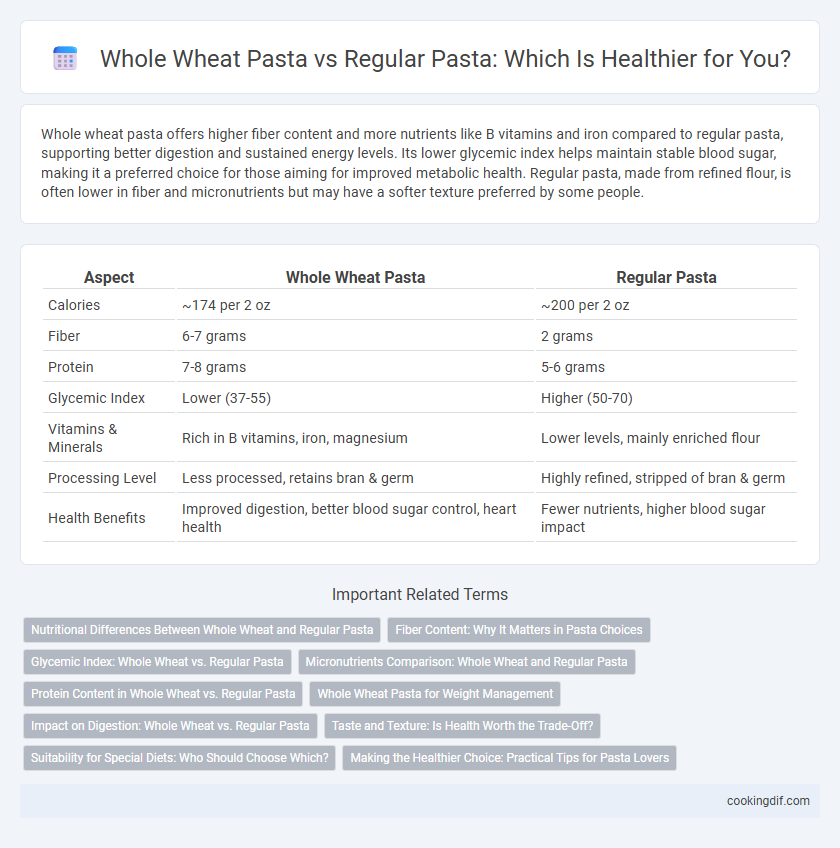
Whole wheat pasta offers higher fiber content and more nutrients like B vitamins and iron compared to regular pasta, supporting better digestion and sustained energy levels. Its lower glycemic index helps maintain stable blood sugar, making it a preferred choice for those aiming for improved metabolic health. Regular pasta, made from refined flour, is often lower in fiber and micronutrients but may have a softer texture preferred by some people.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Whole Wheat Pasta | Regular Pasta |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | ~174 per 2 oz | ~200 per 2 oz |
| Fiber | 6-7 grams | 2 grams |
| Protein | 7-8 grams | 5-6 grams |
| Glycemic Index | Lower (37-55) | Higher (50-70) |
| Vitamins & Minerals | Rich in B vitamins, iron, magnesium | Lower levels, mainly enriched flour |
| Processing Level | Less processed, retains bran & germ | Highly refined, stripped of bran & germ |
| Health Benefits | Improved digestion, better blood sugar control, heart health | Fewer nutrients, higher blood sugar impact |
Nutritional Differences Between Whole Wheat and Regular Pasta
Whole wheat pasta contains higher fiber content, approximately 6-8 grams per serving, compared to regular pasta's 2-3 grams, promoting better digestive health. It also offers more essential nutrients such as magnesium, zinc, and B vitamins, which are significantly reduced in refined white pasta. The lower glycemic index of whole wheat pasta contributes to slower blood sugar spikes, making it a preferable option for blood sugar management and sustained energy levels.
