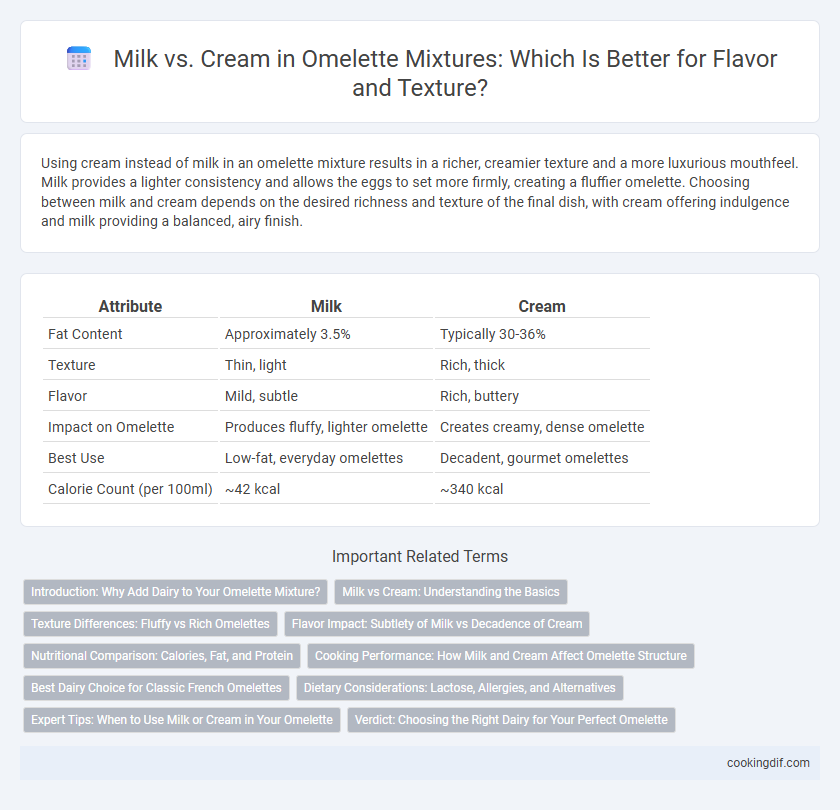
Using cream instead of milk in an omelette mixture results in a richer, creamier texture and a more luxurious mouthfeel. Milk provides a lighter consistency and allows the eggs to set more firmly, creating a fluffier omelette. Choosing between milk and cream depends on the desired richness and texture of the final dish, with cream offering indulgence and milk providing a balanced, airy finish.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Milk | Cream |
|---|---|---|
| Fat Content | Approximately 3.5% | Typically 30-36% |
| Texture | Thin, light | Rich, thick |
| Flavor | Mild, subtle | Rich, buttery |
| Impact on Omelette | Produces fluffy, lighter omelette | Creates creamy, dense omelette |
| Best Use | Low-fat, everyday omelettes | Decadent, gourmet omelettes |
| Calorie Count (per 100ml) | ~42 kcal | ~340 kcal |
Introduction: Why Add Dairy to Your Omelette Mixture?
Adding dairy like milk or cream to your omelette mixture enhances texture and flavor by increasing moisture and richness. Milk offers a lighter, fluffier consistency due to its lower fat content, while cream provides a denser, creamier result with higher fat levels that contribute to a velvety mouthfeel. These dairy additives help improve the omelette's tenderness, preventing dryness and yielding a more palatable, soft finish.
Milk vs Cream: Understanding the Basics
Milk provides a lighter texture and lower fat content in an omelette, creating a fluffier and less rich result. Cream, with its higher fat content, yields a denser, creamier omelette that is richer in flavor and moisture. Choosing between milk and cream depends on desired texture and taste, with milk favoring lightness and cream enhancing richness.
Texture Differences: Fluffy vs Rich Omelettes
Milk in an omelette mixture creates a lighter, fluffier texture by adding moisture without overwhelming richness, ideal for a tender bite. Cream contributes a denser, richer consistency with a smooth, velvety mouthfeel, enhancing the omelette's decadence. Choosing milk results in airier folds, while cream yields a more indulgent and creamy dish.
Flavor Impact: Subtlety of Milk vs Decadence of Cream
Milk in omelette mixtures enhances flavor with a subtle, light creaminess that allows the eggs' natural taste to shine, while cream contributes a rich, decadent texture and a fuller, buttery flavor profile. Using milk results in a tender, fluffy omelette with a mild sweetness, whereas cream creates a velvety, indulgent mouthfeel that elevates the overall experience. The choice between milk and cream directly influences the omelette's flavor intensity and texture, catering to different preferences for richness and subtlety.
Nutritional Comparison: Calories, Fat, and Protein
Using milk in an omelette mixture typically results in lower calories and fat compared to cream, making it a lighter option suitable for calorie-conscious diets. Cream adds a richer texture and higher fat content, often increasing the calorie count significantly due to its concentrated dairy fat. Protein content between milk and cream varies less dramatically, with milk providing modest amounts and cream offering slightly less per serving.
Cooking Performance: How Milk and Cream Affect Omelette Structure
Using milk in an omelette mixture results in a lighter and fluffier texture due to its higher water content, which creates steam during cooking and helps the eggs rise. Cream, with its higher fat content, contributes to a richer, denser structure and a more tender mouthfeel, as the fat interferes with protein coagulation and keeps the omelette moist. The choice between milk and cream directly impacts the omelette's firmness, moisture retention, and overall cooking performance.
Best Dairy Choice for Classic French Omelettes
Cream is the best dairy choice for a classic French omelette due to its higher fat content, which results in a richer, silkier texture and enhances the omelette's tenderness. Milk often thins the mixture, leading to a less creamy consistency and a firmer texture that deviates from the traditional velvety finish. Using heavy cream preserves the delicate balance of moisture and richness that defines an authentic French omelette.
Dietary Considerations: Lactose, Allergies, and Alternatives
Using milk or cream in an omelette mixture affects lactose content and allergy risk, with milk generally containing less fat but similar lactose levels as cream, which can cause discomfort for lactose-intolerant individuals. Alternatives such as lactose-free milk, almond milk, or coconut milk provide options for those with dairy allergies or lactose sensitivity while maintaining a creamy texture. Choosing the right substitute depends on dietary restrictions and desired flavor profile, ensuring a safe and enjoyable omelette experience.
Expert Tips: When to Use Milk or Cream in Your Omelette
Milk creates a lighter, fluffier omelette texture with subtle richness, ideal for everyday breakfasts, while cream adds a denser, silkier mouthfeel perfect for indulgent, restaurant-style dishes. Experts recommend using milk when you want a tender and airy consistency without overwhelming the eggs' natural flavor, and cream when aiming for extra moisture and a luxurious taste. Balancing the liquid ratio--typically 1 tablespoon per two eggs--ensures an omelette that's neither too runny nor dry.
Verdict: Choosing the Right Dairy for Your Perfect Omelette
Using cream in an omelette mixture results in a richer, creamier texture with a slightly denser consistency, while milk yields a lighter, fluffier omelette with a more delicate taste. The higher fat content in cream enhances flavor depth and moisture retention, making it ideal for indulgent recipes, whereas milk keeps the dish lighter and healthier. For the perfect omelette, choose cream for decadence and moisture or milk for a tender, airy bite that complements a variety of fillings.
Milk vs cream for mixture Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com