Adding cheese to an omelette enhances its creamy texture and rich flavor, making the dish more indulgent and satisfying. Without cheese, the omelette has a lighter, more delicate taste that allows other ingredients like vegetables or herbs to shine. Choosing cheese or no cheese depends on dietary preferences and desired flavor balance, with cheese providing added protein and calcium.
Table of Comparison
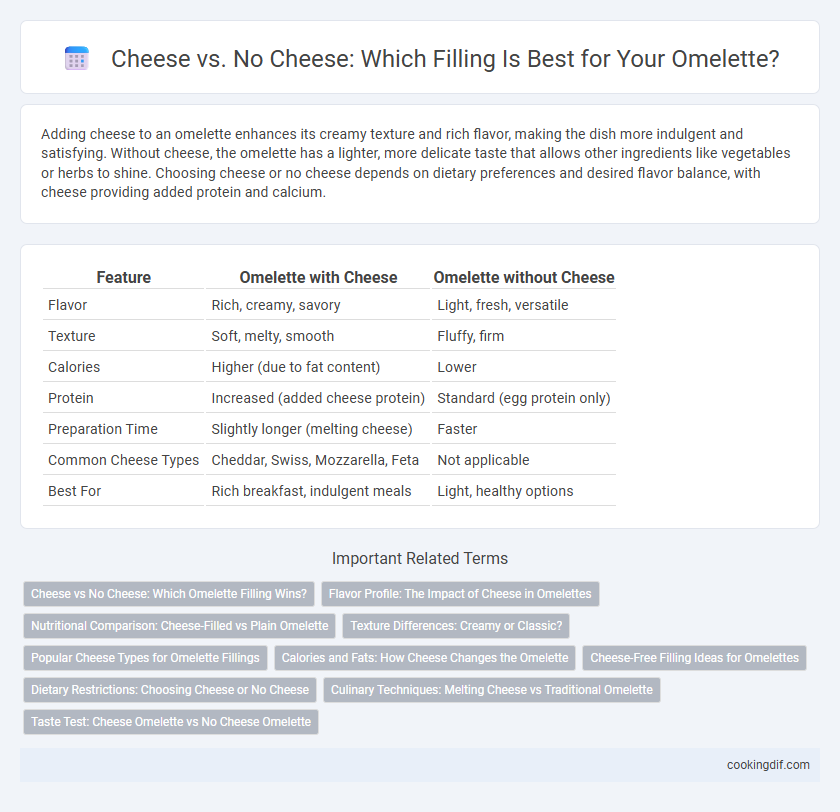
| Feature | Omelette with Cheese | Omelette without Cheese |
|---|---|---|
| Flavor | Rich, creamy, savory | Light, fresh, versatile |
| Texture | Soft, melty, smooth | Fluffy, firm |
| Calories | Higher (due to fat content) | Lower |
| Protein | Increased (added cheese protein) | Standard (egg protein only) |
| Preparation Time | Slightly longer (melting cheese) | Faster |
| Common Cheese Types | Cheddar, Swiss, Mozzarella, Feta | Not applicable |
| Best For | Rich breakfast, indulgent meals | Light, healthy options |
Cheese vs No Cheese: Which Omelette Filling Wins?
Choosing cheese as an omelette filling enhances flavor with creamy, melty texture that complements eggs, while also adding protein and calcium. Omelettes without cheese emphasize other fillings like vegetables or meats, allowing fresher, lighter taste profiles and reduced calories. Ultimately, cheese-filled omelettes appeal to those seeking richness and indulgence, whereas no-cheese options cater to health-conscious or dairy-free preferences.
Flavor Profile: The Impact of Cheese in Omelettes
Cheese enhances omelettes with a rich, creamy texture and a savory, slightly tangy flavor that complements eggs, elevating the overall taste experience. Without cheese, the omelette relies on the natural, delicate flavor of eggs and other fillings, resulting in a lighter and more subtly flavored dish. Popular cheese varieties like cheddar, Swiss, and feta contribute distinct flavor notes, ranging from sharp to mild, which transform the omelette into a more indulgent meal.
