Bronze-cut pasta has a rougher, porous surface that allows sauces to cling better, enhancing the overall flavor and texture of the dish. Teflon-cut pasta features a smooth, slick finish that cooks faster but offers less sauce adherence. Choosing bronze-cut noodles is ideal for hearty, rich sauces, while teflon-cut works well with lighter preparations.
Table of Comparison
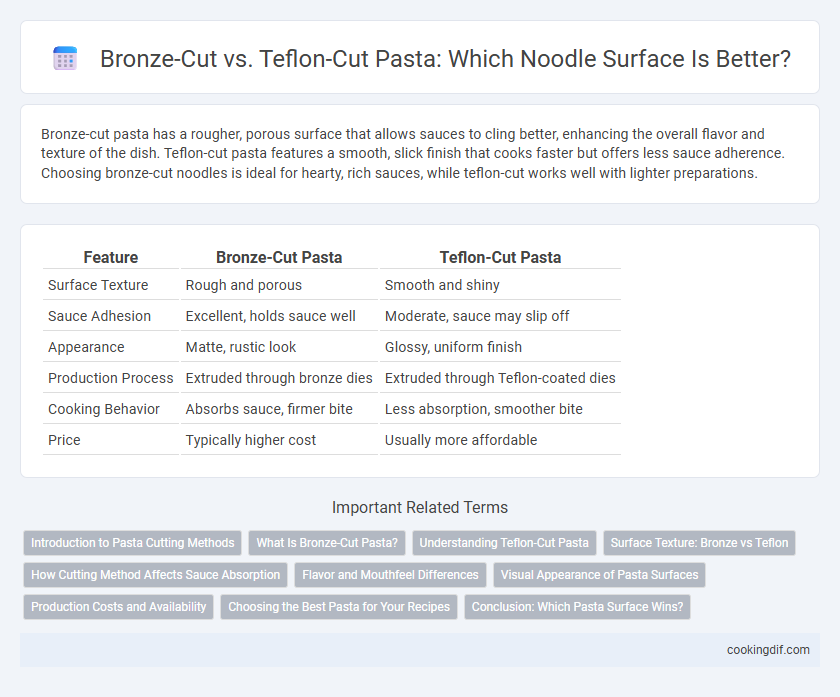
| Feature | Bronze-Cut Pasta | Teflon-Cut Pasta |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Texture | Rough and porous | Smooth and shiny |
| Sauce Adhesion | Excellent, holds sauce well | Moderate, sauce may slip off |
| Appearance | Matte, rustic look | Glossy, uniform finish |
| Production Process | Extruded through bronze dies | Extruded through Teflon-coated dies |
| Cooking Behavior | Absorbs sauce, firmer bite | Less absorption, smoother bite |
| Price | Typically higher cost | Usually more affordable |
Introduction to Pasta Cutting Methods
Bronze-cut pasta features a rough, porous surface that enhances sauce adhesion, providing a traditional texture preferred in artisanal pasta-making. Teflon-cut pasta, created with non-stick molds, yields a smoother surface that cooks faster but holds less sauce, favoring mass production. Understanding these cutting methods is essential for selecting pasta that matches culinary techniques and desired mouthfeel.
What Is Bronze-Cut Pasta?
Bronze-cut pasta is made by extruding dough through bronze dies, creating a rough and porous surface that helps sauces cling better for enhanced flavor absorption. The coarse texture of bronze-cut noodles contrasts with the smooth, slippery finish of teflon-cut pasta, resulting in a more authentic and textured eating experience. Artisanal pasta makers often prefer bronze-cut methods to preserve traditional quality and improve sauce adherence.
Understanding Teflon-Cut Pasta
Teflon-cut pasta features a smooth surface achieved by using Teflon-coated dies, which reduces dough adhesion during extrusion. This results in noodles with a sleek texture that cooks faster and absorbs less sauce compared to bronze-cut pasta. Its non-porous finish offers a delicate bite but may lack the sauce-gripping ability preferred in traditional Italian cooking.
Surface Texture: Bronze vs Teflon
Bronze-cut pasta features a rough, porous surface that holds sauces better, enhancing flavor absorption and creating a more authentic Italian texture. Teflon-cut pasta has a smooth, slippery surface, resulting in a firmer bite but less sauce adherence. The choice between bronze and Teflon cutting significantly affects the noodle's ability to retain sauce and overall mouthfeel.
How Cutting Method Affects Sauce Absorption
Bronze-cut pasta features a rougher, porous surface that enhances sauce adhesion by allowing sauces to cling better, resulting in a more flavorful bite. Teflon-cut pasta, with its smooth and polished finish, tends to repel sauces, causing them to slide off and leading to less sauce absorption. The microtexture differences between bronze-cut and Teflon-cut noodles critically influence the overall pasta dish by affecting how well the sauce integrates with each strand.
Flavor and Mouthfeel Differences
Bronze-cut pasta features a rough, porous surface that better retains sauces, enhancing flavor absorption and delivering a more authentic, hearty mouthfeel. Teflon-cut pasta has a smooth, polished texture that produces a silkier bite but tends to hold less sauce, resulting in a milder taste profile. Chefs often prefer bronze-cut pasta for its superior ability to balance robust flavors and provide a satisfying, chewy texture.
Visual Appearance of Pasta Surfaces
Bronze-cut pasta features a rough, porous surface that enhances sauce adhesion and displays a traditional, artisanal appearance with a matte finish. Teflon-cut pasta, on the other hand, has a smooth, glossy surface due to its polished extrusion process, resulting in a uniform and sleek visual texture. The distinct textures between bronze-cut and Teflon-cut noodles influence not only sauce absorption but also the aesthetic appeal on the plate.
Production Costs and Availability
Bronze-cut pasta production involves pressing dough through coarse bronze dies, creating a rough surface that enhances sauce adhesion but increases manufacturing costs due to slower extrusion and higher wear on equipment. Teflon-cut pasta uses smooth Teflon-coated dies that speed up production and reduce maintenance expenses, resulting in lower overall costs and greater availability in mass markets. The choice between bronze-cut and Teflon-cut directly impacts pricing strategies and supply chain efficiency within the pasta industry.
Choosing the Best Pasta for Your Recipes
Bronze-cut pasta features a rougher surface that clings better to sauces, enhancing flavor absorption and texture in traditional Italian dishes. Teflon-cut pasta offers a smoother finish, resulting in a firmer bite and a polished appearance ideal for delicate, light sauces. Choosing the best pasta depends on recipe type and desired sauce adherence, with bronze-cut pasta preferred for hearty ragus and Teflon-cut suited for simple, subtle dressings.
Conclusion: Which Pasta Surface Wins?
Bronze-cut pasta features a rougher, porous surface that holds sauces better, enhancing flavor absorption and texture. Teflon-cut pasta has a smoother finish, resulting in a slicker surface but less sauce adherence. For authentic taste and superior sauce clinging, bronze-cut pasta consistently outperforms Teflon-cut varieties.
Bronze-cut vs Teflon-cut for noodle surface Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com