Baker's percentage offers a precise method for scaling bread recipes by expressing each ingredient as a percentage of the flour weight, ensuring consistency and accuracy in dough hydration and texture. Unlike cup measurements, which can vary due to ingredient density and packing, baker's percentage allows bakers to easily adjust batch sizes while maintaining the intended ratio of ingredients. This method is essential for professional bakers seeking reliable reproducibility and optimal bread quality across different production volumes.
Table of Comparison
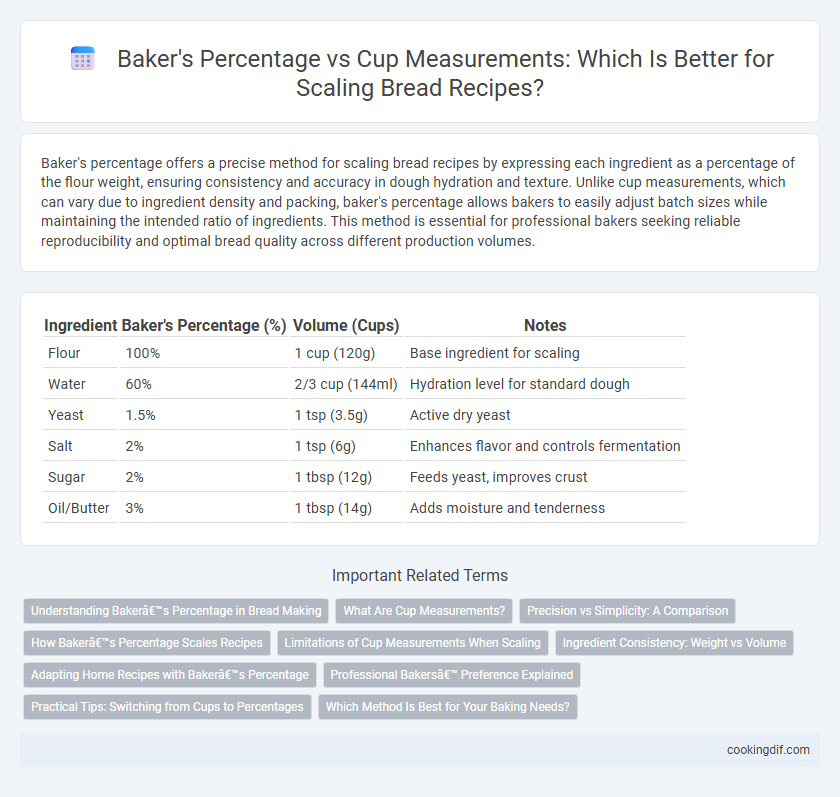
| Ingredient | Baker's Percentage (%) | Volume (Cups) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flour | 100% | 1 cup (120g) | Base ingredient for scaling |
| Water | 60% | 2/3 cup (144ml) | Hydration level for standard dough |
| Yeast | 1.5% | 1 tsp (3.5g) | Active dry yeast |
| Salt | 2% | 1 tsp (6g) | Enhances flavor and controls fermentation |
| Sugar | 2% | 1 tbsp (12g) | Feeds yeast, improves crust |
| Oil/Butter | 3% | 1 tbsp (14g) | Adds moisture and tenderness |
Understanding Baker’s Percentage in Bread Making
Baker's percentage simplifies scaling recipes by expressing each ingredient as a percentage of the total flour weight, allowing precise adjustments regardless of batch size. Unlike cup measurements, which vary in weight depending on ingredient density and packing, baker's percentage provides consistency and accuracy essential for professional bread making. Mastering this system enables bakers to maintain dough hydration, fermentation balance, and texture outcomes across different loaf sizes.
What Are Cup Measurements?
Cup measurements quantify ingredients by volume, commonly used in home baking to simplify recipe execution without a scale. Unlike baker's percentage, which provides precise ratios based on flour weight, cup measurements can vary due to ingredient density and packing. Understanding these differences is crucial for scaling bread recipes accurately and achieving consistent results.
Precision vs Simplicity: A Comparison
Baker's percentage offers precision by expressing ingredient ratios relative to flour weight, enabling consistent scaling across different batch sizes. Cup measurements provide simplicity and convenience but often lack the accuracy needed for replicable results in bread baking. Using baker's percentage ensures uniform texture and flavor, while cup measurements may introduce variability due to differences in ingredient density and packing.
How Baker’s Percentage Scales Recipes
Baker's percentage scales recipes by weight, assigning flour a baseline of 100%, with all other ingredients calculated as a percentage relative to the flour weight, ensuring precise ingredient ratios regardless of batch size. This method allows for consistent dough hydration, yeast activity, and fermentation control, which are crucial for predictable bread texture and flavor. Unlike cup measurements, Baker's percentage accommodates scaling from small artisan loaves to large commercial production with exact proportional accuracy.
Limitations of Cup Measurements When Scaling
Cup measurements lack precision and consistency, leading to significant variability in bread recipes. Baker's percentage provides accurate scaling by expressing ingredient ratios relative to flour weight, ensuring consistent dough hydration and texture. Relying on cup measurements can cause errors in ingredient proportions, affecting fermentation and final bread quality.
Ingredient Consistency: Weight vs Volume
Baker's percentage offers precise ingredient consistency by using weight measurements, ensuring accuracy regardless of ingredient density or humidity variations. Cup measurements rely on volume, often leading to inconsistent results due to packing differences and ingredient settling. Using weight-based Baker's percentage allows scalable recipes with reliable hydration levels, crucial for achieving consistent dough texture and bread quality.
Adapting Home Recipes with Baker’s Percentage
Baker's percentage uses the flour weight as 100%, making it easier to scale bread recipes accurately for any batch size, unlike inconsistent cup measurements. This method ensures precise ingredient ratios, improving dough consistency and bread quality across different oven types and altitudes. Adapting home recipes with baker's percentage allows bakers to convert familiar cup measurements into a reliable format for consistent, scalable results.
Professional Bakers’ Preference Explained
Professional bakers prefer baker's percentage over cup measurements for scaling due to its precision and consistency in recipe formulation. Bakers use baker's percentage to express ingredient ratios relative to flour weight, allowing easy adaptation to different batch sizes without altering dough hydration or texture. This method ensures more accurate control over bread quality, essential in commercial baking environments.
Practical Tips: Switching from Cups to Percentages
Switching from cup measurements to baker's percentages improves scaling accuracy for bread recipes by expressing each ingredient as a ratio of the flour weight, allowing easy adjustments for batch size. Bakers should start by weighing flour precisely, then calculate other ingredients' weights as percentages of that flour weight, ensuring consistency across different quantities. Using a digital scale and converting cups to grams helps maintain recipe integrity, especially when scaling up or down.
Which Method Is Best for Your Baking Needs?
Baker's percentage offers precise scalability by expressing each ingredient as a percentage of the flour weight, enabling consistent results regardless of batch size, which is essential for professional bakers and large-scale baking. Cup measurements are more convenient for home bakers or small quantities but can lead to variability due to differences in ingredient density and measuring technique. Choosing between Baker's percentage and cup measurements depends on the need for accuracy, scalability, and ease of use in your baking process.
Baker’s percentage vs cup measurements for scaling Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com