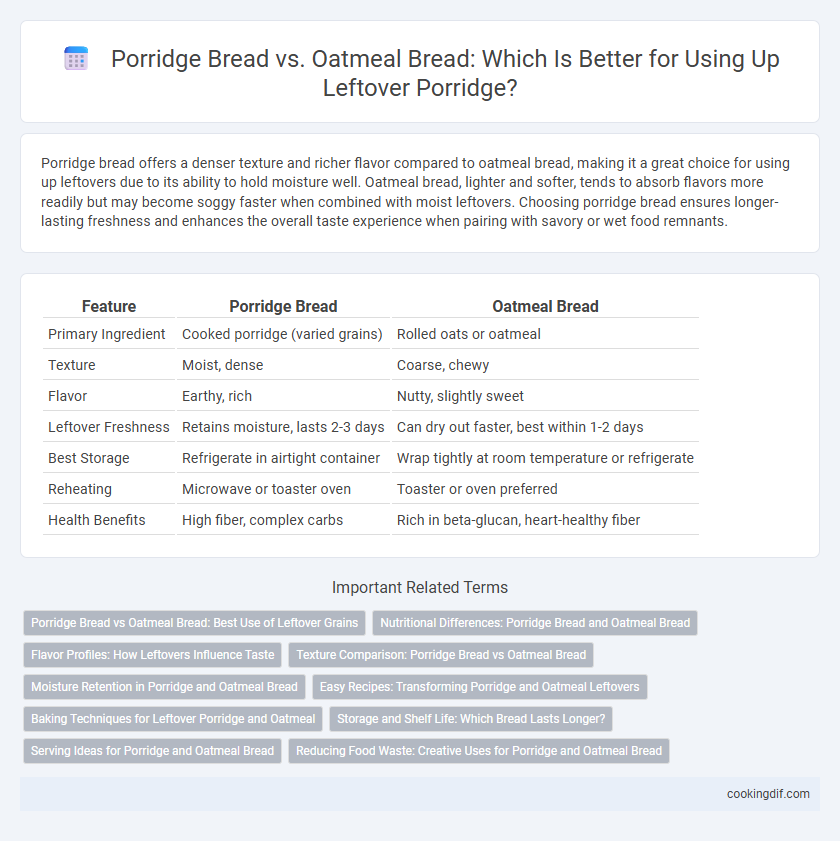
Porridge bread offers a denser texture and richer flavor compared to oatmeal bread, making it a great choice for using up leftovers due to its ability to hold moisture well. Oatmeal bread, lighter and softer, tends to absorb flavors more readily but may become soggy faster when combined with moist leftovers. Choosing porridge bread ensures longer-lasting freshness and enhances the overall taste experience when pairing with savory or wet food remnants.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Porridge Bread | Oatmeal Bread |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Ingredient | Cooked porridge (varied grains) | Rolled oats or oatmeal |
| Texture | Moist, dense | Coarse, chewy |
| Flavor | Earthy, rich | Nutty, slightly sweet |
| Leftover Freshness | Retains moisture, lasts 2-3 days | Can dry out faster, best within 1-2 days |
| Best Storage | Refrigerate in airtight container | Wrap tightly at room temperature or refrigerate |
| Reheating | Microwave or toaster oven | Toaster or oven preferred |
| Health Benefits | High fiber, complex carbs | Rich in beta-glucan, heart-healthy fiber |
Porridge Bread vs Oatmeal Bread: Best Use of Leftover Grains
Porridge bread utilizes leftover cooked grains, resulting in a moist, dense loaf that enhances flavor complexity and reduces waste by repurposing soft porridge textures. Oatmeal bread incorporates raw or soaked oats, providing a chewier, fiber-rich crumb that preserves the grain's structural integrity and delivers a heartier texture. Choosing between porridge bread and oatmeal bread depends on desired texture and moisture level, with porridge bread excelling at moisture retention and oatmeal bread offering a nutty, grain-forward bite.
Nutritional Differences: Porridge Bread and Oatmeal Bread
Porridge bread typically contains a higher moisture content and a blend of grains, offering a richer vitamin and mineral profile compared to oatmeal bread, which is denser and primarily composed of oat flour, providing more soluble fiber and beta-glucan. The higher beta-glucan content in oatmeal bread supports improved cholesterol levels and digestive health, while porridge bread offers increased iron and B vitamins from diverse grains. Both breads differ in glycemic index, with oatmeal bread generally causing a lower blood sugar spike due to its oat fiber concentration.
