Using eggs as the base for an omelette provides a rich, natural flavor and a fluffy texture that many prefer for its authenticity and nutritional benefits, including high-quality protein and essential vitamins. Egg substitutes, often made from plant-based ingredients or egg whites, offer a lower-cholesterol alternative that suits vegan diets and people with egg allergies, though they may lack the same creamy consistency and depth of taste. Choosing between eggs and egg substitutes depends on dietary preferences and desired texture, with eggs delivering classic taste and substitutes catering to health and ethical considerations.
Table of Comparison
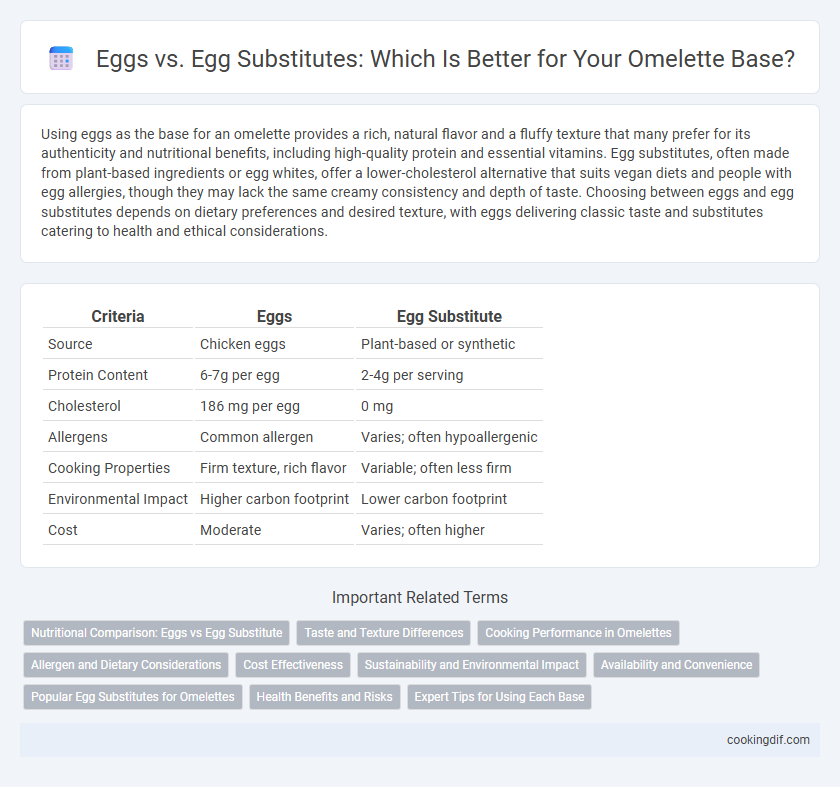
| Criteria | Eggs | Egg Substitute |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Chicken eggs | Plant-based or synthetic |
| Protein Content | 6-7g per egg | 2-4g per serving |
| Cholesterol | 186 mg per egg | 0 mg |
| Allergens | Common allergen | Varies; often hypoallergenic |
| Cooking Properties | Firm texture, rich flavor | Variable; often less firm |
| Environmental Impact | Higher carbon footprint | Lower carbon footprint |
| Cost | Moderate | Varies; often higher |
Nutritional Comparison: Eggs vs Egg Substitute
Eggs contain essential nutrients such as high-quality protein, vitamin B12, choline, and selenium, providing approximately 70 calories and 6 grams of protein per large egg. Egg substitutes, often made from egg whites or plant-based ingredients, generally offer lower calories and fat, with reduced cholesterol and similar protein content, making them suitable for heart-healthy diets. While eggs supply fat-soluble vitamins like vitamin D, many substitutes are fortified to bridge these nutritional gaps, although they may lack some bioactive compounds found in whole eggs.
