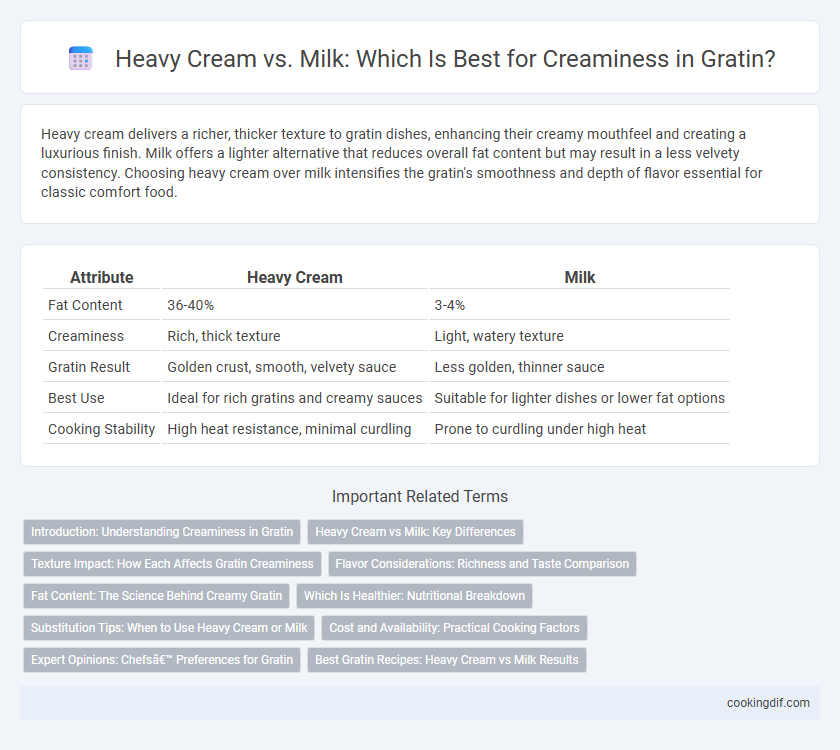
Heavy cream delivers a richer, thicker texture to gratin dishes, enhancing their creamy mouthfeel and creating a luxurious finish. Milk offers a lighter alternative that reduces overall fat content but may result in a less velvety consistency. Choosing heavy cream over milk intensifies the gratin's smoothness and depth of flavor essential for classic comfort food.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Heavy Cream | Milk |
|---|---|---|
| Fat Content | 36-40% | 3-4% |
| Creaminess | Rich, thick texture | Light, watery texture |
| Gratin Result | Golden crust, smooth, velvety sauce | Less golden, thinner sauce |
| Best Use | Ideal for rich gratins and creamy sauces | Suitable for lighter dishes or lower fat options |
| Cooking Stability | High heat resistance, minimal curdling | Prone to curdling under high heat |
Introduction: Understanding Creaminess in Gratin
Heavy cream provides a richer, more velvety texture in gratin due to its higher fat content, typically around 36-40%, compared to milk, which usually contains 3-4% fat. The increased fat in heavy cream emulsifies with the cheese and other ingredients, creating a thick, luscious sauce that enhances the gratin's creaminess. Milk results in a lighter texture but often requires additional thickening agents, making heavy cream the preferred choice for achieving optimal creaminess in gratin dishes.
Heavy Cream vs Milk: Key Differences
Heavy cream contains approximately 36-40% fat, providing a rich, velvety texture essential for achieving the perfect gratin's creamy consistency, whereas milk typically contains around 3-4% fat, resulting in a thinner, less luscious sauce. The higher fat content in heavy cream helps create a smooth, luxurious mouthfeel and prevents curdling during baking, which is crucial for the gratin's signature golden crust. Milk's lower fat makes it a lighter alternative but often requires additional thickening agents to match the creaminess that heavy cream naturally delivers.
Texture Impact: How Each Affects Gratin Creaminess
Heavy cream enhances gratin texture by contributing rich, velvety smoothness and a thicker consistency, resulting in a luxurious, creamy mouthfeel. Milk produces a lighter, less dense texture, making the gratin less indulgent but more delicate and slightly more fluid. The higher fat content in heavy cream creates a stable, luscious sauce that clings to ingredients better than milk, significantly intensifying overall creaminess.
Flavor Considerations: Richness and Taste Comparison
Heavy cream delivers a richer, more indulgent flavor and a velvety texture that enhances the gratin's overall creaminess, making it ideal for a deeply savory and luxurious dish. Milk provides a lighter, milder taste with less fat content, resulting in a subtler flavor and softer consistency that highlights other ingredients without overpowering them. Choosing heavy cream intensifies richness and caramelization, while milk creates a delicate balance perfect for a less decadent gratin.
Fat Content: The Science Behind Creamy Gratin
Heavy cream contains approximately 36-40% fat, significantly higher than whole milk's 3.5-4%, which directly impacts the rich, velvety texture of gratin dishes. The elevated fat content in heavy cream enhances emulsification and prevents curdling during baking, resulting in a luxurious, creamy finish that milk cannot replicate. Choosing heavy cream over milk optimizes the gratin's mouthfeel and golden crust development through superior browning and moisture retention.
Which Is Healthier: Nutritional Breakdown
Heavy cream contains about 52 grams of fat and 340 calories per cup, making it significantly higher in fat and calories compared to milk, which has roughly 8 grams of fat and 150 calories per cup. Milk provides essential nutrients like calcium, vitamin D, and protein with lower saturated fat content, benefiting heart health and weight management. Choosing milk over heavy cream in gratin recipes reduces calorie density and saturated fat intake, promoting a healthier nutritional profile while maintaining some creaminess.
Substitution Tips: When to Use Heavy Cream or Milk
Heavy cream delivers rich, luscious texture ideal for gratins requiring intense creaminess and a golden, bubbly top, while milk offers a lighter option suited for those seeking a less dense dish. Use heavy cream when aiming for a decadent, velvety consistency that holds well during baking; substitute with milk in recipes favoring a milder taste and reduced fat content, adjusting quantities to maintain moisture levels. For optimal results, combine milk with a small amount of butter as a practical substitute to mimic heavy cream's richness without overpowering the dish.
Cost and Availability: Practical Cooking Factors
Heavy cream provides richer texture and superior creaminess in gratin but comes at a higher cost and can be less available in some regions, especially outside major supermarkets. Milk offers a more affordable and widely accessible alternative, though it results in a lighter, less luscious dish due to its lower fat content. For budget-conscious cooks or those facing limited ingredient options, milk remains a practical choice without significantly compromising the essence of a gratin.
Expert Opinions: Chefs’ Preferences for Gratin
Chefs prefer heavy cream over milk for gratin due to its higher fat content, which creates a richer, creamier texture essential for the dish's signature indulgence. Heavy cream's ability to thicken without curdling ensures a smooth, luxurious sauce that envelops the ingredients perfectly. Milk, while lighter and less calorie-dense, often results in a thinner, less decadent gratin texture that some experts consider less authentic.
Best Gratin Recipes: Heavy Cream vs Milk Results
Heavy cream enhances gratin dishes by providing rich texture and a velvety mouthfeel, contributing to a superior creamy consistency compared to milk. Milk can result in a lighter gratin with less fat, which may reduce the overall creaminess but allows the other flavors to shine through more distinctly. In best gratin recipes, heavy cream is preferred for achieving a luxurious, thick sauce, while milk offers a healthier, subtler alternative without compromising the dish's fundamental qualities.
Heavy cream vs Milk for creaminess Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com