Vegetarian chili offers a nutrient-rich alternative to meat-based chili, providing high levels of fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants from ingredients like beans, vegetables, and spices. Meat-based chili often contains higher protein and iron but can also be higher in saturated fats and calories. Choosing vegetarian chili supports a heart-healthy diet and may reduce the risk of chronic diseases compared to traditional meat-based recipes.
Table of Comparison
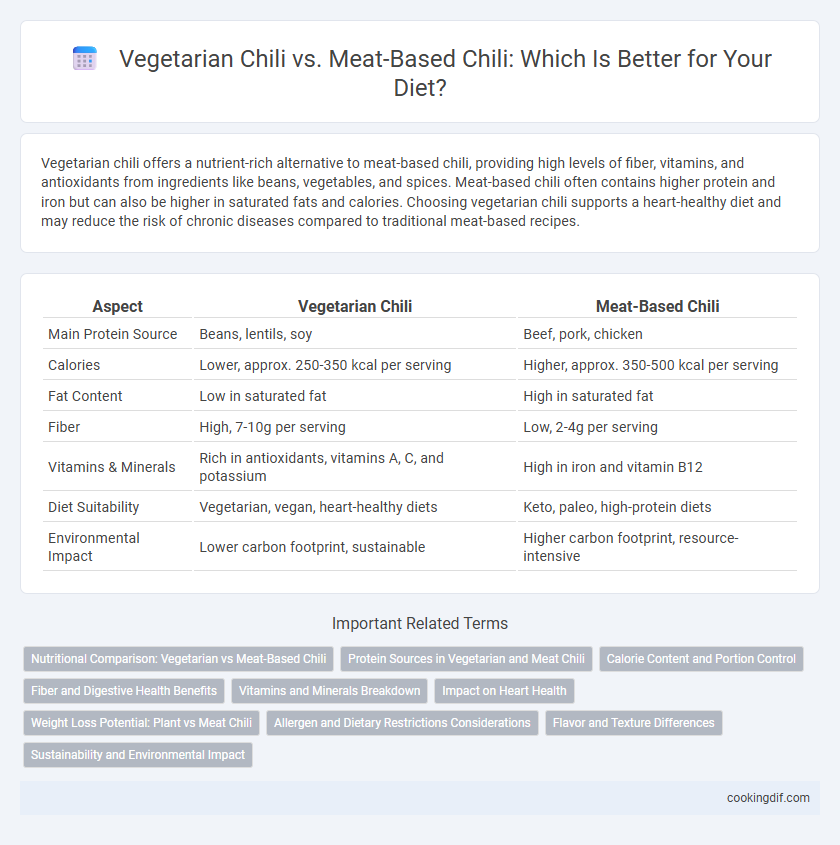
| Aspect | Vegetarian Chili | Meat-Based Chili |
|---|---|---|
| Main Protein Source | Beans, lentils, soy | Beef, pork, chicken |
| Calories | Lower, approx. 250-350 kcal per serving | Higher, approx. 350-500 kcal per serving |
| Fat Content | Low in saturated fat | High in saturated fat |
| Fiber | High, 7-10g per serving | Low, 2-4g per serving |
| Vitamins & Minerals | Rich in antioxidants, vitamins A, C, and potassium | High in iron and vitamin B12 |
| Diet Suitability | Vegetarian, vegan, heart-healthy diets | Keto, paleo, high-protein diets |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, sustainable | Higher carbon footprint, resource-intensive |
Nutritional Comparison: Vegetarian vs Meat-Based Chili
Vegetarian chili typically offers higher fiber content, essential vitamins, and antioxidants from beans, vegetables, and legumes, supporting digestive health and weight management. Meat-based chili provides a richer source of complete protein and vital nutrients like iron and vitamin B12, important for muscle repair and energy production. Calorie and fat content tend to be lower in vegetarian chili, making it a heart-healthier option compared to the often saturated fat-rich meat-based chili.