Flavor Profiles: How Leftovers Influence Taste
Porridge bread develops a richer, creamier flavor profile when using leftovers due to the retained moisture and natural sweetness from the porridge base, creating a soft, tender crumb. Oatmeal bread made with leftover cooked oats tends to have a nuttier, heartier taste with a denser texture, as the oats absorb more flavor and moisture, intensifying the bread's earthiness. Both breads benefit from fermentation, but porridge bread often yields a milder, slightly sweet aftertaste, while oatmeal bread offers a more robust, chewy bite influenced by the leftover grain concentration.
Texture Comparison: Porridge Bread vs Oatmeal Bread
Porridge bread offers a denser and moister crumb due to the cooked grains incorporated into the dough, enhancing softness and preventing dryness in leftovers. Oatmeal bread, made with raw or lightly processed oats, tends to have a coarser texture and a slightly chewier bite when reheated. The presence of gelatinized starches in porridge bread maintains a tender mouthfeel longer than the bran-rich structure found in oatmeal bread.
Moisture Retention in Porridge and Oatmeal Bread
Porridge bread typically retains moisture better than oatmeal bread due to its higher water content and gelatinized starches from cooked grains. This moisture retention results in a softer crumb and longer freshness of leftovers. Oatmeal bread, containing more whole oat groats or flakes, tends to lose moisture faster, leading to a firmer, drier texture upon storage.
Easy Recipes: Transforming Porridge and Oatmeal Leftovers
Porridge bread and oatmeal bread each offer unique textures and flavors when repurposing leftovers, with porridge bread providing a denser, moist crumb and oatmeal bread delivering a nuttier, chewier bite. Easy recipes for transforming these leftovers often incorporate simple ingredients like flour, eggs, and baking powder to create quick, wholesome loaves that minimize waste. Utilizing these methods enhances nutritional value by preserving fiber and protein content while producing versatile breads perfect for sandwiches or toasts.
Baking Techniques for Leftover Porridge and Oatmeal
Baking techniques for leftover porridge and oatmeal differ mainly in moisture content and texture adaptation; porridge bread benefits from higher hydration levels to maintain softness, while oatmeal bread requires adjustments in flour ratios to balance the denser consistency of oats. Using a blend of whole wheat and white flour supports the structure of oatmeal bread, preventing it from becoming too heavy, whereas porridge bread often integrates eggs and baking powder to enhance rise and tenderness. Both breads require careful temperature control, generally baking at moderate heat around 350degF (175degC), ensuring even cooking without drying out the residual grains.
Storage and Shelf Life: Which Bread Lasts Longer?
Porridge bread typically contains higher moisture content than oatmeal bread, making its shelf life shorter and requiring refrigeration to prevent mold growth beyond 2-3 days. Oatmeal bread, which has a denser texture and lower moisture, can stay fresh at room temperature for up to 5 days without significant spoilage. Proper storage in airtight containers significantly extends the freshness of both breads, but oatmeal bread generally lasts longer due to its composition.
Serving Ideas for Porridge and Oatmeal Bread
Porridge bread and oatmeal bread both offer versatile serving options that enhance leftover meals. Porridge bread pairs well with savory toppings like melted cheese, eggs, or avocado, providing a hearty base for breakfast or snacks. Oatmeal bread's mildly sweet, nutty flavor complements fruit preserves, nut butters, or honey, making it an excellent choice for quick and nutritious serving ideas.
Reducing Food Waste: Creative Uses for Porridge and Oatmeal Bread
Porridge bread, made from leftover porridge, offers a moist texture and subtle sweetness that enhances its reuse potential, making it ideal for reducing food waste by transforming surplus porridge into a nutritious loaf. Oatmeal bread, incorporating oats, provides a heartier crumb and higher fiber content, efficiently utilizing leftover oats while extending shelf life and minimizing discard. Both breads creatively repurpose leftovers, turning excess porridge and oats into versatile, wholesome products that contribute to sustainable food practices.
Porridge bread vs oatmeal bread for leftovers Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com