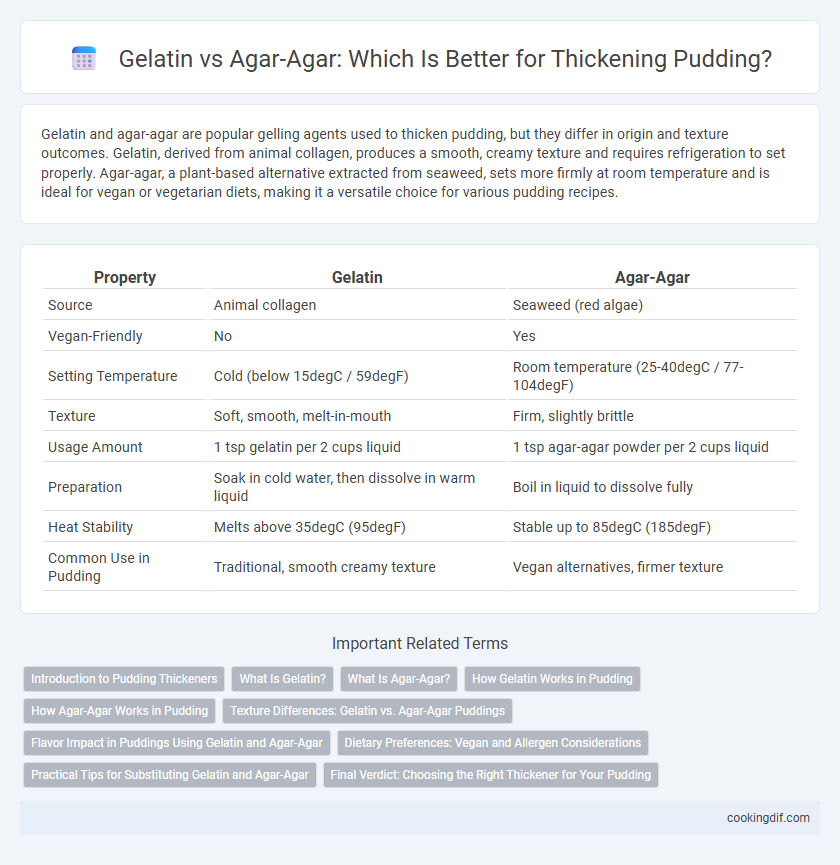
Gelatin and agar-agar are popular gelling agents used to thicken pudding, but they differ in origin and texture outcomes. Gelatin, derived from animal collagen, produces a smooth, creamy texture and requires refrigeration to set properly. Agar-agar, a plant-based alternative extracted from seaweed, sets more firmly at room temperature and is ideal for vegan or vegetarian diets, making it a versatile choice for various pudding recipes.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Gelatin | Agar-Agar |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Animal collagen | Seaweed (red algae) |
| Vegan-Friendly | No | Yes |
| Setting Temperature | Cold (below 15degC / 59degF) | Room temperature (25-40degC / 77-104degF) |
| Texture | Soft, smooth, melt-in-mouth | Firm, slightly brittle |
| Usage Amount | 1 tsp gelatin per 2 cups liquid | 1 tsp agar-agar powder per 2 cups liquid |
| Preparation | Soak in cold water, then dissolve in warm liquid | Boil in liquid to dissolve fully |
| Heat Stability | Melts above 35degC (95degF) | Stable up to 85degC (185degF) |
| Common Use in Pudding | Traditional, smooth creamy texture | Vegan alternatives, firmer texture |
Introduction to Pudding Thickeners
Gelatin and agar-agar are popular thickeners used in pudding preparation, each offering unique textures and properties. Gelatin, derived from animal collagen, provides a smooth and creamy consistency but requires refrigeration to set. Agar-agar, a plant-based alternative extracted from seaweed, sets more firmly at room temperature and is preferred in vegan and vegetarian recipes.
What Is Gelatin?
