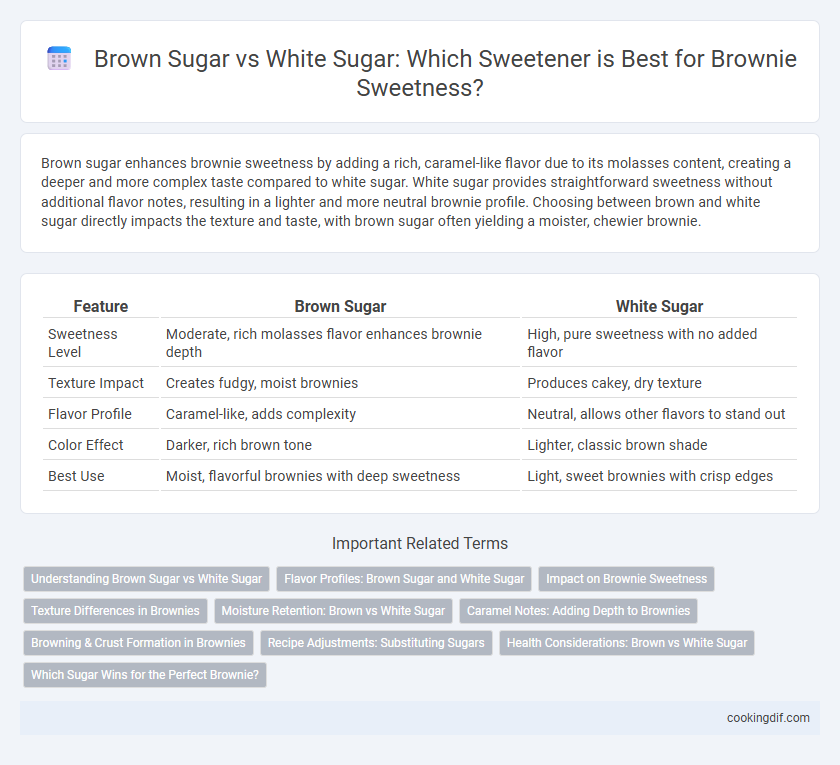
Brown sugar enhances brownie sweetness by adding a rich, caramel-like flavor due to its molasses content, creating a deeper and more complex taste compared to white sugar. White sugar provides straightforward sweetness without additional flavor notes, resulting in a lighter and more neutral brownie profile. Choosing between brown and white sugar directly impacts the texture and taste, with brown sugar often yielding a moister, chewier brownie.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Brown Sugar | White Sugar |
|---|---|---|
| Sweetness Level | Moderate, rich molasses flavor enhances brownie depth | High, pure sweetness with no added flavor |
| Texture Impact | Creates fudgy, moist brownies | Produces cakey, dry texture |
| Flavor Profile | Caramel-like, adds complexity | Neutral, allows other flavors to stand out |
| Color Effect | Darker, rich brown tone | Lighter, classic brown shade |
| Best Use | Moist, flavorful brownies with deep sweetness | Light, sweet brownies with crisp edges |
Understanding Brown Sugar vs White Sugar
Brown sugar contains molasses, which adds moisture and a richer, caramel-like flavor to brownies, enhancing overall sweetness and texture compared to white sugar. White sugar provides a cleaner, more straightforward sweetness but can result in a drier, crisper brownie texture. Understanding the differences in moisture retention and flavor profiles between brown sugar and white sugar helps bakers achieve the desired sweetness and consistency in brownies.
Flavor Profiles: Brown Sugar and White Sugar
Brown sugar adds a rich, molasses-infused flavor that deepens the sweetness and enhances the chewy texture of brownies, creating a more complex and moist dessert. White sugar provides a cleaner, more neutral sweetness, resulting in a lighter texture and crispier edges. Combining both sugars balances the caramel notes of brown sugar with the straightforward sweetness of white sugar for an optimal brownie flavor profile.
Impact on Brownie Sweetness
Brown sugar contains molasses, which adds moisture and a deeper, caramel-like sweetness to brownies, enhancing their rich flavor profile. White sugar, being more refined, provides a cleaner, sharper sweetness that results in a lighter, crisper texture. The choice between brown and white sugar significantly impacts the overall sweetness intensity and texture of the brownie, with brown sugar delivering a more complex and moist sweetness.
Texture Differences in Brownies
Brown sugar in brownies contributes moisture and a chewier texture due to its higher molasses content, which also enhances a deeper caramel flavor. White sugar produces a crisper, lighter crumb with a more neutral sweetness, resulting in a firmer texture. Choosing brown sugar over white sugar significantly impacts the chewiness and overall mouthfeel of brownies.
Moisture Retention: Brown vs White Sugar
Brown sugar contains molasses, which provides higher moisture retention compared to white sugar, making brownies softer and chewier. White sugar lacks these molasses compounds, resulting in drier, crisper edges in brownies. The moisture retention benefits of brown sugar contribute to a richer texture and prolonged freshness in baked goods.
Caramel Notes: Adding Depth to Brownies
Brown sugar imparts rich caramel notes to brownies, enhancing their depth and complexity compared to the neutral sweetness of white sugar. The molasses content in brown sugar intensifies the flavor profile, giving brownies a moist texture and a subtle, toasted caramel undertone. Choosing brown sugar over white sugar results in brownies with a more layered sweetness and a slightly chewy bite, elevating the overall dessert experience.
Browning & Crust Formation in Brownies
Brown sugar enhances brownie sweetness by promoting superior browning and crust formation through its molasses content, which reacts during baking to create a rich, caramelized flavor and crunchy edge. White sugar caramelizes more evenly but lacks the depth of flavor and moisture retention that brown sugar provides, resulting in a less pronounced crust. The higher moisture in brown sugar also contributes to a chewier texture with a well-defined browned crust on brownies.
Recipe Adjustments: Substituting Sugars
When substituting brown sugar for white sugar in brownie recipes, the higher moisture content and molasses in brown sugar contribute to a denser, chewier texture and richer caramel flavor. Adjusting the sugar ratio may require reducing additional liquid ingredients to maintain batter consistency and prevent excess moisture, which can affect baking time. Using brown sugar often enhances sweetness complexity but might necessitate slight tweaks in baking temperature or time to achieve the ideal fudgy brownie.
Health Considerations: Brown vs White Sugar
Brown sugar contains molasses, providing trace minerals like calcium, potassium, and iron, which white sugar lacks, making it a slightly healthier option for brownie sweetness. Brown sugar's higher moisture content contributes to a denser, chewier brownie texture, while white sugar produces a crisper, lighter outcome. Both sugars impact blood glucose levels similarly, so moderation is essential for maintaining healthy blood sugar control.
Which Sugar Wins for the Perfect Brownie?
Brown sugar contains molasses, adding moisture and a deeper caramel flavor that enhances brownie sweetness and chewiness, making it a top choice for rich, fudgy brownies. White sugar offers a cleaner, more neutral sweetness that creates a lighter texture and crispier edges, preferred for cakey brownies. For the perfect balance of moistness and sweetness, brown sugar typically wins, delivering that classic, indulgent brownie experience.
Brown sugar vs white sugar for brownie sweetness Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com