Fiber Content: Why It Matters in Pasta Choices
Whole wheat pasta contains significantly higher dietary fiber compared to regular pasta, often providing around 6-7 grams of fiber per serving versus 2 grams in refined pasta. High fiber content aids digestion, promotes satiety, and helps regulate blood sugar levels, making whole wheat pasta a healthier option for weight management and cardiovascular health. Choosing whole wheat pasta supports sustained energy release and improved gut health due to its rich fiber profile.
Glycemic Index: Whole Wheat vs. Regular Pasta
Whole wheat pasta has a significantly lower glycemic index (GI) compared to regular pasta, typically ranging from 37 to 66 versus 49 to 65 for regular pasta. This lower GI helps in slower digestion and gradual blood sugar release, benefiting individuals managing diabetes or seeking sustained energy. Choosing whole wheat pasta supports better glycemic control and reduces the risk of insulin spikes associated with high-GI foods.
Micronutrients Comparison: Whole Wheat and Regular Pasta
Whole wheat pasta provides significantly higher levels of micronutrients such as magnesium, zinc, and iron compared to regular pasta, thanks to the retention of the bran and germ during processing. Regular pasta, typically made from refined flour, offers fewer vitamins and minerals but may contain added folic acid to compensate for nutrient loss. Choosing whole wheat pasta supports better micronutrient intake essential for metabolic and immune functions.
Protein Content in Whole Wheat vs. Regular Pasta
Whole wheat pasta contains approximately 7-8 grams of protein per 56-gram serving, compared to regular pasta which provides about 5-6 grams for the same portion size. The higher protein content in whole wheat pasta supports muscle repair and growth while also offering more dietary fiber and essential nutrients. Choosing whole wheat pasta enhances nutritional intake, making it a preferable option for individuals focused on increased protein consumption and overall health benefits.
Whole Wheat Pasta for Weight Management
Whole wheat pasta contains higher fiber content and complex carbohydrates compared to regular pasta, which helps promote satiety and stabilize blood sugar levels, aiding weight management. The increased fiber in whole wheat pasta supports digestive health and reduces overall calorie intake by curbing hunger. Choosing whole wheat pasta over regular pasta can enhance metabolic rate and facilitate fat loss due to its lower glycemic index and nutrient density.
Impact on Digestion: Whole Wheat vs. Regular Pasta
Whole wheat pasta contains higher dietary fiber compared to regular pasta, which promotes better digestion by supporting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation. The increased fiber content in whole wheat pasta also aids in regulating blood sugar levels and improving gut health through enhanced microbiota activity. Regular pasta, made from refined flour, lacks these digestive benefits due to its lower fiber and nutrient content.
Taste and Texture: Is Health Worth the Trade-Off?
Whole wheat pasta offers a nuttier, denser texture compared to the smoother, more neutral taste of regular pasta, which some may find less palatable. Nutritionally, whole wheat pasta delivers higher fiber and micronutrients, supporting digestive health and sustained energy release. Choosing whole wheat pasta balances flavor and health benefits, making it a worthwhile option for those prioritizing nutrition without sacrificing acceptable taste and texture.
Suitability for Special Diets: Who Should Choose Which?
Whole wheat pasta offers higher fiber and nutrient content, making it ideal for individuals seeking better blood sugar control or digestive health, such as those with diabetes or IBS. Regular pasta, typically lower in fiber and protein, may be preferred by those with sensitive digestive systems or struggling with certain grain intolerances. People following specialized diets like gluten-free or low-carb should consider alternative pastas to meet their unique dietary requirements.
Making the Healthier Choice: Practical Tips for Pasta Lovers
Whole wheat pasta contains higher dietary fiber, essential vitamins, and minerals compared to regular pasta, supporting better digestion and sustained energy levels. Opting for whole wheat varieties can aid in blood sugar regulation and weight management due to their lower glycemic index. Incorporate whole wheat pasta gradually into meals by pairing it with nutrient-rich vegetables and lean proteins to enhance overall nutritional value while maintaining familiar flavors.
Whole wheat pasta vs regular pasta for health preference Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com