light snacks due to their rich texture and subtle sweetness. Patisserie offers a broader range of delicate, often intricately decorated desserts such as eclairs, tarts, and macarons, perfect for special occasions or indulgent treats. Selecting between Viennoiserie and patisserie depends on whether you prefer a simple, comforting pastry or an elaborate, refined dessert.
Viennoiserie vs patisserie for pastry classification Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com