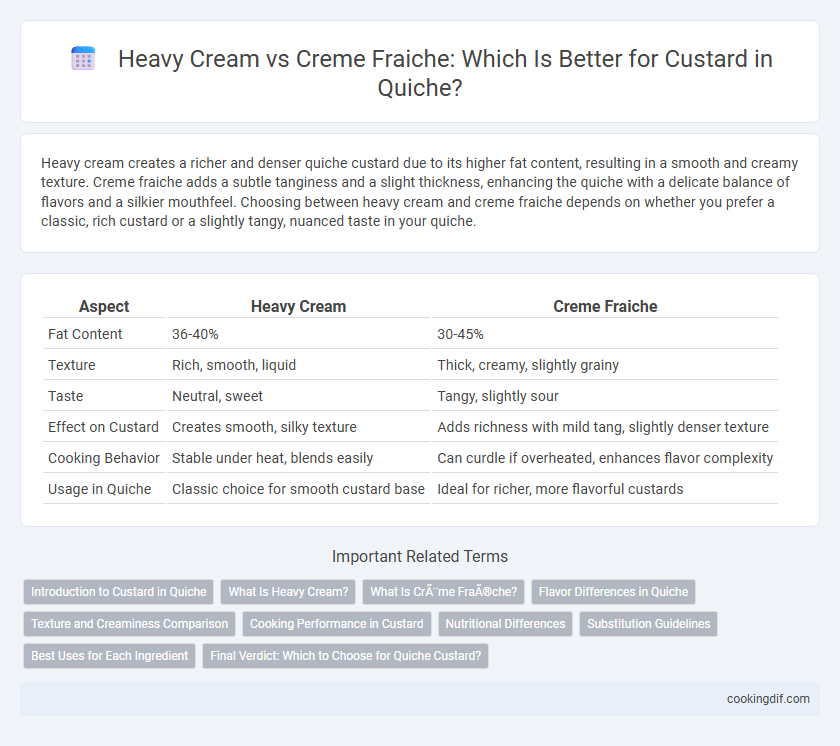
Heavy cream creates a richer and denser quiche custard due to its higher fat content, resulting in a smooth and creamy texture. Creme fraiche adds a subtle tanginess and a slight thickness, enhancing the quiche with a delicate balance of flavors and a silkier mouthfeel. Choosing between heavy cream and creme fraiche depends on whether you prefer a classic, rich custard or a slightly tangy, nuanced taste in your quiche.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Heavy Cream | Creme Fraiche |
|---|---|---|
| Fat Content | 36-40% | 30-45% |
| Texture | Rich, smooth, liquid | Thick, creamy, slightly grainy |
| Taste | Neutral, sweet | Tangy, slightly sour |
| Effect on Custard | Creates smooth, silky texture | Adds richness with mild tang, slightly denser texture |
| Cooking Behavior | Stable under heat, blends easily | Can curdle if overheated, enhances flavor complexity |
| Usage in Quiche | Classic choice for smooth custard base | Ideal for richer, more flavorful custards |
Introduction to Custard in Quiche
Heavy cream provides a rich, dense texture for quiche custard, contributing to a velvety mouthfeel and hearty consistency. Creme fraiche adds a tangy flavor and a slightly lighter, silkier custard, with its higher acidity enhancing the overall taste complexity. Both ingredients influence the custard's richness and texture, making the choice key to achieving the desired balance between creaminess and flavor depth in quiche.
What Is Heavy Cream?
Heavy cream, also known as heavy whipping cream, contains around 36-40% milk fat, providing a rich and velvety texture ideal for quiche custards. Its high fat content allows it to create a smooth, creamy base that sets well during baking, resulting in a tender and luscious filling. Unlike creme fraiche, heavy cream is less tangy and more neutral, making it a versatile ingredient in traditional custard recipes.
What Is Crème Fraîche?
Creme fraiche is a cultured dairy product with a rich, tangy flavor and a creamy texture, made by fermenting heavy cream with bacterial cultures. Unlike heavy cream, which is pure cream with a high fat content around 36-40%, creme fraiche contains live cultures that give it a slightly sour taste and a thicker consistency, making it ideal for quiche custards that require stability when baked. Its ability to maintain texture without curdling at high temperatures enhances the richness and smoothness of quiche fillings compared to heavy cream alone.
Flavor Differences in Quiche
Heavy cream creates a rich and silky custard with a mild, buttery flavor that enhances the overall creaminess of quiche. Creme fraiche adds a tangy, slightly nutty complexity, providing a subtle acidity that balances the richness of the eggs and cheese. Selecting creme fraiche results in a more nuanced flavor profile, while heavy cream offers a smoother, more neutral taste.
Texture and Creaminess Comparison
Heavy cream produces a rich, dense custard with a smooth texture, offering luxurious creaminess due to its high fat content. Creme fraiche adds a slightly tangy flavor and creates a custard with a lighter, silkier texture while maintaining creaminess through its cultured dairy properties. Choosing between heavy cream and creme fraiche alters the custard's mouthfeel and taste profile, impacting the overall quiche experience.
Cooking Performance in Custard
Heavy cream creates a richer and denser custard with a smooth texture due to its high fat content, ideal for a creamy quiche filling. Creme fraiche offers a slightly tangy flavor and thicker consistency, enhancing the custard's depth while providing stability that reduces curdling during baking. Using heavy cream results in a more traditional, luscious custard, whereas creme fraiche adds complexity and a silkier mouthfeel, balancing richness with subtle acidity.
Nutritional Differences
Heavy cream contains approximately 36-40% fat and contributes to a richer, more calorie-dense custard in quiche, whereas creme fraiche typically has around 30% fat and adds a tangy flavor with lower calories. Creme fraiche also offers beneficial probiotics due to its fermentation process, enhancing digestive health. Choosing between the two depends on the desired texture, flavor profile, and nutritional goals for the quiche custard.
Substitution Guidelines
Heavy cream can substitute creme fraiche in quiche custard, but it lacks the tangy flavor and thicker texture that creme fraiche provides; for best results, add a small amount of lemon juice or vinegar to heavy cream to mimic the acidity. Use a ratio of 1 cup heavy cream plus 1 tablespoon acid to replace 1 cup creme fraiche, ensuring the custard sets similarly and has a comparable richness. Avoid using low-fat creams, as the fat content directly impacts the creamy consistency and mouthfeel essential to a classic quiche custard.
Best Uses for Each Ingredient
Heavy cream provides a rich, silky texture and higher fat content ideal for a smooth, custard-like quiche filling that sets firmly. Creme fraiche offers a tangy flavor and thicker consistency, enhancing quiches with a creamy, slightly tart profile and preventing curdling during baking. Use heavy cream for classic, dense custards and creme fraiche when a richer taste and softer, custard with a subtle acidity is desired.
Final Verdict: Which to Choose for Quiche Custard?
Heavy cream produces a rich, silky quiche custard with a smooth texture due to its high fat content, while creme fraiche adds a slight tanginess and a thicker consistency, enhancing depth of flavor. For a classic quiche with a creamy and luscious filling, heavy cream is ideal, whereas creme fraiche is preferred for a more complex, slightly tangy custard that holds its shape well. Choosing between heavy cream and creme fraiche depends on whether you prioritize richness and smoothness or a balanced tang and thicker custard texture.
Heavy cream vs crème fraîche for custard Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com