Taste and Texture Differences
Eggs provide a rich, creamy texture and robust flavor that traditional omelettes are known for, offering a natural elasticity that melts smoothly in the mouth. Egg substitutes, often made from plant-based proteins or tofu, tend to have a milder taste and a slightly firmer, sometimes grainier texture that can lack the fluffiness of real eggs. While substitutes cater to dietary restrictions, the authentic taste and delicate texture of eggs remain preferred by most culinary experts for classic omelette preparation.
Cooking Performance in Omelettes
Eggs provide superior binding and rich flavor, creating a fluffy and cohesive omelette texture. Egg substitutes often lack the same protein structure, resulting in a denser or sometimes rubbery consistency. Cooking performance varies significantly, with real eggs offering better browning and lift, essential for traditional omelette quality.
Allergen and Dietary Considerations
Eggs provide a naturally rich source of protein and essential nutrients but can trigger allergies in sensitive individuals, making egg substitutes a crucial alternative. Egg substitutes, often made from plant-based ingredients like tofu, chickpea flour, or commercial egg replacers, cater to vegan, cholesterol-conscious, and allergen-sensitive diets without compromising texture. Choosing between eggs and egg substitutes depends on dietary restrictions, allergen avoidance, and nutritional goals, with substitutes offering versatility for those with egg allergies or vegan preferences.
Cost Effectiveness
Eggs offer a more cost-effective base for omelettes compared to egg substitutes, with a dozen eggs typically priced significantly lower than equivalent servings of plant-based or powdered alternatives. Egg substitutes often incur higher production costs due to specialized ingredients and processing, driving up retail prices and reducing affordability for budget-conscious consumers. Home cooks prioritizing cost-effectiveness find real eggs deliver better value while maintaining flavor and texture in omelette preparation.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Choosing egg substitutes over traditional eggs as the base for omelettes significantly reduces environmental impact by lowering greenhouse gas emissions, water usage, and land consumption. Plant-based alternatives such as chickpea flour, tofu, or commercial egg replacers promote sustainable food production and decrease reliance on livestock farming, which is a major contributor to climate change. Incorporating egg substitutes supports a more eco-friendly diet while maintaining nutritional value and versatility in culinary applications.
Availability and Convenience
Eggs remain the most widely available and convenient base for omelettes, found in virtually all grocery stores and requiring no special preparation. Egg substitutes, such as plant-based liquids or powdered mixes, offer a convenient option for vegans or those with allergies but may not be as readily stocked in every market. Both options cater to different dietary needs, with eggs providing natural protein and substitutes offering ease of use for specialized diets.
Popular Egg Substitutes for Omelettes
Popular egg substitutes for omelettes include silken tofu, chickpea flour, and commercial egg replacers, which provide similar texture and protein content while being suitable for vegans or those with egg allergies. Silken tofu offers a creamy consistency and is rich in plant-based protein, while chickpea flour creates a fluffy, savory base with added fiber and nutrients. Commercial egg replacers, often made from starches and leavening agents, mimic eggs' binding qualities and are convenient for quick preparation.
Health Benefits and Risks
Eggs provide a rich source of high-quality protein, essential vitamins like B12 and D, and minerals such as selenium, supporting muscle health and immune function. Egg substitutes often contain lower cholesterol and saturated fat, making them a preferred choice for those managing heart health or cholesterol levels. However, some substitutes may include additives or lack complete amino acid profiles found in whole eggs, which can affect nutritional value and satiety.
Expert Tips for Using Each Base
Choosing between eggs and egg substitutes for omelette bases depends on desired texture, flavor, and dietary needs. Eggs provide a rich, fluffy texture and authentic taste, ideal for classic omelettes, while egg substitutes, often made from plant proteins or aquafaba, cater to vegan or allergy-friendly diets with a lighter, sometimes denser consistency. Expert tips include whisking eggs thoroughly for maximum fluffiness and incorporating nutritional yeast or kala namak into substitutes to enhance umami flavor and mimic the egg's savory profile.
Eggs vs Egg substitute for base Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com