Nutritional Comparison: Cheese-Filled vs Plain Omelette
Cheese-filled omelettes offer higher protein and calcium levels compared to plain omelettes, enhancing bone health and muscle repair. Plain omelettes are lower in calories and saturated fat, making them suitable for weight management and heart-conscious diets. Choosing between cheese or no cheese depends on balancing nutrient intake with dietary goals like calorie control or increased calcium consumption.
Texture Differences: Creamy or Classic?
Cheese-filled omelettes offer a creamy, rich texture that melts seamlessly into the eggs, creating a smooth and indulgent mouthfeel. In contrast, omelettes without cheese maintain a classic, firmer texture that highlights the natural fluffiness of the eggs and any other fresh fillings. Choosing between cheese or no cheese significantly alters the overall texture, with cheese adding moisture and softness, while no cheese preserves a drier, more structured bite.
Popular Cheese Types for Omelette Fillings
Popular cheese types for omelette fillings include cheddar, mozzarella, and Swiss, each offering distinct flavors and creamy textures that enhance the egg's taste. Cheddar provides a sharp, tangy kick, mozzarella contributes a mild and stretchy quality, while Swiss adds a nutty and slightly sweet profile. Choosing cheese influences the overall richness and meltability of the omelette, making it a favored option compared to no cheese fillings.
Calories and Fats: How Cheese Changes the Omelette
Adding cheese to an omelette significantly increases its calorie content, often by 50 to 100 calories per serving, depending on the type and amount of cheese used. The fat content also rises notably, with cheese contributing both saturated and unsaturated fats that impact the overall nutritional profile. Choosing no cheese keeps the omelette lower in calories and fats, making it a lighter option for those monitoring their intake.
Cheese-Free Filling Ideas for Omelettes
Cheese-free omelette fillings offer vibrant flavors and nutritional diversity, incorporating ingredients like spinach, mushrooms, bell peppers, and fresh herbs to keep the dish light and wholesome. Nutrient-rich vegetables such as tomatoes and zucchini provide texture and moisture, while protein options like smoked salmon or tofu chunks add satisfying substance without dairy. These alternatives cater to lactose-intolerant individuals and those seeking lower-fat omelette variants without compromising taste or visual appeal.
Dietary Restrictions: Choosing Cheese or No Cheese
Selecting cheese for an omelette filling can enhance flavor and provide extra protein and calcium but may not suit individuals with lactose intolerance or dairy allergies. Opting for no cheese allows for a more versatile, lower-fat, and dairy-free option, accommodating vegan diets and those with dietary restrictions. Careful consideration of dietary needs ensures the omelette remains both delicious and suitable for varied nutritional requirements.
Culinary Techniques: Melting Cheese vs Traditional Omelette
Melting cheese in an omelette requires precise temperature control to achieve a creamy texture without curdling, enhancing flavor complexity and mouthfeel. Traditional omelettes without cheese rely on perfectly cooked eggs folded to maintain a tender, fluffy interior, showcasing the pure egg flavor. The culinary technique differences highlight how cheese influences moisture retention and structural integrity compared to classic preparations.
Taste Test: Cheese Omelette vs No Cheese Omelette
Cheese omelettes deliver a rich, creamy flavor and a gooey texture that enhances the overall taste, appealing to those who enjoy savory and indulgent fillings. No cheese omelettes offer a lighter, more delicate flavor, allowing the eggs and other ingredients like vegetables or herbs to stand out without the added fat or saltiness of cheese. Taste tests often reveal a preference for cheese omelettes due to their satisfying mouthfeel and depth of flavor, though no cheese versions attract those seeking a fresher, cleaner taste profile.
Cheese vs No cheese for filling Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com