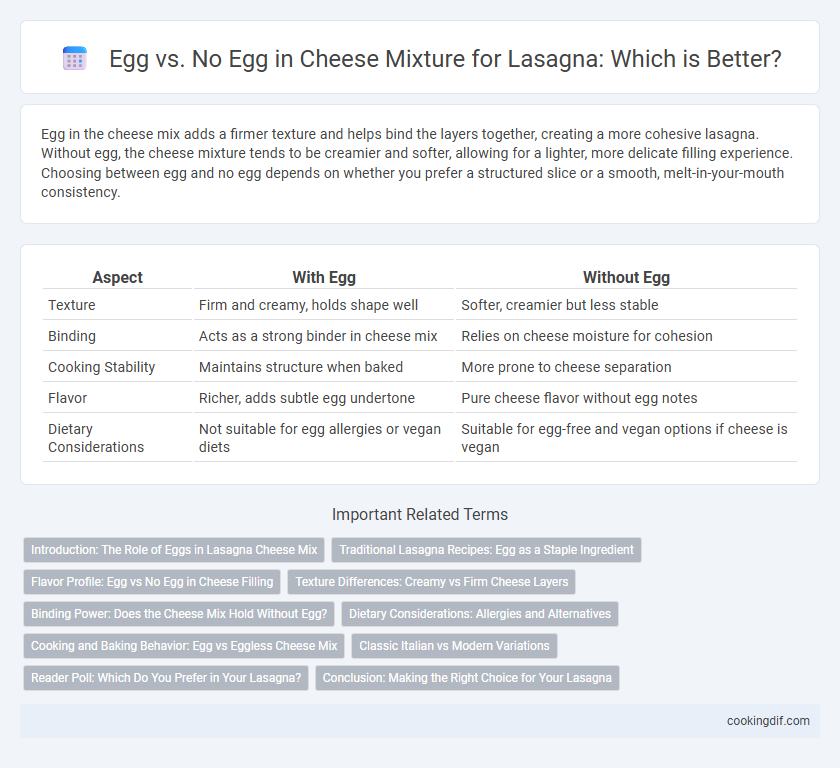
Egg in the cheese mix adds a firmer texture and helps bind the layers together, creating a more cohesive lasagna. Without egg, the cheese mixture tends to be creamier and softer, allowing for a lighter, more delicate filling experience. Choosing between egg and no egg depends on whether you prefer a structured slice or a smooth, melt-in-your-mouth consistency.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | With Egg | Without Egg |
|---|---|---|
| Texture | Firm and creamy, holds shape well | Softer, creamier but less stable |
| Binding | Acts as a strong binder in cheese mix | Relies on cheese moisture for cohesion |
| Cooking Stability | Maintains structure when baked | More prone to cheese separation |
| Flavor | Richer, adds subtle egg undertone | Pure cheese flavor without egg notes |
| Dietary Considerations | Not suitable for egg allergies or vegan diets | Suitable for egg-free and vegan options if cheese is vegan |
Introduction: The Role of Eggs in Lasagna Cheese Mix
Eggs in lasagna cheese mix act as a binding agent, providing structure and stability to the ricotta or cottage cheese layer, preventing it from becoming too watery during baking. Cheese mixes without eggs tend to be softer and creamier but may lack firmness and hold, which can affect the slicing and presentation of the lasagna. The choice between egg and no egg depends on texture preferences and desired consistency in the final dish.
Traditional Lasagna Recipes: Egg as a Staple Ingredient
Traditional lasagna recipes often incorporate egg in the cheese mixture to enhance texture and binding, creating a creamier, more cohesive filling. The egg acts as a natural emulsifier, preventing the ricotta or cottage cheese from becoming watery during baking. Omitting egg results in a looser, less structured cheese layer, which may affect the dish's authenticity and mouthfeel.
Flavor Profile: Egg vs No Egg in Cheese Filling
Egg in lasagna cheese filling enhances richness and creaminess, contributing to a velvety texture and a slightly custard-like flavor that deepens the overall profile. Cheese mixtures without egg tend to be lighter and tangier, allowing the natural sharpness of ricotta or mozzarella to stand out more distinctly. The presence of egg binds the filling, creating a smoother blend of flavors, while its absence often results in a fresher, more pronounced cheese taste.
Texture Differences: Creamy vs Firm Cheese Layers
In lasagna, incorporating egg into the cheese mixture creates a firmer, more structured texture that holds its shape when sliced. Omitting egg results in a creamier, softer cheese layer that melts seamlessly, offering a rich and gooey consistency. The choice between egg and no egg significantly influences the mouthfeel and stability of the lasagna's cheese layers.
Binding Power: Does the Cheese Mix Hold Without Egg?
The binding power in lasagna cheese mix relies heavily on eggs for structure, as eggs coagulate during baking and hold the mixture together, preventing it from becoming watery or falling apart. Without eggs, cheese mixes can still hold but often require additional thickeners like ricotta or mozzarella with lower moisture content to improve firmness. A no-egg cheese mixture may result in a looser texture, especially with high-moisture cheeses, affecting slicing and presentation.
Dietary Considerations: Allergies and Alternatives
Lasagna recipes with egg in the cheese mix may trigger allergic reactions in individuals with egg allergies or sensitivities. Using egg-free cheese mixtures provides a safe alternative for those following vegan or egg-free diets while maintaining a creamy texture. Substitutes like silken tofu, cashew cream, or commercial egg replacers enhance dietary inclusivity without compromising flavor or consistency.
Cooking and Baking Behavior: Egg vs Eggless Cheese Mix
Egg in cheese mix acts as a binder that improves the structural integrity of lasagna layers during baking, preventing separation and creating a firmer texture. Eggless cheese mixtures tend to release more moisture, which may result in a softer, sometimes runnier consistency that requires careful drainage or additional thickening agents. Baking temperature and time must be adjusted accordingly to avoid curdling in egg-based mixes or excessive wateriness in eggless versions, ensuring even cooking and a balanced texture.
Classic Italian vs Modern Variations
Traditional classic Italian lasagna recipes typically incorporate eggs in the cheese mixture, especially in ricotta blends, to provide richness and help the filling set during baking. Modern variations often omit eggs to create a lighter texture or to accommodate dietary preferences such as vegan or egg-free diets, relying instead on alternative binding agents like plant-based cheeses or tofu. This shift influences the creaminess and firmness of the cheese layer, distinguishing traditional authentic flavors from contemporary adaptations.
Reader Poll: Which Do You Prefer in Your Lasagna?
Choosing between an egg or no egg in the cheese mix significantly affects lasagna's texture and firmness. Lasagna enthusiasts often prefer an egg for a creamier, more cohesive filling that holds shape well during slicing. Reader polls reveal a near-even split, with many favoring the egg for traditional recipes while others opt out to achieve a lighter, less dense cheese layer.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Lasagna
Choosing between egg and no egg in your cheese mix impacts the texture and firmness of your lasagna layers. Incorporating egg provides a richer, firmer filling that holds its shape well when sliced, ideal for traditional recipes. Opting for no egg results in a creamier, softer texture that appeals to those seeking a lighter, more delicate bite.
Egg vs No egg in cheese mix Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com