Meat sauce for lasagna offers a rich, savory flavor with ground beef or sausage providing a hearty texture that complements the layers of pasta and cheese. Vegetarian sauce alternatives typically use ingredients like mushrooms, lentils, or roasted vegetables to create a complex and satisfying taste, while remaining lighter and suitable for various dietary preferences. Both options enhance the lasagna's moistness and depth, allowing for customizable meals that cater to meat lovers and vegetarians alike.
Table of Comparison
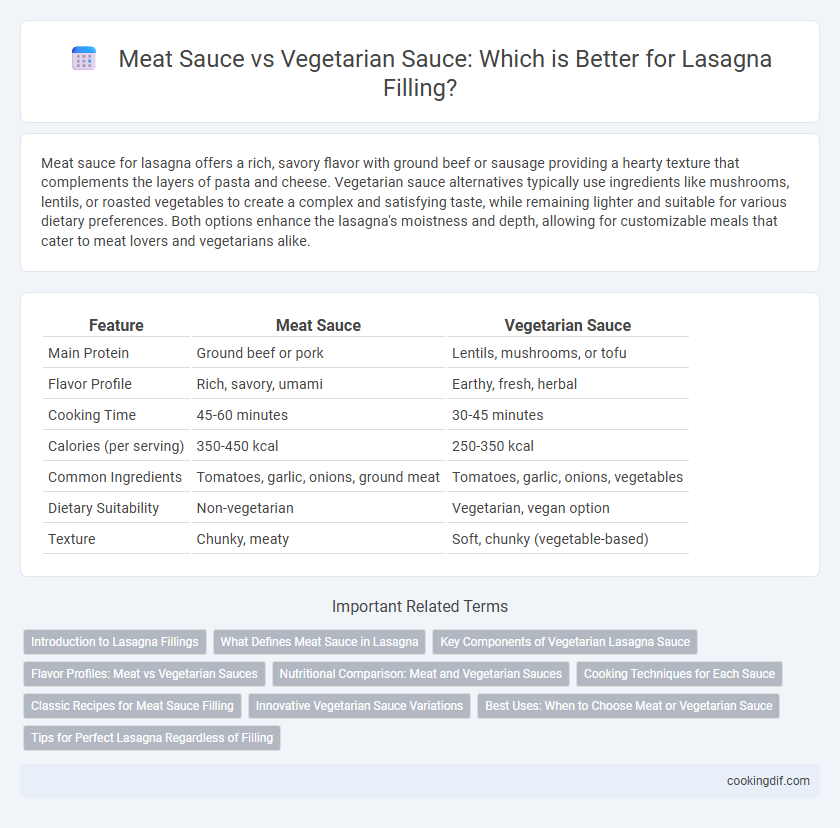
| Feature | Meat Sauce | Vegetarian Sauce |
|---|---|---|
| Main Protein | Ground beef or pork | Lentils, mushrooms, or tofu |
| Flavor Profile | Rich, savory, umami | Earthy, fresh, herbal |
| Cooking Time | 45-60 minutes | 30-45 minutes |
| Calories (per serving) | 350-450 kcal | 250-350 kcal |
| Common Ingredients | Tomatoes, garlic, onions, ground meat | Tomatoes, garlic, onions, vegetables |
| Dietary Suitability | Non-vegetarian | Vegetarian, vegan option |
| Texture | Chunky, meaty | Soft, chunky (vegetable-based) |
Introduction to Lasagna Fillings
Lasagna fillings vary significantly between meat sauce and vegetarian sauce, offering diverse flavors and textures that define the dish's character. Meat sauce typically combines ground beef, pork, or veal with tomatoes, garlic, and herbs, providing a rich, savory base packed with protein. Vegetarian sauces often incorporate layered vegetables such as spinach, mushrooms, eggplant, or zucchini, blended with tomato or bechamel sauce to create a lighter, nutrient-dense alternative.
What Defines Meat Sauce in Lasagna
Meat sauce in lasagna is defined by its rich combination of ground beef, pork, or sausage, simmered with tomatoes, onions, garlic, and Italian herbs, creating a hearty and flavorful filling. The meat provides a robust texture and savory depth that contrasts with the softness of pasta and cheese layers. Unlike vegetarian sauce, which relies on vegetables, legumes, and plant-based proteins, meat sauce offers a traditional carnivorous taste integral to classic lasagna recipes.