Gelatin is a protein derived from animal collagen, commonly used as a gelling agent to thicken puddings, providing a smooth and elastic texture. It dissolves in hot liquid and solidifies upon cooling, creating a stable gel structure that enhances pudding consistency. Unlike plant-based alternatives like agar-agar, gelatin offers a melt-in-the-mouth quality preferred in many traditional pudding recipes.
What Is Agar-Agar?
Agar-agar is a natural gelling agent derived from red seaweed, commonly used as a vegetarian substitute for gelatin in pudding recipes. Unlike gelatin, which is animal-based and requires refrigeration to set, agar-agar sets at room temperature and produces a firm, slightly brittle texture. Its high fiber content and ability to withstand higher cooking temperatures make agar-agar an ideal thickener for both hot and cold puddings.
How Gelatin Works in Pudding
Gelatin works in pudding by forming a protein network that traps water, creating a smooth and creamy texture as it cools and sets. Its unique ability to melt at mouth temperature ensures a melt-in-the-mouth sensation, enhancing the overall eating experience. Unlike agar-agar, gelatin provides a more elastic and tender consistency, making it ideal for traditional creamy puddings.
How Agar-Agar Works in Pudding
Agar-agar thickens pudding through a natural gelling process derived from red seaweed, forming a firm, heat-stable gel as it cools. Unlike gelatin, agar-agar sets at room temperature and remains stable even in warm environments, making it ideal for vegan and vegetarian puddings. Its ability to create a smooth, elastic texture enhances pudding consistency without the animal-based limitations of gelatin.
Texture Differences: Gelatin vs. Agar-Agar Puddings
Gelatin creates a smooth, creamy texture in puddings with a delicate, melt-in-the-mouth consistency, while agar-agar produces a firmer, more brittle gel that holds its shape better at room temperature. Puddings thickened with gelatin tend to have a silky, elastic feel, whereas agar-agar yields a slightly granular texture and a sharper, less flexible bite. Choosing between gelatin and agar-agar depends on the desired pudding firmness and mouthfeel, with agar-agar being preferred for vegan recipes due to its plant-based origin.
Flavor Impact in Puddings Using Gelatin and Agar-Agar
Gelatin imparts a subtle richness and smooth texture to puddings, enhancing the creamy mouthfeel without altering the original flavor. Agar-agar, derived from seaweed, can introduce a slightly vegetal or oceanic note, affecting the overall taste profile of the pudding. Choosing between gelatin and agar-agar depends on the desired flavor neutrality and texture in the final dessert.
Dietary Preferences: Vegan and Allergen Considerations
Gelatin, derived from animal collagen, is unsuitable for vegan diets and individuals with certain allergies, while agar-agar, sourced from seaweed, offers a plant-based alternative free from common allergens. Agar-agar sets more firmly and at room temperature, making it ideal for vegan pudding recipes that require a stable, allergen-free gelling agent. Choosing agar-agar supports dietary restrictions without compromising texture or flavor in pudding preparations.
Practical Tips for Substituting Gelatin and Agar-Agar
Gelatin and agar-agar differ in origin and setting properties, making substitution practical when considering texture and dietary needs. Use agar-agar in a 1:1 ratio to replace gelatin but dissolve agar-agar in boiling water before mixing, as it sets firmer and faster at room temperature. For vegan or vegetarian pudding, agar-agar provides a stable gel without refrigeration, while gelatin requires chilling to properly set.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Right Thickener for Your Pudding
Gelatin provides a smooth, creamy texture and melts in the mouth, making it ideal for traditional puddings that require a delicate firmness. Agar-agar, derived from seaweed, sets more firmly and is suitable for vegan or vegetarian diets, offering a slightly firmer, less elastic gel. Choosing between gelatin and agar-agar depends on dietary preferences and the desired pudding texture, with gelatin favored for richness and agar-agar for plant-based versatility.
Gelatin vs agar-agar for thickening pudding Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com