Protein Sources in Vegetarian and Meat Chili
Vegetarian chili relies on protein-rich ingredients such as beans, lentils, and tofu to provide essential amino acids, making it a nutrient-dense alternative to meat-based chili. Meat chili typically uses beef, chicken, or turkey, which offer complete proteins with all essential amino acids and higher bioavailability. For those prioritizing protein intake, vegetarian options combine diverse plant proteins, while meat-based chili provides concentrated animal protein sources beneficial for muscle repair and growth.
Calorie Content and Portion Control
Vegetarian chili typically contains fewer calories per serving compared to meat-based chili due to the lower fat content in plant-based ingredients like beans, vegetables, and legumes. Meat-based chili often has higher calorie density, requiring more precise portion control to manage caloric intake effectively. Choosing vegetarian chili supports easier adherence to calorie goals while providing fiber and essential nutrients that help maintain satiety.
Fiber and Digestive Health Benefits
Vegetarian chili typically contains beans, vegetables, and legumes, offering high fiber content that promotes digestive health and regular bowel movements. In contrast, meat-based chili provides protein but often lacks the dietary fiber essential for gut microbiome diversity and improved digestion. Incorporating plant-based ingredients in chili supports sustained fiber intake, aiding in reduced constipation and enhanced nutrient absorption.
Vitamins and Minerals Breakdown
Vegetarian chili provides a rich source of vitamins A, C, and K, along with essential minerals such as potassium, magnesium, and iron derived from beans, tomatoes, and assorted vegetables. Meat-based chili offers higher levels of vitamin B12, zinc, and heme iron, which are crucial for energy metabolism and immune function but contains fewer antioxidants compared to plant-based options. Both chili types contribute significantly to daily nutrient requirements, with vegetarian chili excelling in fiber and phytochemicals, while meat-based chili supports protein needs and micronutrients associated with animal products.
Impact on Heart Health
Vegetarian chili, rich in fiber, antioxidants, and plant-based proteins, supports heart health by reducing cholesterol and lowering blood pressure. Meat-based chili often contains higher levels of saturated fats and cholesterol, which can increase the risk of heart disease and hypertension. Choosing vegetarian chili aligns with dietary recommendations for cardiovascular benefits and improved heart health outcomes.
Weight Loss Potential: Plant vs Meat Chili
Vegetarian chili, rich in fiber and low in saturated fat, supports weight loss by enhancing satiety and reducing calorie intake. Meat-based chili, higher in protein but also saturated fats, can promote muscle retention but may increase overall calorie consumption. Choosing plant-based chili aligns with a lower-calorie, nutrient-dense diet conducive to effective weight management.
Allergen and Dietary Restrictions Considerations
Vegetarian chili offers a plant-based alternative free from common allergens such as dairy and eggs often found in meat-based recipes, making it suitable for vegans and those with lactose intolerance. Meat-based chili provides a complete protein source but may contain gluten or additives that pose challenges for people with celiac disease or certain food sensitivities. Considering dietary restrictions, vegetarian chili aligns better with low-fat, cholesterol-free diets, while meat-based chili requires careful ingredient selection to avoid allergens and accommodate specific health needs.
Flavor and Texture Differences
Vegetarian chili offers a robust flavor profile enhanced by diverse vegetables, beans, and spices, creating a hearty yet lighter texture compared to the dense, rich mouthfeel of meat-based chili. Meat-based chili delivers a savory depth through slow-cooked beef or pork, providing a chewy, satisfying bite that is often complemented by a thicker sauce. The contrast in texture and flavor between plant-based ingredients and animal protein plays a crucial role in the overall chili experience, influencing dietary preferences and nutritional content.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Vegetarian chili significantly reduces environmental impact compared to meat-based chili by lowering greenhouse gas emissions, water usage, and land consumption associated with livestock farming. Incorporating plant-based ingredients like beans, vegetables, and spices supports sustainable agriculture practices while providing essential nutrients and fiber. Choosing vegetarian chili promotes eco-friendly eating habits that help mitigate climate change and preserve natural resources.
Vegetarian Chili vs Meat-Based Chili for diet Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com