Key Components of Vegetarian Lasagna Sauce
Vegetarian lasagna sauce features key components such as ripe tomatoes, garlic, onions, and a medley of fresh vegetables like zucchini, mushrooms, and bell peppers, creating rich layers of flavor without meat. Herbs like basil, oregano, and thyme enhance the depth, while often including lentils or textured vegetable protein adds protein and texture. This sauce offers a nutrient-dense, fiber-rich alternative to traditional meat sauce, appealing to plant-based diet preferences.
Flavor Profiles: Meat vs Vegetarian Sauces
Meat sauce for lasagna delivers a rich umami depth with savory, hearty flavors from ground beef, pork, or sausage, enhanced by slow-simmered tomatoes and aromatic herbs like oregano and basil. Vegetarian sauces rely on robust combinations of mushrooms, roasted vegetables, and lentils or beans, creating a complex, earthy profile with natural sweetness from caramelized onions and garlic. Both sauces offer distinct layers of taste--meat sauces provide a bold, meaty richness, while vegetarian versions emphasize freshness and vegetable-driven savoriness.
Nutritional Comparison: Meat and Vegetarian Sauces
Meat sauce for lasagna typically contains higher protein and iron levels, derived from ground beef or pork, contributing essential amino acids and B vitamins. Vegetarian sauces, often made with lentils, mushrooms, or tofu, offer lower saturated fat and cholesterol while providing fiber, antioxidants, and plant-based proteins. Choosing between meat and vegetarian sauces influences caloric intake and nutrient profiles, impacting dietary preferences and health goals.
Cooking Techniques for Each Sauce
Meat sauce for lasagna typically requires browning ground beef or sausage to develop rich umami flavors before simmering with tomatoes and aromatics to achieve a thick, hearty consistency. Vegetarian sauces often utilize sauteed vegetables like mushrooms, zucchini, and bell peppers, cooked slowly to release moisture and intensify natural sweetness, combined with herbs and tomato base for depth. Both sauces benefit from simmering to meld flavors, but meat sauce demands precise deglazing and fat rendering techniques, while vegetarian sauces focus on moisture reduction and balancing textures.
Classic Recipes for Meat Sauce Filling
Classic meat sauce filling for lasagna features a rich blend of ground beef, Italian sausage, tomatoes, onions, garlic, and aromatic herbs like basil and oregano, delivering a hearty, savory flavor that defines traditional recipes. In contrast, vegetarian sauce options often substitute meat with ingredients such as mushrooms, lentils, or a medley of seasonal vegetables, emphasizing freshness and texture without compromising depth. Meat-based sauces typically require slow simmering to develop a robust umami profile, essential in authentic Italian lasagna layers.
Innovative Vegetarian Sauce Variations
Innovative vegetarian sauces for lasagna fillings often incorporate ingredients like roasted red peppers, lentils, or mushrooms to mimic the texture and rich flavor of traditional meat sauces. These variations provide a protein-rich, nutrient-dense alternative while maintaining a hearty consistency essential for a satisfying lasagna. Using blends of cashew cream or tofu can further enhance creaminess and depth, appealing to both vegetarians and those seeking healthier options.
Best Uses: When to Choose Meat or Vegetarian Sauce
Meat sauce in lasagna offers rich, savory flavors ideal for hearty meals and occasions where protein is desired, such as family dinners or celebrations. Vegetarian sauce, often made with tomato, mushrooms, and assorted vegetables, suits lighter or health-conscious meals and appeals to vegetarian or vegan diets. Choosing between the two depends on dietary preferences, desired meal richness, and the occasion's formality level.
Tips for Perfect Lasagna Regardless of Filling
Achieving perfect lasagna relies on evenly layering sauces and ensuring proper moisture balance, whether using meat sauce rich in ground beef and tomatoes or a vegetarian sauce packed with roasted vegetables and herbs. Using a combination of bechamel or ricotta cheese can prevent dryness and create a creamy texture that complements both filling types. Slow simmer the sauce to develop depth of flavor and avoid watery fillings by draining excess liquid from vegetables or using thicker tomato paste.
Meat sauce vs Vegetarian sauce for filling Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com